Abstract
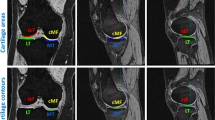
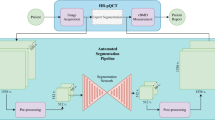
Diffusion tensor imaging of physis and metaphysis can be used as a biomarker to predict height change in the pediatric population. Current application of this technique requires manual segmentation of the physis which is time-consuming and introduces interobserver variability. UNET Transformers (UNETR) can be used for automatic segmentation to optimize workflow. Three hundred and eighty-five DTI scans from 191 subjects with mean age of 12.6 years ± 2.01 years were retrospectively used for training and validation. The mean Dice correlation coefficient was 0.81 for the UNETR model and 0.68 for the UNET. Manual extraction and segmentation took 15 min per volume, whereas both deep learning segmentation techniques took < 1 s per volume and were deterministic, always producing the same result for a given input. Intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) for ROI-derived femur diffusion metrics was excellent for tract count (0.95), volume (0.95), and FA (0.97), and good for tract length (0.87). The results support the hypothesis that a hybrid UNETR model can be trained to replace the manual segmentation of physeal DTI images, therefore automating the process.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated and analyzed for this study are not openly available as they contained protected health information. Deidentified data is available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Lanzman RS, Wittsack HJ. Diffusion tensor imaging in abdominal organs. NMR in Biomedicine. 2015; 30(3):e3434
Oudeman J, Nederveen AJ, Strijkers GJ, et al. Techniques and applications of skeletal muscle diffusion tensor imaging: A review. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2016 Apr; 43(4):773-88. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.25016.
Jaramillo D, Connolly SA, Vajapeyam S, et al. Normal and ischemic epiphysis of the femur: diffusion MR imaging study in piglets. Radiology. 2003; 227(3): 825-32. PMID: 12773684
Jaimes C, Berman JI, Delgado J, et al. Diffusion-tensor imaging of the growing ends of long bones: pilot demonstration of columnar structure in the physes and metaphyses of the knee. Radiology. 2014; 273(2):491-501. PMID: 25102295
Bedoya MA, Delgado J, Berman JI, et al. Diffusion-Tensor Imaging of the Physes: A Possible Biomarker for Skeletal Growth-Experience with 151 Children. Radiology. 2017; 284(1):210-218. PMID: 28156202
Barrera CA, Bedoya MA, Delgado J, Berman JI, Chauvin NA, Edgar JC, Jaramillo D. Correlation between diffusion tensor imaging parameters of the distal femoral physis and adjacent metaphysis, and subsequent adolescent growth. Pediatr Radiol. 2019 Aug;49(9):1192-1200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-019-04443-z. Epub 2019 Jun 8. PMID: 31177318.
Delgado J, Jaramillo D, Chauvin NA, Guo M, Stratton MS, Sweeney HE, Barrera CA, Mostoufi-Moab S. Evaluating growth failure with diffusion tensor imaging in pediatric survivors of high-risk neuroblastoma treated with high-dose cis-retinoic acid. Pediatr Radiol. 2019 Jul;49(8):1056–1065. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-019-04409-1. Epub 2019 May 4. PMID: 31055614; PMCID: PMC6599475.
Duong P, Mostoufi-Moab S, Raya JG, Jaimes C, Delgado J, Jaramillo D. Imaging Biomarkers of the Physis: Cartilage Volume on MRI vs. Tract Volume and Length on Diffusion Tensor Imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2020 Aug;52(2):544–551. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.27076. Epub 2020 Feb 10. PMID: 32039525; PMCID: PMC7410391.
Kvist O, Damberg P, Dou Z, Berglund JS, Flodmark CE, Nilsson O, Diaz S. Magnetic resonance and diffusion tensor imaging of the adolescent rabbit physis of the knee. Magn Reson Med. 2022 Sep 15. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.29432. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 36110062.
Litjens G, Kooi T, Bejnordi BE, et al. A survey on deep learning in medical imaging analysis. Medical Image Analysis. 2017 Dec; 42:60-88.
He K, Gan C, Li Z, Rekik I, Yin Z, Ji W, Gao Y, Wang Q, Zhang J, Shen D. Transformers in medical image analysis: A review. Intelligent Medicine. 2022 Aug 24.
Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, Uszkoreit J, Jones L, Gomez AN, Kaiser Ł, Polosukhin I. Attention is all you need. Advances in neural information processing systems. 2017;30.
