Abstract
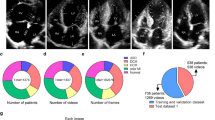
Automated recognition of heart shunts using saline contrast transthoracic echocardiography (SC-TTE) has the potential to transform clinical practice, enabling non-experts to assess heart shunt lesions. This study aims to develop a fully automated and scalable analysis pipeline for distinguishing heart shunts, utilizing a deep neural network–based framework. The pipeline consists of three steps: (1) chamber segmentation, (2) ultrasound microbubble localization, and (3) disease classification model establishment. The study’s normal control group included 91 patients with intracardiac shunts, 61 patients with extracardiac shunts, and 84 asymptomatic individuals. Participants’ SC-TTE images were segmented using the U-Net model to obtain cardiac chambers. The segmentation results were combined with ultrasound microbubble localization to generate multivariate time series data on microbubble counts in each chamber. A classification model was then trained using this data to distinguish between intracardiac and extracardiac shunts. The proposed framework accurately segmented heart chambers (dice coefficient = 0.92 ± 0.1) and localized microbubbles. The disease classification model achieved high accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, F1 score, kappa value, and AUC value for both intracardiac and extracardiac shunts. For intracardiac shunts, accuracy was 0.875 ± 0.008, sensitivity was 0.891 ± 0.002, specificity was 0.865 ± 0.012, F1 score was 0.836 ± 0.011, kappa value was 0.735 ± 0.017, and AUC value was 0.942 ± 0.014. For extracardiac shunts, accuracy was 0.902 ± 0.007, sensitivity was 0.763 ± 0.014, specificity was 0.966 ± 0.008, F1 score was 0.830 ± 0.012, kappa value was 0.762 ± 0.017, and AUC value was 0.916 ± 0.006. The proposed framework utilizing deep neural networks offers a fast, convenient, and accurate method for identifying intracardiac and extracardiac shunts. It aids in shunt recognition and generates valuable quantitative indices, assisting clinicians in diagnosing these conditions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Velthuis, E. Buscarini, M. W. F. van Gent, P. Gazzaniga, G. Manfredi, C. Danesino, W. J. Schonewille, C. J. J. Westermann, R. J. Snijder, J. J. Mager, and M. C. Post. Grade of Pulmonary Right-to-Left Shunt on Contrast Echocardiography and Cerebral Complications, Chest 542–548, 2013.
P. Y. Ng, A. K.-Y. Ng, B. Subramaniam, S. M. Burns, F. Herisson, F. P. Timm, C. Med, M. I. Rudolph, C. Med, F. Scheffenbichler, C. Med, S. Friedrich, C. Med, T. T. Houle, D. L. Bhatt, and M. Eikermann. Association of Preoperatively Diagnosed Patent Foramen Ovale With Perioperative Ischemic Stroke. JAMA 319(5):452–462, 2018
Giblett JP, Williams LK, Kyranis S, Shapiro LM, Calvert PA. Patent Foramen Ovale Closure: State of the Art. Interv Cardiol 15:e15, 2020
Miranda B, Fonseca AC, Ferro JM. Patent foramen ovale and stroke. J Neurol 265(8):1943–1949,2018
J.-L. Mas, L. Derex, P. Guérin, B. Guillon, G. Habib, J.-M. Juliard, E. Marijon, E. Massardier, N. Meneveau, and F. Vuillier. Transcatheter closure of patent foramen ovale to prevent stroke recurrence in patients with otherwise unexplained ischaemic stroke: Expert consensus of the French Neurovascular Society and the French Society of Cardiology. Arch Cardiovasc Dis 12(8-9):532–542, 2019
J.-M. Vedrinne, S. Duperret, C. Magnin, J. Motin, T. Bizollon, C. Trepo, and C. Ducerf. Comparison of transesophageal and transthoracic contrast echocardiography for detection of an intrapulmonary shunt in liver disease. Chest 111(5):1236–1240, 1997
