Abstract
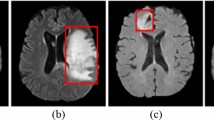
Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer that affects humans and is usually diagnosed by initial clinical screening, which is followed by dermoscopic analysis. Automated classification of skin lesions is still a challenging task because of the high visual similarity between melanoma and benign lesions. This paper proposes a new residual deep convolutional neural network (RDCNN) for skin lesions diagnosis. The proposed neural network is trained and tested using six well-known skin cancer datasets, PH2, DermIS and Quest, MED-NODE, ISIC2016, ISIC2017, and ISIC2018. Three different experiments are carried out to measure the performance of the proposed RDCNN. In the first experiment, the proposed RDCNN is trained and tested using the original dataset images without any pre-processing or segmentation. In the second experiment, the proposed RDCNN is tested using segmented images. Finally, the utilized trained model in the second experiment is saved and reused in the third experiment as a pre-trained model. Then, it is trained again using a different dataset. The proposed RDCNN shows significant high performance and outperforms the existing deep convolutional networks.























Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Cancer Society: Cancer facts and figures. Available from: https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancer-org/research/cancer-facts-and-statistics/annual-cancer-facts-and-figures/2018/cancer-facts-and-figures-2018.pdf, Cited 2 Aug 2018.
RL. Siegel, KD. Miller, and A. Jemal, Cancer statistics, 2018, CA. a Cancer Journal for Clinicians, vol. 68, no.1, pp.7-30, 2018. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21442 PMID: 29313949.
Binder M., Schwarz M., Winkler A., Steiner A., Kaider A., Wolff K., et al. Epiluminescence microscopy. A useful tool for the diagnosis of pigmented skin lesions for formally trained Dermatologists, Archives of Dermatology., vol. 131, no. 3, pp. 286–291, 1995.
Ravi D, Wong C, Deligianni F, Berthelot M, Andreu-Perez J, Lo B, Yang GZ, Deep learning for health informatics, IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, vol. 21, no. 1, pp. 4–21, 2017.
Cheng Lu, and Mrinal Mandal, Automated analysis and diagnosis of skin melanoma on whole slide histopathological images, Pattern Recognition, Volume 48, Issue 8, p. 2738-2750, 2015.
Catarina Barata, M. Emre Celebi, and Jorge S. Marques, Development of a clinically oriented system for melanoma diagnosis, Pattern Recognition, Volume 69, p. 270-285, 2017
Maciel Zortea, Eliezer Flores, and Jacob Scharcanski, A simple weighted thresholding method for the segmentation of pigmented skin lesions in macroscopic images, Pattern Recognition, Volume 64, p. 92-104, 2017.
Zilong Hu, Jinshan Tang, Ziming Wang, Kai Zhang, and Qingling Sun, Deep learning for image-based cancer detection and diagnosis — a survey, Pattern Recognition, Volume 83, p. 134-149, 2018.
Lei Bi, Jinman Kim, Euijoon Ahn, Ashnil Kumar, Feng Dagan, and Michael Fulham, Step-wise integration of deep class-specific learning for dermoscopic image segmentation, Pattern Recognition, Volume 85, p.78-89, 2019.
Argenziano G, Soyer HP, Chimenti S, Talamini R, Corona R, Sera F, Binder M, Cerroni L, De Rosa G, Ferrara G et al., Dermoscopy of pigmented skin lesions: results of a consensus meeting via the internet, Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, vol. 48, no. 5, pp.679–693, 2003.
Almaraz J., Ponomaryov V., Gonzalez E., Melanoma CADe based on ABCD Rule and Haralick Texture Features in 9th Int. Kharkiv Symposium on Physics and Engineering of Microwaves, Millimeter, and Submillimeter Waves (MSMW), IEEE, pp. 1–4, 2016.
Kostopoulos S A, Asvestas PA, Kalatzis IK, Sakellaropoulos GC, Sakkis TH, Cavouras DA, et al. Adaptable pattern recognition system for discriminating Melanocytic Nevi from Malignant Melanomas using plain photography images from different image databases, International Journal of Medical Informatics, Vol. 105, pp. 1–10, 2017.
