Abstract
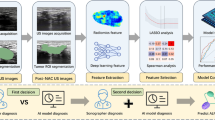
The purpose of this study was to fuse conventional radiomic and deep features from digital breast tomosynthesis craniocaudal projection (DBT-CC) and ultrasound (US) images to establish a multimodal benign-malignant classification model and evaluate its clinical value. Data were obtained from a total of 487 patients at three centers, each of whom underwent DBT-CC and US examinations. A total of 322 patients from dataset 1 were used to construct the model, while 165 patients from datasets 2 and 3 formed the prospective testing cohort. Two radiologists with 10–20 years of work experience and three sonographers with 12–20 years of work experience semiautomatically segmented the lesions using ITK-SNAP software while considering the surrounding tissue. For the experiments, we extracted conventional radiomic and deep features from tumors from DBT-CCs and US images using PyRadiomics and Inception-v3. Additionally, we extracted conventional radiomic features from four peritumoral layers around the tumors via DBT-CC and US images. Features were fused separately from the intratumoral and peritumoral regions. For the models, we tested the SVM, KNN, decision tree, RF, XGBoost, and LightGBM classifiers. Early fusion and late fusion (ensemble and stacking) strategies were employed for feature fusion. Using the SVM classifier, stacking fusion of deep features and three peritumoral radiomic features from tumors in DBT-CC and US images achieved the optimal performance, with an accuracy and AUC of 0.953 and 0.959 [CI: 0.886–0.996], a sensitivity and specificity of 0.952 [CI: 0.888–0.992] and 0.955 [0.868–0.985], and a precision of 0.976. The experimental results indicate that the fusion model of deep features and peritumoral radiomic features from tumors in DBT-CC and US images shows promise in differentiating benign and malignant breast tumors.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Siegel, R.L., Miller, K.D., Fuchs, H.E., Jemal, A.: Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 72, 7–33 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21708
Coughlin, S.S.: Social determinants of breast cancer risk, stage, and survival. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 177, 537–548 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-019-05340-7
Cardoso, F., Kyriakides, S., Ohno, S., Penault-Llorca, F., Poortmans, P., Rubio, I.T., Zackrisson, S., Senkus, E.: Early breast cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Annals of Oncology. 30, 1194–1220 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdz173
Kim, J., Kim, J., Han, A., Nguyen, M.C.: Leisure time physical activity, social support, health perception, and mental health among women with breast cancer. Leisure Studies. 40, 352–362 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/02614367.2020.1869290
Barrios, C.H.: Global challenges in breast cancer detection and treatment. The Breast. 62, S3–S6 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.breast.2022.02.003
Nazari, S.S., Mukherjee, P.: An overview of mammographic density and its association with breast cancer. Breast Cancer. 25, 259–267 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-018-0857-5
Brentnall, A.R., Cuzick, J., Buist, D.S.M., Bowles, E.J.A.: Long-Term accuracy of breast cancer risk assessment combining classic risk factors and breast density. JAMA Oncol. 4, (2018). https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.0174
Comstock, C.E., Gatsonis, C., Newstead, G.M., Snyder, B.S., Gareen, I.F., Bergin, J.T., Rahbar, H., Sung, J.S., Jacobs, C., Harvey, J.A., Nicholson, M.H., Ward, R.C., Holt, J., Prather, A., Miller, K.D., Schnall, M.D., Kuhl, C.K.: Comparison of Abbreviated Breast MRI vs Digital Breast Tomosynthesis for Breast Cancer Detection among Women with Dense Breasts Undergoing Screening. JAMA. 323, 746–756 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.0572
Sassi, A., Salminen, A., Jukkola, A., Tervo, M., Mäenpää, N., Turtiainen, S., Tiainen, L., Liimatainen, T., Tolonen, T., Huhtala, H., Rinta-Kiikka, I., Arponen, O.: Breast density and the likelihood of malignant MRI-detected lesions in women diagnosed with breast cancer. Eur Radiol. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-023-10072-w
Guo, R., Lu, G., Qin, B., Fei, B.: Ultrasound imaging technologies for breast cancer detection and management: a review. Ultrasound Med Biol. 44, 37–70 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2017.09.012
Choi, J.S., Han, B.K., Ko, E.S., Bae, J.M., Ko, E.Y., Song, S.H., Kwon, M.R., Shin, J.H., Hahn, S.Y.: Effect of a deep learning framework-based computer-aided diagnosis system on the diagnostic performance of radiologists in differentiating between malignant and benign masses on breast ultrasonography. Korean J Radiol. 20, 749–758 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.0530