M. J. Krowka, M. B. Fallon, S. M. Kawut, V. Fuhrmann, J. K. Heimbach, M. A. E. Ramsay, O. Sitbon, and R. J. Sokol. International Liver Transplant Society Practice Guidelines: Diagnosis and Management of Hepatopulmonary Syndrome and Portopulmonary Hypertension. Transplantation 100(7):1440–1452, 2016
J.-L. Mas, G. Derumeaux, B. Guillon, E. Massardier, H. Hosseini, L. Mechtouff, C. Arquizan, Y. Béjot, F. Vuillier, O. Detante, C. Guidoux, S. Canaple, C. Vaduva, N. Dequatre-Ponchelle, I. Sibon, P. Garnier, A. Ferrier, S. Timsit, E. Robinet-Borgomano, D. Sablot, J.-C. Lacour, M. Zuber, P. Favrole, J.-F. Pinel, M. Apoil, P. Reiner, C. Lefebvre, P. Guérin, C. Piot, R. Rossi, J.-L. Dubois-Randé, J.-C. Eicher, N. Meneveau, J.-R. Lusson, B. Bertrand, J.-M. Schleich, F. Godart, J.-B. Thambo, L. Leborgne, P. Michel, L. Pierard, G. Turc, M. Barthelet, A. Charles-Nelson, C. Weimar, T. Moulin, J.-M. Juliard, and G. Chatellier. Patent Foramen Ovale Closure or Anticoagulation vs. Antiplatelets after Stroke. N Engl J Med 377(11):1011–1021, 2017
D. M. Kent, I. J. Dahabreh, R. Ruthazer, A. J. Furlan, M. Reisman, J. D. Carroll, J. L. Saver, R. W. Smalling, P. Jüni, H. P. Mattle, B. Meier, and D. E. Thaler. Device Closure of Patent Foramen Ovale After Stroke: Pooled Analysis of Completed Randomized Trials. J Am Coll Cardiol 67(8):907–917, 2016
Gramiak R, Shah PM. Echocardiography of the aortic root. Invest Radiol 3:356–66, 1968
Gramiak R, Shah PM, Kramer DH. Ultrasound cardiography: contrast studies in anatomy and function. Radiology 92:939–48, 1969
Seward JB, Tajik AJ, Spangler JG, Ritter DG. Echocardiographic contrast studies: initial experience. Mayo Clin Proc 50:163–92, 1975
Shub C, Tajik AJ, Seward JB, Dines DE. Detecting intrapulmonary right-to-left shunt with contrast echocardiography. Observations in a patient with diffuse pulmonary arteriovenous fistulas. Mayo Clin Proc 51(2):81–84,1976
F. E. Silvestry, M. S. Cohen, L. B. Armsby, N. J. Burkule, C. E. Fleishman, Z. M. Hijazi, R. M. Lang, J. J. Rome, and Y. Wang. Guidelines for the Echocardiographic Assessment of Atrial Septal Defect and Patent Foramen Ovale: From the American Society of Echocardiography and Society for Cardiac Angiography and Interventions. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 28(8):910–958, 2015
Bernard S, Churchill TW, Namasivayam M, Bertrand PB. Agitated Saline Contrast Echocardiography in the Identification of Intra- and Extracardiac Shunts: Connecting the Dots. J Am Soc Echocardiogr Oct 23:S0894–7317(20)30615–5, 2020
Attaran RR, Ata I, Kudithipudi V, Foster L, Sorrell VL. Protocol for optimal detection and exclusion of a patent foramen ovale using transthoracic echocardiography with agitated saline microbubbles. Echocardiography 23:616–22,2006
Woods T, Ramamurthy S. Small pulmonary arteriovenous malformations identified by saline contrast echocardiography are associated with migraine headache. American College of Chest Physicians Scientific Sessions 128;4(Suppl):288S (abstract), 2005
Freeman JA, Woods TD. Use of saline contrast echo timing to distinguish intracardiac and extracardiac shunts: failure of the 3- to 5-beat rule. Echocardiography 25(10):1127–30, 2008
Rasalingam R, Novak E, Rifkin RD. Improved differential diagnosis of intracardiac and extracardiac shunts using acoustic intensity mapping of saline contrast studies. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 21(3):307–317, 2020
