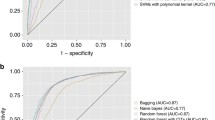
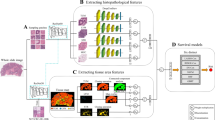
Abstract
Survival analysis is an integral part of medical statistics that is extensively utilized to establish prognostic indices for mortality or disease recurrence, assess treatment efficacy, and tailor effective treatment plans. The identification of prognostic biomarkers capable of predicting patient survival is a primary objective in the field of cancer research. With the recent integration of digital histology images into routine clinical practice, a plethora of Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based methods for digital pathology has emerged in scholarly literature, facilitating patient survival prediction. These methods have demonstrated remarkable proficiency in analyzing and interpreting whole slide images, yielding results comparable to those of expert pathologists. The complexity of AI-driven techniques is magnified by the distinctive characteristics of digital histology images, including their gigapixel size and diverse tissue appearances. Consequently, advanced patch-based methods are employed to effectively extract features that correlate with patient survival. These computational methods significantly enhance survival prediction accuracy and augment prognostic capabilities in cancer patients. The review discusses the methodologies employed in the literature, their performance metrics, ongoing challenges, and potential solutions for future advancements. This paper explains survival analysis and feature extraction methods for analyzing cancer patients. It also compiles essential acronyms related to cancer precision medicine. Furthermore, it is noteworthy that this is the inaugural review paper in the field. The target audience for this interdisciplinary review comprises AI practitioners, medical statisticians, and progressive oncologists who are enthusiastic about translating AI-driven solutions into clinical practice. We expect this comprehensive review article to guide future research directions in the field of cancer research.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Cao, Y.: Tumorigenesis as a process of gradual loss of original cell identity and gain of properties of neural precursor/progenitor cells. Cell & Bioscience 7(1), 1–14 (2017)
Gospodarowicz, M.K., O’Sullivan, B.: Prognostic factors in cancer patient care. TNM Online (2003)
Cartwright, L.A., Dumenci, L., Siminoff, L.A., Matsuyama, R.K.: Cancer patients’ understanding of prognostic information. Journal of Cancer Education 29(2), 311–317 (2014)
Mackillop, W.J.: The importance of prognosis in cancer medicine. TNM Online (2003)
Hansebout, R.R., Cornacchi, S.D., Haines, T., Goldsmith, C.H.: How to use an article about prognosis. Canadian Journal of Surgery 52(4), 328 (2009)
Maltoni, M., Caraceni, A., Brunelli, C., Broeckaert, B., Christakis, N., Eychmueller, S., Glare, P., Nabal, M., Vigano, A., Larkin, P., et al.: Prognostic factors in advanced cancer patients: evidence-based clinical recommendations-a study by the steering committee of the european association for palliative care. Journal of clinical oncology (2005)
Chen, J.-M., Qu, A.-P., Wang, L.-W., Yuan, J.-P., Yang, F., Xiang, Q.-M., Maskey, N., Yang, G.-F., Liu, J., Li, Y.: New breast cancer prognostic factors identified by computer-aided image analysis of he stained histopathology images. Scientific reports 5(1), 1–13 (2015)
Akinyemiju, T.: Chapter 9 - epigenetic biomarkers in cancer epidemiology. In: Saldanha, S. (ed.) Epigenetic Mechanisms in Cancer. Translational Epigenetics, vol. 3, pp. 223–241. Academic Press, Boston (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-809552-2.00009-7. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128095522000097
Kilty, C.G., Keenan, J., Shaw, M.: Histologically defined biomarkers in toxicology. Expert Opinion on Drug Safety 6(2), 207–215 (2007)
