Abstract
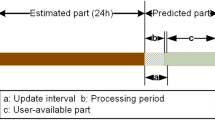
A precise Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) satellite orbit is an essential prerequisite for precise point positioning (PPP). Due to the daily orbit discontinuities (DODs) between adjacent daily orbit products provided by the International GNSS Service, the interpolation accuracy at the epochs near the day boundaries cannot be as high as expected and can significantly degrade the positioning accuracy. This is especially for the emerging Beidou and Galileo satellites with larger DODs. In this study, a new interpolation strategy was proposed to mitigate the DOD effect by estimating the zero- to second-order biases between the orbits of two adjacent days. The results show that the proposed interpolation strategy outperforms the traditional interpolation strategies. The 3D orbit interpolation error for the last 10 min on each day is reduced from almost a few centimeters or even meters to millimeters, an improvement of approximately 86–99% for all satellites. PPP validation also provides concrete evidence of this improvement, as the DOD-induced satellite phase residuals are reduced significantly. Thus, the new interpolation strategy mitigates the DOD effect and helps multi-GNSS users obtain the highest interpolation accuracy at the day boundaries, which can be comparable to that at the non-day boundaries.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The WUM MGEX products and the multi-GNSS observation data used by this study are available from the websites, ftp://igs.gnsswhu.cn/pub/gnss/products/mgex/ and https://cddis.nasa.gov/Data_and_Derived_Products/GNSS/gnss_mgex.html, respectively. The other datasets are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
An X, Meng X, Chen H, Jiang W, Xi R, Chen Q, Zhou X (2019) Improving integrated precise orbit determination of GPS, GLONASS, BDS and Galileo through integer ambiguity resolution. GPS Solut, 23(2). doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-019-0830-6
Arnold D, Meindl M, Beutler G, Dach R, Schaer S, Lutz S, Jäggi A (2015) CODE’s new solar radiation pressure model for GNSS orbit determination. J Geodesy 89(8):775–791. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-015-0814-4
Beutler G, Brockmann E, Gurtner W, Hugentobler U, Mervart L, Rothacher M, Verdun A (1994) Extended orbit modeling techniques at the CODE processing center of the international GPS service for geodynamics (IGS): theory and initial results. Manuscr Geod 19:367–386
Epperson JF (1987) On the Runge example. Am Math Mon 94(4):329–341
Feng Y, Zheng Y (2005) Efficient interpolations to GPS orbits for precise wide area applications. GPS Solut 9(4):273–282. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-005-0133-y
Griffiths J, Ray JR (2009) On the precision and accuracy of IGS orbits. J Geodesy 83(3–4):277–287. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-008-0237-6
Guo J, Xu X, Zhao Q, Liu J (2015) Precise orbit determination for quad-constellation satellites at Wuhan University: strategy, result validation, and comparison. J Geodesy 90(2):143–159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-015-0862-9
Guo F, Li X, Zhang X, Wang J (2016) Assessment of precise orbit and clock products for Galileo, BeiDou, and QZSS from IGS Multi-GNSS Experiment (MGEX). GPS Solut 21(1):279–290. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-016-0523-3
Guo F, Li X, Zhang X, Wang J (2017) The contribution of multi-GNSS experiment (MGEX) to precise point positioning. Adv Space Res 59(11):2714–2725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2016.05.018
Horemuž M, Andersson JV (2006) Polynomial interpolation of GPS satellite coordinates. GPS Solut 10(1):67–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-005-0018-0
Li X, Ge M, Dai X, Ren X, Fritsche M, Wickert J, Schuh H (2015) Accuracy and reliability of multi-GNSS real-time precise positioning: GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou, and Galileo. J Geodesy 89(6):607–635. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-015-0802-8
Liu T, Yuan Y, Zhang B, Wang N, Tan B, Chen Y (2016) Multi-GNSS precise point positioning (MGPPP) using raw observations. J Geodesy 91(3):253–268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-016-0960-3
Lutz S, Meindl M, Steigenberger P, Beutler G, Sośnica K, Schaer S, Dach R, Arnold D, Thaller D, Jäggi A (2015) Impact of the arc length on GNSS analysis results. J Geodesy 90(4):365–378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-015-0878-1
Malys S, Jensen PA (1990) Geodetic point positioning with GPS carrier beat phase data from the CASA UNO experiment. Geophys Res Lett 17(5):651–654
Montenbruck O, Gill E (2000) Satellite orbits: models, methods and applications. Springer, Berlin
Montenbruck O, Steigenberger P, Prange L, Deng Z, Zhao Q, Perosanz F, Schaer S (2017) The Multi-GNSS Experiment (MGEX) of the International GNSS Service (IGS) – Achievements, prospects and challenges. Adv Space Res 59(7):1671–1697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2017.01.011
Neta B, Clynch JR, Danielson DA, Sagovac CP (1996) Fast interpolation for global positioning system (gps) satellite orbits. In: Proceedings of AIAA/AAS astrodynamics specialist conference. AIAA/AAS, San Diego
Petit G, Luzum B (2010) IERS Conventions (2010) [R]. IERS Convention Centre, Paris
Prange L, Orliac E, Dach R, Arnold D, Beutler G, Schaer S, Jäggi A (2016) CODE’s five-system orbit and clock solution—the challenges of multi-GNSS data analysis. J Geodesy 91(4):345–360. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-016-0968-8
Ray J (2016) Precision, accuracy, and consistency of GNSS products. In: Encyclopedia of geodesy (pp. 1–5).
Remondi BW (1989) Extending the National Geodetic Orbit Formats, NOAA Technical Report NOS 133 NGS 46, 85 pp
Rodriguez-Solano CJ, Hugentobler U, Steigenberger P, Lutz S (2012) Impact of earth radiation pressure on GPS position estimates. J Geodesy 86:309–317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-011-0517-4
Schenewerk M (2003) A brief review of basic GPS orbit interpolation strategies. GPS Solut 6(4):265–267. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-002-0036-0
Sośnica K, Prange L, Kaźmierski K, Bury G, Drożdżewski M, Zajdel R, Hadas T (2017) Validation of Galileo orbits using SLR with a focus on satellites launched into incorrect orbital planes. J Geodesy 92(2):131–148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-017-1050-x
Steigenberger P, Thoelert S, Montenbruck O (2018) GNSS satellite transmit power and its impact on orbit determination. J Geodesy 92:609–624. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-017-1082-2
Steigenberger P, Montenbruck O (2019) Consistency of MGEX orbit and clock products. Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2019.12.005
Xue S, Yang Y (2016) Recursive algorithm for fast GNSS orbit fitting. GPS Solut 20(2):151–157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-014-0424-2
Yousif H, El-Rabbany A (2007) Assessment of several interpolation methods for precise GPS orbit. J Navig 60(03):443–455. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0373463307004250
Zumberge JF, Heflin MB, Jefferson DC, Watkins MM, Webb FH (1997) Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. J Geophys Res: Solid Earth 102(B3):5005–5017. https://doi.org/10.1029/96jb03860
Acknowledgements
This study is partially supported by the Natural Science Innovation Group Foundation of China (No. 41721003), the national science foundation of China (41704030), the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFC1503601), the national science foundation for distinguished young scholars of China (41525014), and the national science foundation of China (42004017). We thank the IGS organization for providing precise ephemeris products.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, C., Chen, H., Jiang, W. et al. An effective interpolation strategy for mitigating the day boundary discontinuities of precise GNSS orbit products. GPS Solut 25, 99 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-021-01130-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-021-01130-1