Kroon S, Van Thor MCJ, Vorselaars VMM, Hosman AE, Swaans MJ, Snijder RJ, Mager HJ, Post MC. The use of echo density to quantify pulmonary right-to-left shunt in transthoracic contrast echocardiography. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 22(10):1190–1196, 2021
Narula S, Shameer K, Salem Omar AM, Dudley JT, Sengupta PP. Machine-Learning Algorithms to Automate Morphological and Functional Assessments in 2D Echocardiography. J Am Coll Cardiol 68(21):2287–2295, 2016
F. Laumer, D. Di Vece, V. L. Cammann, M. Würdinger, V. Petkova, M. Schönberger, A. Schönberger, J. C. Mercier, D. Niederseer, B. Seifert, M. Schwyzer, R. Burkholz, L. Corinzia, A. S. Becker, F. Scherff, S. Brouwers, A. P. Pazhenkottil, S. Dougoud, M. Messerli, F. C. Tanner, T. Fischer, V. Delgado, P. C. Schulze, C. Hauck, L. S. Maier, H. Nguyen, S. Y. Surikow, J. Horowitz, K. Liu, R. Citro, J. Bax, F. Ruschitzka, J.-R. Ghadri, J. M. Buhmann, and C. Templin. Assessment of Artificial Intelligence in Echocardiography Diagnostics in Differentiating Takotsubo Syndrome From Myocardial Infarction. JAMA Cardiol 7(5):494–503, 2022
E. Zhao, Y. Zhang, C. Kang, H. Niu, J. Zhao, L. Sun, and B. Liu. Influence of the Valsalva maneuver on cardiac hemodynamics and right to left shunt in patients with patent foramen ovale . Sci Rep 7: 44280, 2017
Lynch JJ, Schuchard GH, Gross CM, Wann LS. Prevalence of right-to-left atrial shunting in a healthy population: detection by Valsalva maneuver contrast echocardiography. Am J Cardiol 53(10):1478–80, 1984
Ronneberg Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. Lect Notes Comput Sci 9351:234–241, 2015
S. R. Bisht, V. V. Trivedi, R. Bhardwaj, C. K. Jha, D. Ghosh and H. Shekhar. Pulsing and Detection Strategies for Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound: A Narrative Review. IEEE O J Ultrason Ferroelectr FreqControl 3:56–69, 2023
Ackermann D, Schmitz G. Detection and Tracking of Multiple Microbubbles in Ultrasound B-Mode Images. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control 63(1):72–82, 2016
Christensen-Jeffries K, Browning RJ, Tang MX, Dunsby C, Eckersley RJ. In vivo acoustic super-resolution and super-resolved velocity mapping using microbubbles. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 34(2):433–440, 2015
M. Siepmann, G. Schmitz, J. Bzyl, M. Palmowski, and F. Kiessling. Imaging tumor vascularity by tracing single microbubbles. Proc. IEEE Int. Ultrason. Symp. (IUS) 38:1906–1908, 2011
Heiles B, Chavignon A, Hingot V, Lopez P, Teston E, Couture O. Performance benchmarking of microbubble-localization algorithms for ultrasound localization microscopy. Nat Biomed Eng 6(5):605–616, 2022
Karim F, Majumdar S, Darabi H, Harford S. Multivariate LSTM-FCNs for time series classification. Neural Netw 116:237–245,2019
R. J. G. van Sloun, O. Solomon, M. Bruce, Z. Z. Khaing, H. Wijkstra, Y. C. Eldar, and M. Mischi. Super-Resolution Ultrasound Localization Microscopy Through Deep Learning. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 40(3):829–839, 2021
Y. Shu, C. Han, M. Lv, and X. Liu. Fast super-resolution ultrasound imaging with compressed sensing reconstruction method and single plane wave transmission. IEEE Access 6:39298–39306, 2018
Couture O, Hingot V, Heiles B, Muleki-Seya P, Tanter M. Ultrasound Localization Microscopy and Super-Resolution: A State of the Art. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control 65(8):1304–1320, 2018
Shokoohi-Yekta, M., Wang, J., & Keogh, E. On the Non-Trivial Generalization of Dynamic Time Warping to the Multi-Dimensional Case. Proceedings of the 2015 SIAM International Conference on Data Mining 289–297, 2015