Reis, H.C., Turk, V.: Transfer learning approach and nucleus segmentation with medclnet colon cancer database. Journal of Digital Imaging 36(1), 306–325 (2023)
Lu, M.Y., Chen, R.J., Kong, D., Lipkova, J., Singh, R., Williamson, D.F., Chen, T.Y., Mahmood, F.: Federated learning for computational pathology on gigapixel whole slide images. Medical image analysis 76, 102298 (2022)
Baidar Bakht, A., Javed, S., Gilani, S.Q., Karki, H., Muneeb, M., Werghi, N.: Deepbls: Deep feature-based broad learning system for tissue phenotyping in colorectal cancer wsis. Journal of Digital Imaging, 1–10 (2023)
Chai, J., Zeng, H., Li, A., Ngai, E.W.: Deep learning in computer vision: A critical review of emerging techniques and application scenarios. Machine Learning with Applications 6, 100134 (2021)
Shao, W., Wang, T., Huang, Z., Han, Z., Zhang, J., Huang, K.: Weakly supervised deep ordinal cox model for survival prediction from whole-slide pathological images. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging 40(12), 3739–3747 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2021.3097319
Tang, B., Li, A., Li, B., Wang, M.: Capsurv: capsule network for survival analysis with whole slide pathological images. IEEE Access 7, 26022–26030 (2019)
Klimov, S., Miligy, I.M., Gertych, A., Jiang, Y., Toss, M.S., Rida, P., Ellis, I.O., Green, A., Krishnamurti, U., Rakha, E.A., et al: A whole slide image-based machine learning approach to predict ductal carcinoma in situ (dcis) recurrence risk. Breast Cancer Research 21(1), 1–19 (2019)
Kather, J.N., Krisam, J., Charoentong, P., Luedde, T., Herpel, E., Weis, C.-A., Gaiser, T., Marx, A., Valous, N.A., Ferber, D., et al: Predicting survival from colorectal cancer histology slides using deep learning: A retrospective multicenter study. PLoS medicine 16(1), 1002730 (2019)
Tabibu, S., Vinod, P., Jawahar, C.: Pan-renal cell carcinoma classification and survival prediction from histopathology images using deep learning. Scientific reports 9(1), 1–9 (2019)
Yao, J., Zhu, X., Huang, J.: Deep multi-instance learning for survival prediction from whole slide images. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, pp. 496–504 (2019). Springer
Hajihosseini, M., Faradmal, J., Sadighi-Pashaki, A.: Survival analysis of breast cancer patients after surgery with an intermediate event: application of illness-death model. Iranian Journal of Public Health 44(12), 1677 (2015)
Tesfay, B., Getinet, T., Derso, E.A.: Survival analysis of time to death of breast cancer patients: in case of ayder comprehensive specialized hospital tigray, ethiopia. Cogent Medicine 8(1), 1908648 (2021)
Adamu, P.I., Adamu, M.O., Okagbue, H.I., Opoola, L., Bishop, S.A.: Survival analysis of cancer patients in North Eastern Nigeria from 2004–2017–a Kaplan-Meier method. Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences 7(4), 643 (2019)
Rich, J.T., Neely, J.G., Paniello, R.C., Voelker, C.C., Nussenbaum, B., Wang, E.W.: A practical guide to understanding kaplan-meier curves. Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery 143(3), 331–336 (2010)
Kumar, D., Klefsjö, B.: Proportional hazards model: a review. Reliability Engineering & System Safety 44(2), 177–188 (1994)
Parvaiz, A., Khalid, M.A., Zafar, R., Ameer, H., Ali, M., Fraz, M.M.: Vision transformers in medical computer vision-a contemplative retrospection. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence 122, 106126 (2023)
Mohammed, B.A., Senan, E.M., Al-Mekhlafi, Z.G., Alazmi, M., Alayba, A.M., Alanazi, A.A., Alreshidi, A., Alshahrani, M.: Hybrid techniques for diagnosis with WSIs for early detection of cervical cancer based on fusion features. Applied Sciences 12(17), 8836 (2022)
Agatonovic-Kustrin, S., Beresford, R.: Basic concepts of artificial neural network (ann) modeling and its application in pharmaceutical research. Journal of pharmaceutical and biomedical analysis 22(5), 717–727 (2000)
