Abstract.
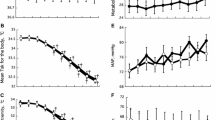
The skin microcirculatory reaction to internally and externally applied cold stimuli and its habituation were studied in 10 subjects. Stimuli were applied, via drinking and injecting water (5 °C) through a probe into the stomach, and by immersing one foot in water (5 °C) 10 times, and the reaction was measured by a LDF. Results showed a decrease in the microcirculation after external stimulation, while no reaction was detected in response to internal stimulations. Repetitive stimulations evoke slow habituation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kolev, O.I. Cutaneous microcirculatory reaction to externally and internally applied cold caloric stimuli and its habituation. Clin Auton Res 13, 295–297 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10286-003-0102-x
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10286-003-0102-x