Zhang, X., Gao, Y., Lin, J., & Lu, C.-T. TapNet: Multivariate Time Series Classification with Attentional Prototypical Network. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence 34(04), 6845–6852, 2021
Leclerc, S., Smistad, E., Pedrosa, J., Ostvik, A., Cervenansky, F., Espinosa, F., Espeland, T., Berg, E. A. R., Jodoin, P. M., Grenier, T., Lartizien, C., Dhooge, J., Lovstakken, L., & Bernard. Deep Learning for Segmentation Using an Open Large-Scale Dataset in 2D Echocardiography. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 38(9), 2198–2210, 2019
P. Kora, C. P. Ooi, O. Faust, U. Raghavendra, A. Gudigar, W. Y. Chan, K. Meenakshi, K. Swaraja, P. Plawiak, and U. Rajendra Acharya. Transfer learning techniques for medical image analysis: A review. Biocybern Biomed Eng 79–107, 2022
Darcy AM, Louie AK, Roberts LW. Machine Learning and the Profession of Medicine. JAMA 315(6):551–552, 2016
Quer G, Arnaout R, Henne M, Arnaout R. Machine Learning and the Future of Cardiovascular Care: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J Am Coll Cardiol 77(3):300–313, 2021
Bernard S, Churchill TW, Namasivayam M, Bertrand PB. Agitated Saline Contrast Echocardiography in the Identification of Intra- and Extracardiac Shunts: Connecting the Dots. J Am Soc Echocardiogr S0894–7317(20)30615–5, 2020
Kroon S, Van Thor MCJ, Vorselaars VMM, Hosman AE, Swaans MJ, Snijder RJ, Mager HJ, Post MC. The use of echo density to quantify pulmonary right-to-left shunt in transthoracic contrast echocardiography. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 20;22(10):1190–1196.,2021
Acknowledgements
The author expresses gratitude to all the participants and patients who took part in this study. Additionally, special thanks are extended to the Department of Cardiovascular Ultrasound at Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital of the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, and the High-performance Computing Center at Southwest Petroleum University for their invaluable assistance.
Funding
The study is funded in part by a research grant from the Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Province (2022NSFSC0833) and the Sichuan Nanchong Science and Technology Bureau (SXHZ019). The study is funded in part by a research grant from the Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Project (2022NSFSC0605) and the Sichuan Provincial Science and Technology Plan (2023YFQ0006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors discussed the original idea. Bo Peng and Hongmei Zhang constructed the overall study design with support from Lexue Yin and Jinshan Tang. Weidong Wang performed programming. Weidong Wang, Bo Peng, and Hongmei Zhang conducted data analysis and drafted this manuscript. Hongmei Zhang, Yizhen Li, Yi Wang, Qingfeng Zhang, Geqi Ding, and Lexue Yin were responsible for data collection and clinical result interpretation. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
This study has obtained approval from the Medical Ethics Committee of Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital.
Consent to Participate
All participants in this study provided informed consent forms.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Consent for Publication
The author confirms the publishing consent of all participants.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Zhang, H., Li, Y. et al. An Automated Heart Shunt Recognition Pipeline Using Deep Neural Networks. J Digit Imaging. Inform. med. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-024-01047-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-024-01047-4