Mahesh, B.: Machine learning algorithms-a review. International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR).[Internet] 9, 381–386 (2020)
O’Shea, K., Nash, R.: An introduction to convolutional neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1511.08458 (2015)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Advances in neural information processing systems 25 (2012)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556 (2014)
Szegedy, C., Liu, W., Jia, Y., Sermanet, P., Reed, S., Anguelov, D., Erhan, D., Vanhoucke, V., Rabinovich, A.: Going deeper with convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1–9 (2015)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Xie, S., Girshick, R., Dollár, P., Tu, Z., He, K.: Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1492–1500 (2017)
Hu, J., Shen, L., Sun, G.: Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7132–7141 (2018)
Huang, G., Liu, Z., Van Der Maaten, L., Weinberger, K.Q.: Densely connected convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4700–4708 (2017)
Tan, M., Le, Q.: Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 6105–6114 (2019). PMLR
Fukui, H., Hirakawa, T., Yamashita, T., Fujiyoshi, H.: Attention branch network: Learning of attention mechanism for visual explanation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 10705–10714 (2019)
Kaplan, E.L., Meier, P.: Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. Journal of the American statistical association 53(282), 457–481 (1958)
Clark, T.G., Bradburn, M.J., Love, S.B., Altman, D.G.: Survival analysis part i: basic concepts and first analyses. British journal of cancer 89(2), 232–238 (2003)
Sabol, P., Sinčák, P., Hartono, P., Kočan, P., Benetinová, Z., Blichárová, A., Verbóová, L., Štammová, E., Sabolová-Fabianová, A., Jašková, A.: Explainable classifier for improving the accountability in decision-making for colorectal cancer diagnosis from histopathological images. Journal of biomedical informatics 109, 103523 (2020)
Fraz, M., Khurram, S.A., Graham, S., Shaban, M., Hassan, M., Loya, A., Rajpoot, N.M.: Fabnet: feature attention-based network for simultaneous segmentation of microvessels and nerves in routine histology images of oral cancer. Neural Computing and Applications 32(14), 9915–9928 (2020)
Rasool, A., Fraz, M.M., Javed, S.: Multiscale unified network for simultaneous segmentation of nerves and micro-vessels in histology images. In: 2021 International Conference on Digital Futures and Transformative Technologies (ICoDT2), pp. 1–6 (2021). IEEE
Bhargava, H.K., Leo, P., Elliott, R., Janowczyk, A., Whitney, J., Gupta, S., Fu, P., Yamoah, K., Khani, F., Robinson, B.D., et al: Computationally derived image signature of stromal morphology is prognostic of prostate cancer recurrence following prostatectomy in african american patientsstroma predicts prostate cancer outcome in african americans. Clinical Cancer Research 26(8), 1915–1923 (2020)
Peng, Y., Chu, Y., Chen, Z., Zhou, W., Wan, S., Xiao, Y., Zhang, Y., Li, J.: Combining texture features of whole slide images improves prognostic prediction of recurrence-free survival for cutaneous melanoma patients. World journal of surgical oncology 18(1), 1–8 (2020)
Wang, X., Chen, Y., Gao, Y., Zhang, H., Guan, Z., Dong, Z., Zheng, Y., Jiang, J., Yang, H., Wang, L., et al: Predicting gastric cancer outcome from resected lymph node histopathology images using deep learning. Nature communications 12(1), 1–13 (2021)
Jiao, Y., Li, J., Qian, C., Fei, S.: Deep learning-based tumor microenvironment analysis in colon adenocarcinoma histopathological whole-slide images. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine 204, 106047 (2021)
Wulczyn, E., Steiner, D.F., Moran, M., Plass, M., Reihs, R., Tan, F., Flament-Auvigne, I., Brown, T., Regitnig, P., Chen, P.-H.C., et al: Interpretable survival prediction for colorectal cancer using deep learning. NPJ digital medicine 4(1), 1–13 (2021)