Kriti, Virmani, J., Agarwal, R.: A Characterization Approach for the Review of CAD Systems Designed for Breast Tumor Classification Using B-Mode Ultrasound Images. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering. 29, 1485–1523 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-021-09620-8
Huynh, B.Q., Li, H., Giger, M.L.: Digital mammographic tumor classification using transfer learning from deep convolutional neural networks. Journal of Medical Imaging. 3, 034501 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1117/1.jmi.3.3.034501
Antropova, N., Huynh, B.Q., Giger, M.L.: A deep feature fusion methodology for breast cancer diagnosis demonstrated on three imaging modality datasets. Med Phys. 44, 5162–5171 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/mp.12453
Letchumanan, N., Wong, J.H.D., Tan, L.K., Ab Mumin, N., Ng, W.L., Chan, W.Y., Rahmat, K.: A Radiomics Study: Classification of Breast Lesions by Textural Features from Mammography Images. J Digit Imaging. 36, 1533–1540 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-022-00753-1
Diwakaran, M., Surendran, D.: Breast Cancer Prognosis Based on Transfer Learning Techniques in Deep Neural Networks. Information Technology and Control. 52, 381–396 (2023). https://doi.org/10.5755/j01.itc.52.2.33208
Maqsood, S., Damaševičius, R., Maskeliūnas, R.: TTCNN: A Breast Cancer Detection and Classification towards Computer-Aided Diagnosis Using Digital Mammography in Early Stages. Applied Sciences (Switzerland). 12, (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/app12073273
Zebari, D.A., Ibrahim, D.A., Zeebaree, D.Q., Mohammed, M.A., Haron, H., Zebari, N.A., Damaševičius, R., Maskeliūnas, R.: Breast cancer detection using mammogram images with improved multi-fractal dimension approach and feature fusion. Applied Sciences (Switzerland). 11, (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/app112412122
Meraj, T., Alosaimi, W., Alouffi, B., Rauf, H.T., Kumar, S.A., Damaševičius, R., Alyami, H.: A quantization assisted U-Net study with ICA and deep features fusion for breast cancer identification using ultrasonic data. PeerJ Comput Sci. 7, (2021). https://doi.org/10.7717/PEERJ-CS.805
Wang, Y., Li, Y., Song, Y., Chen, C., Wang, Z., Li, L., Liu, M., Liu, G., Xu, Y., Zhou, Y., Sun, Q., Shen, S.: Comparison of ultrasound and mammography for early diagnosis of breast cancer among Chinese women with suspected breast lesions: A prospective trial. Thorac Cancer. 13, 3145–3151 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1111/1759-7714.14666
Sahu, A., Das, P.K., Meher, S.: High accuracy hybrid CNN classifiers for breast cancer detection using mammogram and ultrasound datasets. Biomed Signal Process Control. 80, (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2022.104292
Atrey, K., Singh, B.K., Bodhey, N.K., Bilas Pachori, R.: Mammography and ultrasound based dual modality classification of breast cancer using a hybrid deep learning approach. Biomed Signal Process Control. 86, (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2023.104919
Shi, J., Dong, Y., Jiang, W., Qin, F., Wang, X., Cui, L., Liu, Y., Jin, Y., Luo, Y., Jiang, X.: MRI-based peritumoral radiomics analysis for preoperative prediction of lymph node metastasis in early-stage cervical cancer: A multi-center study. Magn Reson Imaging. 88, 1–8 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mri.2021.12.008
Jahangeer, G.S.B., Rajkumar, T.D.: Early detection of breast cancer using hybrid of series network and VGG-16. Multimed Tools Appl. 80, 7853–7886 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09914-2
Singh, R., Ahmed, T., Kumar, A., Singh, A.K., Pandey, A.K., Singh, S.K.: Imbalanced Breast Cancer Classification Using Transfer Learning. In: IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics. pp. 83–93. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc. (2021)
Hassan, S.A., Sayed, M.S., Abdalla, M.I., Rashwan, M.A.: Breast cancer masses classification using deep convolutional neural networks and transfer learning. Multimed Tools Appl. 79, 30735–30768 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09518-w
Al-Haija, Q.A., Adebanjo, A.: Breast cancer diagnosis in histopathological images using ResNet-50 convolutional neural network. In: 2020 IEEE International IOT, Electronics and Mechatronics Conference (IEMTRONICS). pp. 1–7. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc., Canada (2020)
Meattini, I., Bicchierai, G., Saieva, C., De Benedetto, D., Desideri, I., Becherini, C., Abdulcadir, D., Vanzi, E., Boeri, C., Gabbrielli, S., Lucci, F., Sanchez, L., Casella, D., Bernini, M., Orzalesi, L., Vezzosi, V., Greto, D., Mangoni, M., Bianchi, S., Livi, L., Nori, J.: Impact of molecular subtypes classification concordance between preoperative core needle biopsy and surgical specimen on early breast cancer management: Single-institution experience and review of published literature. European Journal of Surgical Oncology. 43, 642–648 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejso.2016.10.025
