Abstract
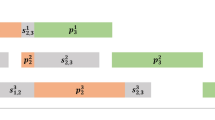
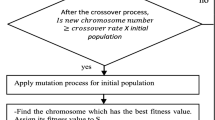
In this article, we address the m-machine no-wait flow shop scheduling problem with sequence dependent setup times. The objective is to minimize total tardiness subject to an upper bound on makespan. Although these constraints and performance measures have all been extensively studied independently, they have never been considered together in this problem before. So, this multi-criteria approach provides more realistic solutions for complex scenarios. To solve the problem, we developed a new heuristic called \(IG_{A}\). The proposed method repeatedly performs a process of destruction and construction of an existing solution in order to improve it. The novelty of this method includes a mechanism capable of adapting the destruction intensity according to the instance size and the number of iterations, calibrating the algorithm during the search. Computational experiments indicate that \(IG_{A}\) outperforms the best literature method for similar applications in overall solution quality by about 35%. Therefore, \(IG_{A}\) is recommended to solve the problem.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldowaisan T, Allahverdi A (2012) Minimizing total tardiness in no-wait flowshops. Found Comput Decis Sci 37(3):149–162
Aldowaisan T, Allahverdi A (2015) Total tardiness performance in m-machine no-wait flowshops with separate setup times. Intell Control Autom 6:38–44
Allahverdi A (2004) A new heuristic for m-machine flowshop scheduling problem with bicriteria of makespan and maximum tardiness. Comput Oper Res 31(2):157–180
Allahverdi A, Aydilek H (2013) Algorithms for no-wait flowshops with total completion time subject to makespan. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 68(9–12):2237–2251
Allahverdi A, Aydilek H (2014) Total completion time with makespan constraint in no-wait flowshops with setup times. Eur J Oper Res 238(3):724–734
Allahverdi A, Aydilek H, Aydilek A (2018) No-wait flowshop scheduling problem with two criteria; total tardiness and makespan. Eur J Oper Res 269(2):590–601
Allahverdi A, Aydilek H, Aydilek A (2020) No-wait flowshop scheduling problem with separate setup times to minimize total tardiness subject to makespan. Appl Math Comput 365(124):688
Ara DC, Nagano MS (2011) A new effective heuristic method for the no-wait flowshop with sequence-dependent setup times problem. Int J Ind Eng Comput 2(1):155–166
Aydilek H, Allahverdi A (2012) Heuristics for no-wait flowshops with makespan subject to mean completion time. Appl Math Comput 219(1):351–359
Baker KR, Trietsch D (2019) Principles of sequencing and scheduling. Wiley, Hoboken
Bianco L, Dell’Olmo P, Giordani S (1999) Flow shop no-wait scheduling with sequence dependent setup times and release dates. INFOR Inf Syst Oper Res 37(1):3–19
Ciavotta M, Minella G, Ruiz R (2013) Multi-objective sequence dependent setup times permutation flowshop: a new algorithm and a comprehensive study. Eur J Oper Res 227(2):301–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2012.12.031
Dubois-Lacoste J, Lopez-Ibanez M, Stutzle T (2011) A hybrid tp plus pls algorithm for bi-objective flow-shop scheduling problems. Comput Oper Res 38(8):1219–1236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cor.2010.10.008
Emmons H, Vairaktarakis G (2013) Flow shop scheduling. Theoretical results, algorithms, and applications. Springer, Berlin
Fernandez-Viagas V, Framinan JM (2015) Neh-based heuristics for the permutation flowshop scheduling problem to minimise total tardiness. Comput Oper Res 60:27–36
Framinan JM, Leisten R (2006) A heuristic for scheduling a permutation flowshop with makespan objective subject to maximum tardiness. Int J Prod Econ 99(1–2):28–40
Framinan JM, Perez-Gonzalez P (2018) Order scheduling with tardiness objective: improved approximate solutions. Eur J Oper Res 266(3):840–850
Franca PM, Tin G Jr, Buriol L (2006) Genetic algorithms for the no-wait flowshop sequencing problem with time restrictions. Int J Prod Res 44(5):939–957
Lee YH, Jung JW (2005) New heuristics for no-wait flowshop scheduling with precedence constraints and sequence dependent setup time. In: International conference on computational science and its applications. Springer, pp 467–476
Li X, Yang Z, Ruiz R et al (2018) An iterated greedy heuristic for no-wait flow shops with sequence dependent setup times, learning and forgetting effects. Inf Sci 453:408–425
Lopez-Ibanez M, Dubois-Lacoste J, Caceres LP et al (2016) The irace package: iterated racing for automatic algorithm configuration. Oper Res Perspect 3:43–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orp.2016.09.002