Xie, J., Pu, X., He, J., Qiu, Y., Lu, C., Gao, W., Wang, X., Lu, H., Shi, J., Xu, Y., et al: Survival prediction on intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma with histomorphological analysis on the whole slide images. Computers in Biology and Medicine 146, 105520 (2022)
Shaban, M., Khurram, S.A., Fraz, M.M., Alsubaie, N., Masood, I., Mushtaq, S., Hassan, M., Loya, A., Rajpoot, N.M.: A novel digital score for abundance of tumour infiltrating lymphocytes predicts disease free survival in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Scientific reports 9(1), 1–13 (2019)
Yamashita, R., Long, J., Saleem, A., Rubin, D.L., Shen, J.: Deep learning predicts postsurgical recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma from digital histopathologic images. Scientific reports 11(1), 1–14 (2021)
Xu, Z., Li, Y., Wang, Y., Zhang, S., Huang, Y., Yao, S., Han, C., Pan, X., Shi, Z., Mao, Y., et al: A deep learning quantified stroma-immune score to predict survival of patients with stage ii–iii colorectal cancer. Cancer cell international 21(1), 1–12 (2021)
Wang, Y., Wang, Y.G., Hu, C., Li, M., Fan, Y., Otter, N., Sam, I., Gou, H., Hu, Y., Kwok, T., et al: Cell graph neural networks enable the precise prediction of patient survival in gastric cancer. NPJ precision oncology 6(1), 45 (2022)
Nasir, E.S., Parvaiz, A., Fraz, M.M.: Nuclei and glands instance segmentation in histology images: a narrative review. Artificial Intelligence Review, 1–56 (2022)
Rashid, S.N., Fraz, M.M.: Nuclei probability and centroid map network for nuclei instance segmentation in histology images. Neural Computing and Applications, 1–14 (2023)
Chen, R.J., Lu, M.Y., Wang, J., Williamson, D.F.K., Rodig, S.J., Lindeman, N.I., Mahmood, F.: Pathomic fusion: An integrated framework for fusing histopathology and genomic features for cancer diagnosis and prognosis. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging 41(4), 757–770 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2020.3021387
Tian, K., Rubadue, C.A., Lin, D.I., Veta, M., Pyle, M.E., Irshad, H., Heng, Y.J.: Automated clear cell renal carcinoma grade classification with prognostic significance. PloS one 14(10), 0222641 (2019)
Alsubaie, N.M., Snead, D., Rajpoot, N.M.: Tumour nuclear morphometrics predict survival in lung adenocarcinoma. IEEE Access 9, 12322–12331 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3049582
Wang, Z., Li, J., Pan, Z., Li, W., Sisk, A., Ye, H., Speier, W., Arnold, C.W.: Hierarchical graph pathomic network for progression free survival prediction. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, pp. 227–237 (2021). Springer
Chen, P., Saad, M.B., Rojas, F.R., Salehjahromi, M., Aminu, M., Bandyopadhyay, R., Hong, L., Ebare, K., Behrens, C., Gibbons, D.L., et al: Cellular architecture on whole slide images allows the prediction of survival in lung adenocarcinoma. In: International Workshop on Computational Mathematics Modeling in Cancer Analysis, pp. 1–10 (2022). Springer
Shaban, M., Awan, R., Fraz, M.M., Azam, A., Tsang, Y.-W., Snead, D., Rajpoot, N.M.: Context-aware convolutional neural network for grading of colorectal cancer histology images. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging (2020)
Bashir, R.M.S., Mahmood, H., Shaban, M., Raza, S.E.A., Fraz, M.M., Khurram, S.A., Rajpoot, N.M.: Automated grade classification of oral epithelial dysplasia using morphometric analysis of histology images. In: Tomaszewski, J.E., Ward, A.D. (eds.) Medical Imaging 2020: Digital Pathology, vol. 11320, pp. 245–250. SPIE, (2020). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2549705
Dogar, G.M., Shahzad, M., Fraz, M.M.: Attention augmented distance regression and classification network for nuclei instance segmentation and type classification in histology images. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 79, 104199 (2023)