Giotis I., Molders N., Land S., Biehl M., junkman M., and Petkov N., MED-NODE: A computer-assisted melanoma diagnosis system using non-dermoscopic images, Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 42, no. 19, pp. 6578–6585, 2015.
Amelard R, Wong A, Clausi DA., Extracting morphological high-level intuitive features (HLIF) for enhancing skin lesion classification, Int. Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, pp.4458–4461, 2012.
I. A. Ozkan, and M. Koklu, Skin lesion classification using machine learning algorithms, Intelligent Systems and Applications in Engineering, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 285-289, 2017.
L. Bi, J. Kim, E. Ahn, D. Feng, and M. Fulham, Automatic melanoma detection via multi-scale lesion-biased representation and joint reverse classification, 13th Int. Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), IEEE, pp. 1055–1058, 2016.
Jafari M., Samavi S., Karimi N., Soroushmehr S., Ward K., and Najarian K., Automatic detection of melanoma using broad extraction of features from digital images, in 38th Int. Con. of the IEEE Eng. in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), pp. 1357–1360, 2016.
R. Chakravorty, S. Liang, M. Abedini, and R. Garnavi, Dermatologist-like feature extraction from skin lesion for improved asymmetry classification in PH2 database, 38th Int. Conf. of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), pp. 3855–3858, 2016.
KM Hosny, MA Kassem, MM Fouad, Skin cancer classification using deep learning and transfer learning, in 9th Cairo International Biomedical Engineering, IEEE, pp.90–93, 2018.
K. M. Hosny, MA Kassem, MM Fouad, Classification of skin lesions using transfer learning and augmentation with Alex-net, PloS one, vol. 14, no. 5, 2019.
K. M. Hosny, M. A. Kassem, and M. M. Foaud, Skin melanoma classification using deep convolutional neural networks, Deep Learning for Computer Vision: Theories and Applications, CRC Press, 2020.
E. Karabulut, and T. Ibrikci, Texture analysis of melanoma images for computer-aided diagnosis, Int. Conference on Intelligent Computing, Computer Science & Information Systems (ICCSIS 16), vol. 2, pp.26–29,2016.
Nasr-Esfahan E., Samavi S., Karimi N., Soroushmehr S., Jafari M., Ward K.et al. Melanoma detection by analysis of clinical images using convolutional neural network, Int. Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, vol. 137, pp. 1373–1376, 2016.
Esteva A., Kuprel B., Novoa R., Ko J., Swetter S., Blau H., et al., Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks, Nature, vol. 542, pp. 115–118, 2017.
Pham TC., Luong CM, Visani M., and Hoang VD, Deep CNN and data augmentation for skin lesion classification, Intelligent Information and Database Systems, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Springer, vol. 10752, pp. 573–582, 2018
Yu L., Chen H., Dou Q., Qin J., and Heng P., Automated melanoma recognition in dermoscopy images via very deep residual networks, IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, vol. 36, no. 4, pp. 994–1004, 2017.
X. Wang, X. Jiang, H. Ding, and J. Liu, Bi-directional dermoscopic feature learning and multi-scale consistent decision fusion for skin lesion segmentation, IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, vol. 29, pp. 3039-3051, 2020.
Javeria Amin, Abida Sharif, Nadia Gul, Muhammad Almas Anjum, Muhammad Wasif Nisar, Faisal Azam, and Syed Ahmad Chan Bukhari, Integrated design of deep features fusion for localization and classification of skin cancer, Pattern Recognition Letters, Volume 131, p. 63-70, 2020.
M. A. Khan, M. Sharif, T. Akram, S. A. C. Bukhari, and R. S. Nayak, Developed Newton-Raphson based deep features selection framework for skin lesion recognition, Pattern Recognition Letters, Volume 129, p. 293-303, 2020.
A. Mahbod, G. Schaefer, I. Ellinger, R. Ecker, A. Pitiot, C. Wang, Fusing fine-tuned deep features for skin lesion classification, Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics, Vol. 71, pp. 19-29, 2019.
A. Soudani, W. Barhoumi, An image-based segmentation recommender using crowdsourcing and transfer learning for skin lesion extraction, Expert Systems with Applications, Vol. 118, pp. 400-410, 2019.
P. Pereira, R. Pinto, R. P. Paiva, P Assuncao, L. Tavora, L. A. Thomaz, S. Faria, Skin lesion classification enhancement using border-line features — the melanoma vs. nevus problem, Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, Vol. 57, pages 101765, 2020.
