Abstract
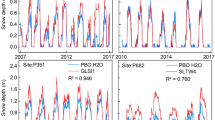
In recent years, Global Navigation Satellite System-Interferometric Reflectometry (GNSS-IR), a new remote sensing technique, has been widely used to monitor surface signature parameters. In the classical GNSS-IR technology, poor signal separation will seriously affect the accuracy of the inversion results. In order to better separate the signal-to-noise ratio trend item, the variational mode decomposition (VMD) algorithm is introduced. We use the GNSS data of P351 station in 2013–2014 and AB33 station in 2017 in the Earthscope Plate Boundary Observatory network to carry out snow depth inversion experiments. The measured snow depths provided by the Snowpack Telemetry network were used for the validation of the inversion accuracy. The feasibility and superiority of the VMD algorithm in GNSS-IR snow depth inversion experiments were verified by analyzing the experimental results. The root-mean-square error (RMSE) and correlation coefficient of the inversion results of P351 station in 2013–2014 were 13.41 cm and 0.99, respectively, which improved the inversion accuracy by about 54%. Moreover, the number of inversion points during the experimental period increased from 19,997 to about 26,958, which is an increase of about 35%. Similarly, the RMSE and correlation coefficient of the inversion results of AB33 station in 2017 reached 8.55 cm and 0.97. Compared with the traditional algorithm, the accuracy and the number of inversion points increased by about 15% and 22%, respectively.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The GPS data for P351 station and AB33 station were provided by the Earthscope Plate Boundary Observatory (PBO) network (https://cires1.colorado.edu/portal/). The measured snow depth was provided by the US Department of Agriculture Natural Resources Conservation Service Organization (NRCS, https://www.wcc.nrcs.usda.gov/snow/).
References
Bagheri A, Ozbulut OE, Harris DK (2018) Structural system identification based on variational mode decomposition. J Sound Vib 417:182–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2017.12.014
Beniston M (2003) Climatic change in mountain regions: a review of possible impacts. Clim Var Change High Elev Reg past Present Future. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-015-1252-7_2
Bilich A, Larson KM, Axelrad P (2004) Observations of signal-to-noise ratios (SNR) at geodetic GPS site CASA: implications for phase multipath. Proc Centre Eur Geodyn Seismol 23:77–83
Boniface K, Braun J, McCreight J, Nievinski F (2015) Comparison of snow data assimilation system with GPS reflectometry snow depth in the western United States. Hydrol Processes 29:2425–2437. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.10346
Dow JM, Neilan RE, Rizos C (2009) The international GNSS service in a changing landscape of global navigation satellite systems. J Geod 83:191–198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-009-0315-4
Dragomiretskiy K, Zosso D (2013) Variational mode decomposition. IEEE Trans Signal Process 62:531–544. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSP.2013.2288675
Herring TA et al (2016) Plate Boundary Observatory and related networks: GPS data analysis methods and geodetic products. Rev Geophys 54:759–808. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016RG000529
Karaim M, Elsheikh M, Noureldin A, Rustamov R (2018) GNSS error sources. Multifunct Oper Appl GPS. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.75493
Larson KM, Nievinski FG (2013) GPS snow sensing: results from the EarthScope plate boundary observatory. GPS Solut 17(1):41–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-012-0259-7
Larson KM, Small EE (2016) Estimation of snow depth using L1 GPS signal-to-noise ratio data. IEEE J Sel Top Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens 9:4802–4808. https://doi.org/10.1109/jstars.2015.2508673
Larson KM, Small EE, Gutmann E, Bilich A, Axelrad P, Braun J (2008) Using GPS multipath to measure soil moisture fluctuations: initial results. GPS Solut 12(3):173–177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-007-0076-6
Larson KM, Gutmann ED, Zavorotny VU, Braun JJ, Williams MW, Nievinski FG (2009) Can we measure snow depth with GPS receivers? Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009GL039430
Li Y, Chang X, Yu K, Wang S, Li J (2019) Estimation of snow depth using pseudorange and carrier phase observations of GNSS single-frequency signal. GPS Solut 23(4):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-019-0912-5
Li Z, Chen P, Zheng N, Liu H (2021) Accuracy analysis of GNSS-IR snow depth inversion algorithms. Adv Space Res 67:1317–1332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2020.11.021
McCreight JL, Small EE, Larson KM (2014) Snow depth, density, and SWE estimates derived from GPS reflection data: Validation in the western US. Water Resour Res 50:6892–6909. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014WR015561
Munoz-Martin JF, Perez A, Camps A, Ribó S, Cardellach E, Stroeve J, Pastena M (2020) Snow and ice thickness retrievals using GNSS-R: preliminary results of the MOSAiC experiment. Remote Sens 12(24):4038. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12244038
Nievinski FG, Larson KM (2014) Forward modeling of GPS multipath for near-surface reflectometry and positioning applications. GPS Solut 18(2):309–322. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-013-0331-y