Wulczyn, E., Steiner, D.F., Xu, Z., Sadhwani, A., Wang, H., Flament-Auvigne, I., Mermel, C.H., Chen, P.-H.C., Liu, Y., Stumpe, M.C.: Deep learning-based survival prediction for multiple cancer types using histopathology images. PloS one 15(6), 0233678 (2020)
Zadeh Shirazi, A., Fornaciari, E., Bagherian, N.S., Ebert, L.M., Koszyca, B., Gomez, G.A.: Deepsurvnet: deep survival convolutional network for brain cancer survival rate classification based on histopathological images. Medical & biological engineering & computing 58(5), 1031–1045 (2020)
Liao, H., Xiong, T., Peng, J., Xu, L., Liao, M., Zhang, Z., Wu, Z., Yuan, K., Zeng, Y.: Classification and prognosis prediction from histopathological images of hepatocellular carcinoma by a fully automated pipeline based on machine learning. Annals of surgical oncology 27, 2359–2369 (2020)
Zheng, Q., Yang, R., Ni, X., Yang, S., Xiong, L., Yan, D., Xia, L., Yuan, J., Wang, J., Jiao, P., et al: Accurate diagnosis and survival prediction of bladder cancer using deep learning on histological slides. Cancers 14(23), 5807 (2022)
Courtiol, P., Maussion, C., Moarii, M., Pronier, E., Pilcer, S., Sefta, M., Manceron, P., Toldo, S., Zaslavskiy, M., Le Stang, N., et al: Deep learning-based classification of mesothelioma improves prediction of patient outcome. Nature medicine 25(10), 1519–1525 (2019)
Knuutila, J.S., Riihilä, P., Karlsson, A., Tukiainen, M., Talve, L., Nissinen, L., Kähäri, V.-M.: Identification of metastatic primary cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma utilizing artificial intelligence analysis of whole slide images. Scientific reports 12(1), 9876 (2022)
Javed, S., Mahmood, A., Fraz, M.M., Koohbanani, N.A., Benes, K., Tsang, Y.-W., Hewitt, K., Epstein, D., Snead, D., Rajpoot, N.: Cellular community detection for tissue phenotyping in colorectal cancer histology images. Medical Image Analysis 63, 696–714 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2020.101696
Xu, H., Park, S., Clemenceau, J.R., Choi, J., Lee, S.H., Hwang, T.H.: Spatial heterogeneity and organization of tumor mutation burden with immune infiltrates within tumors based on whole slide images correlated with patient survival in bladder cancer. Journal of Pathology Informatics, 100105 (2022)
Lu, Z., Xu, S., Shao, W., Wu, Y., Zhang, J., Han, Z., Feng, Q., Huang, K.: Deep-learning–based characterization of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in breast cancers from histopathology images and multiomics data. JCO clinical cancer informatics 4, 480–490 (2020)
Chen, S., Zhang, N., Jiang, L., Gao, F., Shao, J., Wang, T., Zhang, E., Yu, H., Wang, X., Zheng, J.: Clinical use of a machine learning histopathological image signature in diagnosis and survival prediction of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. International journal of cancer 148(3), 780–790 (2021)
Comes, M.C., Fucci, L., Mele, F., Bove, S., Cristofaro, C., De Risi, I., Fanizzi, A., Milella, M., Strippoli, S., Zito, A., et al: A deep learning model based on whole slide images to predict disease-free survival in cutaneous melanoma patients. Scientific Reports 12(1), 20366 (2022)
Bychkov, D., Linder, N., Turkki, R., Nordling, S., Kovanen, P.E., Verrill, C., Walliander, M., Lundin, M., Haglund, C., Lundin, J.: Deep learning based tissue analysis predicts outcome in colorectal cancer. Scientific reports 8(1), 1–11 (2018)
Hao, J., Kosaraju, S.C., Tsaku, N.Z., Song, D.H., Kang, M.: Page-net: interpretable and integrative deep learning for survival analysis using histopathological images and genomic data. In: Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing 2020, pp. 355–366 (2019). World Scientific
Turkki, R., Byckhov, D., Lundin, M., Isola, J., Nordling, S., Kovanen, P.E., Verrill, C., von Smitten, K., Joensuu, H., Lundin, J., et al: Breast cancer outcome prediction with tumour tissue images and machine learning. Breast cancer research and treatment 177(1), 41–52 (2019)