Z. Yu, X. Jiang, F. Zhou, J. Qin, et al., Melanoma recognition in dermoscopy images via aggregated deep convolutional features, IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, vol. 66, no. 4, pp. 1006-1016, 2019.
T. Majtner, S Yildirim-Yayilgan, and J. Y. Hardeberg, Optimised deep learning features for improved melanoma detection, Multimedia Tools and Applications, vol. 78, pp. 11883–11903, 2019.
B. A. Albert, Deep learning from limited training data: novel segmentation and ensemble algorithms applied to automatic melanoma diagnosis, IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 31254-31269, 2020.
J. Almaraz-Damian, V. Ponomaryov, S. Sadovnychiy, H. Castillejos-Fernandez, Melanoma and nevus skin lesion classification using hand-craft and deep learning feature fusion via mutual information measures, Entropy, vol. 22, no. pp. 484-507, 2020.
M. A. Al-masni, D. Kim, T.Kim, Multiple skin lesions diagnostics via integrated deep convolutional networks for segmentation and classification, Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, Vol. 190, pages 105351, 2020.
B. Harangi, A. Baran, A. Hajdu, Assisted deep learning framework for multi-class skin lesion classification considering a binary classification support, Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, Vol. 62, pages 102041, 2020.
Y. Xie, J. Zhang, Y. Xia, and C. Shen, A mutual bootstrapping model for automated skin lesion segmentation and classification, IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, vol. 39, no. 7, pp. 2482-2493, July 2020.
K. M. Hosny, M. A. Kassem, and M. M. Fouad, Classification of skin lesions into seven classes using transfer learning with AlexNet, Journal of Digital Imaging, 2020.
M. A. Kassem, K. M. Hosny, and M. M. Fouad, Skin lesions classification into eight classes for ISIC 2019 using deep convolutional neural network and transfer learning , IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 114822-114832, 2020.
K. M. Hosny, M. A. Kassem, and M. M. Fouad, Skin melanoma classification using ROI and data augmentation with deep convolutional neural networks, Multimedia Tools and Applications, Vol. 79, pp. 24029–24055, 2020.
X.W. Gao, R. Hui, Z. Tian, Classification of CT brain images based on deep learning networks, Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, vol.138, pp. 49–56, 2017.
S. Ioffe and C. Szegedy, Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift, In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning – vol. 37, no. 9, pp. 448–456, 2015.
K. Hara, D. Saito, and H. Shouno, Analysis of the function of the rectified linear unit used in deep learning, 2015 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Killarney, pp. 1–8, 2015.
K. He, X. Zhang, S. Ren, and J. Sun, Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, pp. 770–778, 2016.
S. Zagoruyko and N. Komodakis, Wide residual networks, arXiv preprint ar X iv:1605.07146, 2016.
T. Mendonça, P. M. Ferreira, J. S. Marques, A. R. S. Marcal, and J. Rozeira, PH2 — a dermoscopic image database for research and benchmarking, 2013 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Osaka, pp. 5437–5440, 2013.
Dermatology Information System, Available from http://www.dermis.net, 2012, cited 2 Aug 2018.
DermQuest, Available from http://www.dermquest.com, 2012, cited 2 Aug 2018.
Gutman D., Codella N., Celebi E., Helba B., Marchetti M., Mishra N., et al., Skin lesion analysis toward melanoma detection: a challenge at the international symposium on biomedical imaging (ISBI) 2016, hosted by the international skin imaging collaboration (ISIC), 2016, Available from, Cited 2 Aug 2018.
ISIC Archive, 2018. Isic-archive.com [Online]. Available (Accessed 26 Aug 2020) http://isic-archive.com.
T. Fawcett, An introduction to ROC analysis Pattern Recognition Letter, Vol. 27, no. 8, pp. 861–874, 2006.
B. Basavaprasad, and R. S. Hegad, Color image segmentation using adaptive Growcut method, Procedia Computer Science, Vol. 45, PP 328-335, 2015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hosny, K.M., Kassem, M.A. Refined Residual Deep Convolutional Network for Skin Lesion Classification. J Digit Imaging 35, 258–280 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-021-00552-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-021-00552-0