Hatamizadeh A, Tang Y, Nath V, Yang D, Myronenko A, Landman B, Roth HR, Xu D. Unetr: Transformers for 3d medical image segmentation. InProceedings of the IEEE/CVF winter conference on applications of computer vision 2022 (pp. 574–584).
Jaramillo D, Duong P, Nguyen JC, Mostoufi-Moab S, Nguyen MK, Moreau A, Barrera CA, Hong S, Raya JG. Diffusion Tensor Imaging of the Knee to Predict Childhood Growth. Radiology. 2022 Jun;303(3):655–663. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.210484. Epub 2022 Mar 22. PMID: 35315716; PMCID: PMC9131176
Wang, R. & Benner, Thomas & Sorensen, A. & Wedeen, V.J. (2007). Diffusion Toolkit: A Software Package for Diffusion Imaging Data Processing and Tractography. Proc Intl Soc Mag Reson Med. 15.
Dosovitskiy A, Beyer L, Kolesnikov A, Weissenborn D, Zhai X, Unterthiner T, Dehghani M, Minderer M, Heigold G, Gelly S, Uszkoreit J. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11929. 2020 Oct 22.
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T. (2015). U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W., Frangi, A. (eds) Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2015. MICCAI 2015. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 9351. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
MONAI Consortium. (2023). MONAI: Medical Open Network for AI (1.3.0). Zenodo. https://monai.io/index.html.
Loshchilov, I. & Hutter, F. Decoupled weight decay regularization. ICLR. 2019. https://openreview.net/forum?id=Bkg6RiCqY7
Dozat T. Incorporating nesterov momentum into adam [Internet]. OpenReview. 2016 [cited 2023Apr12]. Available from: https://openreview.net/forum?id=OM0jvwB8jIp57ZJjtNEZ
Astuto B, Flament I, Namiri NK, Shah R, Bharadwaj U, Link TM, Bucknor MD, Pedoia V, Majumdar S. Erratum: Automatic Deep Learning-assisted Detection and Grading of Abnormalities in Knee MRI Studies. Radiol Artif Intell. 2021 May 19;3(3):e219001. https://doi.org/10.1148/ryai.2021219001. Erratum for: Radiol Artif Intell. 2021 Jan 20;3(3):e200165. PMID: 34157062; PMCID: PMC8166114.
Chen H, Zhao N, Tan T, Kang Y, Sun C, Xie G, Verdonschot N, Sprengers A. Knee Bone and Cartilage Segmentation Based on a 3D Deep Neural Network Using Adversarial Loss for Prior Shape Constraint. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 May 20;9:792900. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2022.792900. PMID: 35669917; PMCID: PMC9163741
Folle L, Simon D, Tascilar K, Krönke G, Liphardt AM, Maier A, Schett G, Kleyer A. Deep Learning-Based Classification of Inflammatory Arthritis by Identification of Joint Shape Patterns-How Neural Networks Can Tell Us Where to "Deep Dive" Clinically. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Mar 10;9:850552. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2022.850552. PMID: 35360728; PMCID: PMC8960274.
Nadeem MW, Goh HG, Ali A, Hussain M, Khan MA, Ponnusamy VA. Bone Age Assessment Empowered with Deep Learning: A Survey, Open Research Challenges and Future Directions. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020 Oct 3;10(10):781. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10100781. PMID: 33022947; PMCID: PMC7601134.
Zijdenbos AP, Dawant BM, Margolin RA, Palmer AC. Morphometric analysis of white matter lesions in MR images: method and validation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 1994;13:716–724.
Funding
D.J. grants are from the National Institutes of Health and Society for Pediatric Radiology Research and Education Fund, supported by the National Institutes of Health (R01 HD104720 [D.J.].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Guarantors of integrity of entire study, D.J., P.T.D., L.S., H.Y.H; study concepts/study design or data acquisition or data analysis/interpretation, all authors; manuscript drafting or manuscript revision for important intellectual content, all authors; approval of final version of submitted manuscript, all authors; agrees to ensure any questions related to the work are appropriately resolved, all authors; literature research, D.J., P.T.D., L.S., H.Y.H.; clinical studies, P.T.D., L.S., H.Y.H; statistical analysis, L.S. and H.Y.H.; and manuscript editing, all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
The local institutional review board approved this study.
Consent to Participate
The informed consent requirement was waived in compliance with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act.
Consent to Publish
The informed consent requirement was waived in compliance with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Duong, P.T., Santos, L., Hsu, HY. et al. Deep Learning-Assisted Diffusion Tensor Imaging for Evaluation of the Physis and Metaphysis. J Digit Imaging. Inform. med. 37, 756–765 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-024-00993-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-024-00993-3