Chen, R.J., Lu, M.Y., Weng, W.-H., Chen, T.Y., Williamson, D.F., Manz, T., Shady, M., Mahmood, F.: Multimodal co-attention transformer for survival prediction in gigapixel whole slide images. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 4015–4025 (2021)
Jiang, S., Zanazzi, G.J., Hassanpour, S.: Predicting prognosis and idh mutation status for patients with lower-grade gliomas using whole slide images. Scientific reports 11(1), 1–9 (2021)
Agarwal, S., Eltigani Osman Abaker, M., Daescu, O.: Survival prediction based on histopathology imaging and clinical data: A novel, whole slide cnn approach. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, pp. 762–771 (2021). Springer
Sandarenu, P., Millar, E.K., Song, Y., Browne, L., Beretov, J., Lynch, J., Graham, P.H., Jonnagaddala, J., Hawkins, N., Huang, J., et al: Survival prediction in triple negative breast cancer using multiple instance learning of histopathological images. Scientific Reports 12(1), 14527 (2022)
Li, C., Zhu, X., Yao, J., Huang, J.: Hierarchical transformer for survival prediction using multimodality whole slide images and genomics. In: 2022 26th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), pp. 4256–4262 (2022). IEEE
Wetstein, S.C., de Jong, V.M., Stathonikos, N., Opdam, M., Dackus, G.M., Pluim, J.P., van Diest, P.J., Veta, M.: Deep learning-based breast cancer grading and survival analysis on whole-slide histopathology images. Scientific Reports 12(1), 15102 (2022)
Chen, R.J., Lu, M.Y., Shaban, M., Chen, C., Chen, T.Y., Williamson, D.F., Mahmood, F.: Whole slide images are 2d point clouds: Context-aware survival prediction using patch-based graph convolutional networks. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, pp. 339–349 (2021). Springer
Li, R., Yao, J., Zhu, X., Li, Y., Huang, J.: Graph cnn for survival analysis on whole slide pathological images. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, pp. 174–182 (2018). Springer
Di, D., Zhang, J., Lei, F., Tian, Q., Gao, Y.: Big-hypergraph factorization neural network for survival prediction from whole slide image. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 31, 1149–1160 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2021.3139229
Xu, Z., Lim, S., Shin, H.-K., Uhm, K.-H., Lu, Y., Jung, S.-W., Ko, S.-J.: Risk-aware survival time prediction from whole slide pathological images. Scientific Reports 12(1), 21948 (2022)
Lu, M.Y., Chen, R.J., Kong, D., Lipkova, J., Singh, R., Williamson, D.F.K., Chen, T.Y., Mahmood, F.: Federated learning for computational pathology on gigapixel whole slide images. Medical Image Analysis 76, 102298 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2021.102298
Tu, C., Zhang, Y., Ning, Z.: Dual-curriculum contrastive multi-instance learning for cancer prognosis analysis with whole slide images. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 35, 29484–29497 (2022)
Xie, Y., Niu, G., Da, Q., Dai, W., Yang, Y.: Survival prediction for gastric cancer via multimodal learning of whole slide images and gene expression. In: 2022 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), pp. 1311–1316 (2022). IEEE
Mackenzie, C.C., Dawood, M., Graham, S., Eastwood, M., et al: Neural graph modelling of whole slide images for survival ranking. In: Learning on Graphs Conference, pp. 48–1 (2022). PMLR
Benkirane, H., Vakalopoulou, M., Christodoulidis, S., Garberis, I.-J., Michiels, S., Cournède, P.-H.: Hyper-adac: Adaptive clustering-based hypergraph representation of whole slide images for survival analysis. In: Machine Learning for Health, pp. 405–418 (2022). PMLR
Zhu, X., Yao, J., Zhu, F., Huang, J.: Wsisa: Making survival prediction from whole slide histopathological images. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7234–7242 (2017)