Minella G, Ruiz R, Ciavotta M (2008) A review and evaluation of multiobjective algorithms for the flowshop scheduling problem. INFORMS J Comput 20(3):451–471
Minella G, Ruiz R, Ciavotta M (2011) Restarted iterated Pareto greedy algorithm for multi-objective flowshop scheduling problems. Comput Oper Res 38(11):1521–1533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cor.2011.01.010
Miyata HH, Nagano MS, Gupta JN (2019) Integrating preventive maintenance activities to the no-wait flow shop scheduling problem with dependent-sequence setup times and makespan minimization. Comput Ind Eng 135:79–104
Nagano MS, Araújo DC (2014) New heuristics for the no-wait flowshop with sequence-dependent setup times problem. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 36(1):139–151
Nagano MS, Almeida FS, Miyata HH (2020) An iterated greedy algorithm for the no-wait flowshop scheduling problem to minimize makespan subject to total completion time. Eng Optim 53:1–19
Nawaz M, Enscore EE, Ham I (1983) A heuristic algorithm for the m-machine, n-job flowshop sequencing problem. Omega Int J Manag Sci 11(1):91–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/0305-0483(83)90088-9
Pan QK, Ruiz R (2014) An effective iterated greedy algorithm for the mixed no-idle permutation flowshop scheduling problem. Omega Int J Manag Sci 44:41–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omega.2013.10.002
Pinedo M (2016) Scheduling. Theory, algorithms, and systems, 5th edn. Springer, Berlin
Ruiz R, Stützle T (2007) A simple and effective iterated greedy algorithm for the permutation flowshop scheduling problem. Eur J Oper Res 177(3):2033–2049
Ruiz R, Stützle T (2008) An iterated greedy heuristic for the sequence dependent setup times flowshop problem with makespan and weighted tardiness objectives. Eur J Oper Res 187(3):1143–1159
Samarghandi H (2015a) A no-wait flow shop system with sequence dependent setup times and server constraints. IFAC PapersOnLine 48(3):1604–1609
Samarghandi H (2015b) Studying the effect of server side-constraints on the makespan of the no-wait flow-shop problem with sequence-dependent set-up times. Int J Prod Res 53(9):2652–2673
Samarghandi H, ElMekkawy TY (2014) Solving the no-wait flow-shop problem with sequence-dependent set-up times. Int J Comput Integr Manuf 27(3):213–228
Taillard E (1993) Benchmarks for basic scheduling problems. Eur J Oper Res 64(2):278–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/0377-2217(93)90182-M
Tasgetiren MF, Kizilay D, Pan QK et al (2017) Iterated greedy algorithms for the blocking flowshop scheduling problem with makespan criterion. Comput Oper Res 77:111–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cor.2016.07.002
Tkindt V, Billaut JC (2006) Multicriteria scheduling: theory, models and algorithms. Springer, Berlin
Xu T, Zhu X, Li X (2012) Efficient iterated greedy algorithm to minimize makespan for the no-wait flowshop with sequence dependent setup times. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 16th international conference on computer supported cooperative work in design (CSCWD). IEEE, pp 780–785
Yamada T, Nagano M, Miyata H (2021) Minimization of total tardiness in no-wait flowshop production systems with preventive maintenance. Int J Ind Eng Comput 12(4):415–426
Zhu X, Li X, Gupta JN (2013a) Iterative algorithms for no-wait flowshop problems with sequence-dependent setup times. In: 2013 25th Chinese control and decision conference (CCDC). IEEE, pp 1252–1257
Zhu X, Li X, Wang Q (2013b) An adaptive intelligent method for manufacturing process optimization in steelworks. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 17th international conference on computer supported cooperative work in design (CSCWD). IEEE, pp 363–368
Zhuang WJ, Xu T, Sun MY (2014) A hybrid iterated greedy algorithm for no-wait flowshop with sequence dependent setup times to minimize makespan. In: Advanced materials research. Trans Tech Publ, pp 459–466
Funding
Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq)—Brazil under Grant Numbers 306075/2017-2, 430137/2018-4 and 312585/2021-7. Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brazil under Grant Number 88882.379108/2019-01.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, investigation, and original draft preparation FSA and MSN; review and editing, MSN and FSA; supervision, MSN; project administration and funding acquisition, FSA and MSN.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
de Almeida, F.S., Nagano, M.S. An efficient iterated greedy algorithm for a multi-objective no-wait flow shop problem with sequence dependent setup times. 4OR-Q J Oper Res 22, 31–45 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10288-023-00535-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10288-023-00535-7