Abstract
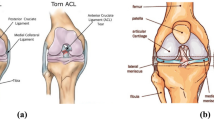
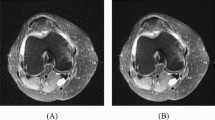
Magnetic resonance (MR) is one of the special imaging techniques used to diagnose orthopedics and traumatology. In this study, a new method has been proposed to detect highly accurate automatic meniscal tear and anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries. In this study, images in three different slices were collected. These are the sagittal, coronal, and axial slices, respectively. Images taken from each slice were categorized in 3 different ways: sagittal database (sDB), coronal database (cDB), and axial database (aDB). The proposed model in the study uses deep feature extraction. In this context, deep features have been obtained by using fully-connected layers of AlexNet architecture. In the second stage of the study, the most significant features were selected using the iterative RelifF (IRF) algorithm. In the last step of the application, the features are classified by using the k-nearest neighbor (kNN) method. Three datasets were used in the study. These datasets, sDB, and cDB, have four classes and consist of 442 and 457 images, respectively. The aDB used in the study has two class labels and consists of 190 images. The model proposed within the scope of the study was applied in 3 datasets. In this context, 98.42%, 100%, and 100% accuracy values were obtained for sDB, cDB, and aDB datasets, respectively. The study results showed that the proposed method detected meniscal tear and anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries with high accuracy.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Englund, A. Guermazi, D. Gale, D.J. Hunter, P. Aliabadi, M. Clancy, D.T. Felson, Incidental meniscal findings on knee MRI in middle-aged and elderly persons, N. Engl. J. Med. 359 (2008) 1108–1115.
M. Jarraya, F.W. Roemer, M. Englund, M.D. Crema, H.I. Gale, D. Hayashi, J.N. Katz, A. Guermazi, Meniscus morphology: does tear type matter? A narrative review with focus on relevance for osteoarthritis research, in: Semin. Arthritis Rheum., Elsevier, 2017: pp. 552–561.
J.H. Ahn, S.H. Jeong, H.W. Kang, Risk factors of false-negative magnetic resonance imaging diagnosis for meniscal tear associated with anterior cruciate ligament tear, Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 32 (2016) 1147–1154.
K.G. Shea, J.L. Carey, Management of anterior cruciate ligament injuries: evidence-based guideline, JAAOS-Journal Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 23 (2015) e1–e5.
N. Maffulli, U.G. Longo, S. Campi, V. Denaro, Meniscal tears, Open Access J. Sport. Med. 1 (2010) 45.
D. Zbrojkiewicz, C. Vertullo, J.E. Grayson, Increasing rates of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in young Australians, 2000–2015, Med. J. Aust. 208 (2018) 354–358.
M. Karia, Y. Ghaly, N. Al-Hadithy, S. Mordecai, C. Gupte, Current concepts in the techniques, indications and outcomes of meniscal repairs, Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 29 (2019) 509–520.
W.-F. Xiao, T. Yang, Y. Cui, C. Zeng, S. Wu, Y.-L. Wang, G.-H. Lei, Risk factors for noncontact anterior cruciate ligament injury: analysis of parameters in proximal tibia using anteroposterior radiography, J. Int. Med. Res. 44 (2016) 157–163.
C.L. Ardern, N.F. Taylor, J.A. Feller, K.E. Webster, Fifty-five per cent return to competitive sport following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis including aspects of physical functioning and contextual factors, Br. J. Sports Med. 48 (2014) 1543–1552.
K. Li, J. Du, L.-X. Huang, L. Ni, T. Liu, H.-L. Yang, The diagnostic accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging for anterior cruciate ligament injury in comparison to arthroscopy: a meta-analysis, Sci. Rep. 7 (2017) 1–10.
H.O. Alanazi, A.H. Abdullah, K.N. Qureshi, A critical review for developing accurate and dynamic predictive models using machine learning methods in medicine and health care, J. Med. Syst. 41 (2017) 69.
H.A. Khan, H. Ahad, P. Sharma, P. Bajaj, N. Hassan, Y. Kamal, Correlation between magnetic resonance imaging and arthroscopic findings in the knee joint, Trauma Mon. 20 (2015).
A. Kim, L. Khoury, M. Schweitzer, L. Jazrawi, C. Ishak, R. Meislin, F. Kummer, O.H. Sherman, Effect of specialty and experience on the interpretation of knee MRI scans, Bull. NYU Hosp. Jt. Dis. 66 (2008) 272.
M.S. Swain, N. Henschke, S.J. Kamper, A.S. Downie, B.W. Koes, C.G. Maher, Accuracy of clinical tests in the diagnosis of anterior cruciate ligament injury: a systematic review, Chiropr. Man. Therap. 22 (2014) 1–10.
M.F.J. Acosta, L.Y.C. Tovar, M.B. Garcia-Zapirain, W.S. Percybrooks, Melanoma diagnosis using deep learning techniques on dermatoscopic images, BMC Med. Imaging. 21 (2021) 1–11.
P.K. Chaudhary, R.B. Pachori, Automatic diagnosis of glaucoma using two-dimensional fourier-bessel series expansion based empirical wavelet transform, Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 64 (2021) 102237.
P. López-Úbeda, M.C. Díaz-Galiano, T. Martín-Noguerol, A. Luna, L.A. Ureña-López, M.T. Martín-Valdivia, Automatic medical protocol classification using machine learning approaches, Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. (2021) 105939.
K.E. Sengun, Y.T. Cetin, M.S. Guzel, S. Can, E. Bostanci, Automatic liver segmentation from CT images using deep learning algorithms: a comparative study, ArXiv Prepr. ArXiv2101.09987. (2021).
A. Krizhevsky, I. Sutskever, G.E. Hinton, Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks, Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 25 (2012) 1097–1105.
M. Robnik-Šikonja, I. Kononenko, Theoretical and empirical analysis of ReliefF and RReliefF, Mach. Learn. 53 (2003) 23–69.
I. Kononenko, Estimating attributes: analysis and extensions of RELIEF, Mach. Learn. ECML-94. (1994) 171–182. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-57868-4_57.
J. Maillo, S. Ramírez, I. Triguero, F. Herrera, kNN-IS: an iterative spark-based design of the k-nearest neighbors classifier for big data, Knowledge-Based Syst. 117 (2017) 3–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2016.06.012.
T. Tuncer, S. Dogan, P. Pławiak, U. Rajendra Acharya, Automated arrhythmia detection using novel hexadecimal local pattern and multilevel wavelet transform with ECG signals, Knowledge-Based Syst. 186 (2019) 104923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2019.104923.
M.J. Warrens, On the equivalence of Cohen’s kappa and the Hubert-Arabie Adjusted Rand Index, J. Classif. 25 (2008) 177–183. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00357-008-9023-7.
D. Chicco, G. Jurman, The advantages of the Matthews correlation coefficient (MCC) over F1 score and accuracy in binary classification evaluation, BMC Genomics. 21 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-019-6413-7.
S. Demir, S. Key, M. Baygin, T. Tuncer, S. Dogan, S. Brahim Belhaouari, A. Kursad Poyraz, M. Gurger, Automated knee ligament injuries classification method based on exemplar pyramid local binary pattern feature extraction and hybrid iterative feature selection, Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 71 (2022) 103191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2021.103191.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
The document of ethics is attached for the data collected.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Key, S., Baygin, M., Demir, S. et al. Meniscal Tear and ACL Injury Detection Model Based on AlexNet and Iterative ReliefF. J Digit Imaging 35, 200–212 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-022-00581-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-022-00581-3