Yao, J., Zhu, X., Jonnagaddala, J., Hawkins, N., Huang, J.: Whole slide images based cancer survival prediction using attention guided deep multiple instance learning networks. Medical Image Analysis 65, 101789 (2020)
Muhammad, H., Xie, C., Sigel, C.S., Doukas, M., Alpert, L., Simpson, A.L., Fuchs, T.J.: Epic-survival: End-to-end part inferred clustering for survival analysis, with prognostic stratification boosting. In: Medical Imaging with Deep Learning (2021)
Liu, T., Su, R., Sun, C., Li, X., Wei, L.: Eocsa: Predicting prognosis of epithelial ovarian cancer with whole slide histopathological images. Expert Systems with Applications 206, 117643 (2022)
Sun, C., Li, B., Wei, G., Qiu, W., Li, D., Li, X., Liu, X., Wei, W., Wang, S., Liu, Z., et al: Deep learning with whole slide images can improve the prognostic risk stratification with stage iii colorectal cancer. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine 221, 106914 (2022)
Chang, J.-R., Lee, C.-Y., Chen, C.-C., Reischl, J., Qaiser, T., Yeh, C.-Y.: Hybrid aggregation network for survival analysis from whole slide histopathological images. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, pp. 731–740 (2021). Springer
Fan, L., Sowmya, A., Meijering, E., Song, Y.: Learning visual features by colorization for slide-consistent survival prediction from whole slide images. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, pp. 592–601 (2021). Springer
Fan, L., Sowmya, A., Meijering, E., Song, Y.: Cancer survival prediction from whole slide images with self-supervised learning and slide consistency. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging (2022)
Vale-Silva, L.A., Rohr, K.: Long-term cancer survival prediction using multimodal deep learning. Scientific Reports 11(1), 1–12 (2021)
Shen, Y., Liu, L., Tang, Z., Chen, Z., Ma, G., Dong, J., Zhang, X., Yang, L., Zheng, Q.: Explainable survival analysis with convolution-involved vision transformer. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 36, pp. 2207–2215 (2022)
Di, D., Li, S., Zhang, J., Gao, Y.: Ranking-based survival prediction on histopathological whole-slide images. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2020: 23rd International Conference, Lima, Peru, October 4–8, 2020, Proceedings, Part V 23, pp. 428–438 (2020). Springer
Acknowledgements
We extend our sincere appreciation to the Islamic World Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (ICESCO) for their invaluable support in establishing the ICESCO Chair of Data Science and Analytics for Business at the National University of Sciences and Technology (NUST). This initiative has significantly contributed to the advancement of research and academic endeavors in the field, and we are grateful for their commitment to fostering excellence and innovation in Data Science and AI education.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed equally to the study’s conception, design, material preparation, data collection, and documentation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
This study provides a summary of previously published research articles sourced from open-access platforms such as PubMed, Google Scholar, and Science Direct.
Consent to Participate
All papers included in this review article are collected from open source platforms. I confirm that all previously published research articles included in this review paper have been properly cited and are used in accordance with copyright and fair use guidelines.
Consent to Publish
The articles in this review paper are included in accordance with applicable copyright and citation guidelines.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Parvaiz, A., Nasir, E.S. & Fraz, M.M. From Pixels to Prognosis: A Survey on AI-Driven Cancer Patient Survival Prediction Using Digital Histology Images. J Digit Imaging. Inform. med. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-024-01049-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-024-01049-2