Ozeki M, Heki K (2012) GPS snow depth meter with geometry-free linear combinations of carrier phases. J Geod 86:209–219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-011-0511-x
Rott H et al (2010) Cold regions hydrology high-resolution observatory for snow and cold land processes. Proc IEEE 98:752–765. https://doi.org/10.1109/JPROC.2009.2038947
Roussel N et al (2015) Sea level monitoring and sea state estimate using a single geodetic receiver. Remote Sens Environ 171:261–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2015.10.011
Santamaria-Gomez A, Watson C, Gravelle M, King M, Woeppelmann G (2015) Levelling co-located GNSS and tide gauge stations using GNSS reflectometry. J Geod 89:241–258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-014-0784-y
Semmling AM, Wickert J, Kreß F, Hoque MM, Divine DV, Gerland S, Spreen G (2021) Sea-ice permittivity derived from GNSS reflection profiles: results of the MOSAiC expedition. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 60:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2021.3121993
Tabibi S, Geremia-Nievinski F, van Dam T (2017) Statistical comparison and combination of GPS, GLONASS, and multi-GNSS multipath reflectometry applied to snow depth retrieval. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 55:3773–3785. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2017.2679899
Vey S, Güntner A, Wickert J, Blume T, Thoss H, Ramatschi M (2016) Monitoring snow depth by GNSS reflectometry in built-up areas: a case study for Wettzell, Germany. IEEE J Sel Top Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens 9:4809–4816. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2516041
Walsh JE (1984) Snow Cover and Atmospheric Variability: Changes in the snow covering the earth’s surface affect both daily weather and long-term climate. Am Sci 72:50–57
Wang Z, Liu K, An J, Lin G (2018) Snow depth detection and error analysis derived from SNR of GPS and BDS. Acta Geod Cartogr Sin 47:8. https://doi.org/10.11947/j.AGCS.2018.20160644
Wang X, Zhang Q, Zhang S (2019) Sea level estimation from SNR data of geodetic receivers using wavelet analysis. GPS Solut 23(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-018-0798-7
Wu W, Wang Z, Zhang J, Ma W, Wang J (2018) Research of the method of determining k value in VMD based on kurtosis. J Mech Transm 42(8):153–157. https://doi.org/10.16578/j.issn.1004.2539.2018.08.030
Yan J, Lu L (2014) Improved Hilbert-Huang transform based weak signal detection methodology and its application on incipient fault diagnosis and ECG signal analysis. Signal Process 98:74–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2013.11.012
Yu K, Ban W, Zhang X, Yu X (2015) Snow depth estimation based on multipath phase combination of GPS triple-frequency signals. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 53:5100–5109. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2015.2417214
Yu K, Li Y, Chang X (2018) Snow depth estimation based on combination of pseudorange and carrier phase of GNSS dual-frequency signals. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 57:1817–1828. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2018.2869284
Zavorotny VU, Gleason S, Cardellach E, Camps A (2014) Tutorial on remote sensing using GNSS bistatic radar of opportunity. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Mag 2:8–45. https://doi.org/10.1109/mgrs.2014.2374220
Zhang S, Wang X, Zhang Q (2017) Avoiding errors attributable to topography in GPS-IR snow depth retrievals. Adv Space Res 59:1663–1669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2016.12.031
Zhang S, Liu K, Liu Q, Zhang C, Zhang Q, Nan Y (2019) Tide variation monitoring based improved GNSS-MR by empirical mode decomposition. Adv Space Res 63:3333–3345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2019.01.046
Beckheinrich J, Hirrle A, Schön S, Beyerle G, Semmling M, Wickert J (2014) Water level monitoring of the Mekong Delta using GNSS reflectometry technique. In: 2014 IEEE geoscience and remote sensing symposium (IGARSS), pp 3798–3801. https://doi.org/10.1109/IGARSS.2014.6947311
Boyd S, Parikh N, Chu E (2011) Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers. Now Publishers Inc. https://doi.org/10.1561/2200000016
Hall C, Cordey R (1988) Multistatic scatterometry. In: International geoscience and remote sensing symposium, 'Remote sensing: moving toward the 21st century'. IEEE, vol 1, pp 561–562. https://doi.org/10.1109/IGARSS.1988.570200
Hofmann-Wellenhof B, Lichtenegger H, Wasle E (2007) GNSS–Global navigation satellite systems: GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and more. Springer WienNewYork. ISBN 978-3-211-73012-6
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Earthscope Plate Boundary Observatory (PBO) network for providing GPS SNR data (https://cires1.colorado.edu/portal/) and the US Department of Agriculture (USDA) Natural Resources Conservation Service Organization (NRCS) for providing measured snow depth data (https://www.wcc.nrcs.usda.gov/snow/). This work was sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52071199), the Shanghai Natural Science Foundation (19ZR1422800) and the National Key Research and Development Plan (No. 2019YFD0901303).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Y., Yuan, X., Liu, W. et al. Snow depth estimation from GNSS SNR data using variational mode decomposition. GPS Solut 27, 33 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-022-01371-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-022-01371-8