Araujo, T., Aresta, G., Castro, E., Rouco, J., Aguiar, P., Eloy, C., Polonia, A., Campilho, A.: Classification of breast cancer histology images using convolutional neural networks. PLoS One. 12, (2017). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0177544
Sandbank, J., Bataillon, G., Nudelman, A., Krasnitsky, I., Mikulinsky, R., Bien, L., Thibault, L., Albrecht Shach, A., Sebag, G., Clark, D.P., Laifenfeld, D., Schnitt, S.J., Linhart, C., Vecsler, M., Vincent-Salomon, A.: Validation and real-world clinical application of an artificial intelligence algorithm for breast cancer detection in biopsies. NPJ Breast Cancer. 8, (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41523-022-00496-w
Kutluer, N., Solmaz, O.A., Yamacli, V., Eristi, B., Eristi, H.: Classification of breast tumors by using a novel approach based on deep learning methods and feature selection. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 200, 183–192 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-023-06970-8
Pang, T., Wong, J.H.D., Ng, W.L., Chan, C.S.: Deep learning radiomics in breast cancer with different modalities: Overview and future, (2020)
Conti, A., Duggento, A., Indovina, I., Guerrisi, M., Toschi, N.: Radiomics in breast cancer classification and prediction. Semin Cancer Biol. 72, 238–250 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.04.002
Atrey, K., Singh, B.K., Bodhey, N.K.: Multimodal classification of breast cancer using feature level fusion of mammogram and ultrasound images in machine learning paradigm. Multimed Tools Appl. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-16414-6
Sahu, A., Das, P.K., Meher, S.: An efficient deep learning scheme to detect breast cancer using mammogram and ultrasound breast images. Biomed Signal Process Control. 87, (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2023.105377
Hamdy, E., Zaghloul, M.S., Badawy, O.: Deep learning supported breast cancer classification with multi-modal image fusion. In: 2021 22nd International Arab Conference on Information Technology, ACIT 2021. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc. (2021)
Arya, N., Saha, S.: Multi-Modal Classification for Human Breast Cancer Prognosis Prediction: Proposal of Deep-Learning Based Stacked Ensemble Model. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 19, 1032–1041 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCBB.2020.3018467
Cui, C., Yang, H., Wang, Y., Zhao, S., Asad, Z., Coburn, L.A., Wilson, K.T., Landman, B.A., Huo, Y.: Deep multimodal fusion of image and non-image data in disease diagnosis and prognosis: a review. Progress in Biomedical Engineering. 5, (2023). https://doi.org/10.1088/2516-1091/acc2fe
Muduli, D., Dash, R., Majhi, B.: Automated diagnosis of breast cancer using multi-modal datasets: A deep convolution neural network based approach. Biomed Signal Process Control. 71, (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2021.102825
Amrane, M., Oukid, S., Gagaoua, I., Ensari, T.: Breast Cancer Classification Using Machine Learning. In: 2018 Electric Electronics, Computer Science, Biomedical Engineerings’ Meeting (EBBT). pp. 1–4 (2018)
Zubair, M., Wang, S., Ali, N.: Advanced Approaches to Breast Cancer Classification and Diagnosis. Front Pharmacol. 11, (2021). https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.632079
Selvaraju, R.R., Cogswell, M., Das, A., Vedantam, R., Parikh, D., Batra, D.: Grad-CAM: Visual Explanations from Deep Networks via Gradient-based Localization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. pp. 618–626 (2017)
Funding
This work was partially supported by the PhD Start-up Fund of Liaoning Province (2021-BS-044) and the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (2022-YGJC-52).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Guoxiu Lu, Wei Yang, and Nannan Zhao. Research direction and experimental design were completed under the guidance of He Ma and Wei Qian. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Ronghui Tian, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of Northeastern University, Shenyang, Liaoning, China (date: September 23, 2021/no. NEU-EC-2021B019S).
Consent to Participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for Publication
The image information in the manuscript is anonymous, and the submitted materials do not include images that may identify the person, so consent is not required.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, R., Lu, G., Zhao, N. et al. Constructing the Optimal Classification Model for Benign and Malignant Breast Tumors Based on Multifeature Analysis from Multimodal Images. J Digit Imaging. Inform. med. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-024-01036-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-024-01036-7