Abstract
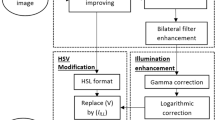
Retinal fundus images are often corrupted by non-uniform and/or poor illumination that occur due to overall imperfections in the image acquisition process. This unwanted variation in brightness limits the pathological information that can be gained from the image. Studies have shown that poor illumination can impede human grading in about 10~15% of retinal images. For automated grading, the effect can be even higher. In this perspective, we propose a novel method for illumination correction in the context of retinal imaging. The method splits the color image into luminosity and chroma (i.e., color) components and performs illumination correction in the luminosity channel based on a novel background estimation technique. Extensive subjective and objective experiments were conducted on publicly available DIARETDB1 and EyePACS images to justify the performance of the proposed method. The subjective experiment has confirmed that the proposed method does not create false color/artifacts and at the same time performs better than the traditional method in 84 out of 89 cases. The objective experiment shows an accuracy improvement of 4% in automated disease grading when illumination correction is performed by the proposed method than the traditional method.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jager RD, Mieler WF, Miller JW: Age-related macular degeneration. N Engl J Med 358(24):2606–2617, 2008
Cheung N, Mitchell P, Wong TY: Diabetic retinopathy. Lancet 376(9735):124–136, 2010 Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20580421
Panwar N, Huang P, Lee J, Keane PA, Chuan TS, Richhariya A, Teoh S, Lim TH, Agrawal R: Fundus photography in the 21st century—a review of recent technological advances and their implications for worldwide healthcare. Telemed e-Health 22(3):198–208, 2016
Cunha-Vaz J, Rui B, Torcato S, et al: Computer-aided detection of diabetic retinopathy progression. Digital Teleretinal Screening, Berlin Heidelberg: Springer 59–66, 2012
Kubecka L, Jan J, Kolar R: Retrospective illumination correction of retinal images. J Biomed Imaging 2010:11, 2010
Likar B, Maintz JA, Viergever MA, Pernus F: Retrospective shading correction based on entropy minimization. J Microsc 197(3):285–295, 2000
Leahy C, O’Brien A, Dainty C: Illumination correction of retinal images using Laplace interpolation. Appl Opt 51(35):8383–8389, 2012
Youssif AAA, Ghalwash AZ, Ghoneim AS: A comparative evaluation of preprocessing methods for automatic detection of retinal anatomy. Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Informatics and Systems (INFOS 07) 2430, 2007
Varnousfaderani ES, Yousefi S, Belghith A, Goldbaum MH: Luminosity and contrast normalization in color retinal images based on standard reference image. SPIE Medical Imaging, International Society for Optics and Photonics: 97843N–97843N, 2016
Foracchia M, Grisan E, Ruggeri A: Luminosity and contrast normalization in retinal images. Med Image Anal 9(3):179–190, 2005
Kumari K, Mittal D: Automated drusen detection technique for age-related macular degeneration. J Biomed Eng Med Imaging 2(1):18, 2015
Xiao D, Vignarajan J, Lock J, Frost S, Tay-Kearney M, Kanagasingam Y: Retinal image registration and comparison for clinical decision support. Australas Med J 5(9):507, 2012
Akram MU, Tariq A, Anjum MA, Javed MY: Automated detection of exudates in colored retinal images for diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy. Appl Opt 51(20):4858–4866, 2012
Kande GB, Savithri TS, Subbaiah PV: Automatic detection of microaneurysms and hemorrhages in digital fundus images. J Digit Imaging 23(4):430–437, 2010
Grisan E, Giani A, Ceseracciu E, Ruggeri A: Model-based illumination correction in retinal images. 3rd IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: Nano to Macro: 984–987, 2006
Kolar R, Odstrcilik J, Jan J, Harabis V: Illumination correction and contrast equalization in colour fundus images. 19th European Signal Processing Conference: 298–302, 2011
Gonzalez RC, Woods RE: Digital image processing. USA: Pearson Prentice Hall, 2008
Russ JC: The image processing handbook, 2nd edition. Boca Raton: IEEE press, 1995
Guillemaud R: Uniformity correction with homomorphic filtering on region of interest. Int Conf Image Process 2:872–875, 1998
Skifstad K, Jain R: Illumination independent change detection for real world image sequences. Comput Vis Graph Image Process 46(3):387–399, 1989
Pham DL, Prince JL: Adaptive fuzzy segmentation of magnetic resonance images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 18(9):737–752, 1999
Vlachos MD, Dermatas ES: Non-uniform illumination correction in infrared images based on a modified fuzzy c-means algorithm. J Biomed Graph Comput 3(1):6, 2012
Finlayson G, Hordley S: Improving gamut mapping color constancy. IEEE Trans Image Process 9(10):1774–1783, 2000
Jobson DJ, Rahman Z, Woodell GA: Properties and performance of a center/surround retinex. IEEE Trans Image Process 6(3):451–462, 1997
Li B, Wang S, Geng Y: Image enhancement based on Retinex and lightness decomposition. 18th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), 3417–3420, 2011
Niemann H, Chrastek R, Lausen B, Kubecka L, Jan J, Mardin CY, Michelson G: Towards automated diagnostic evaluation of retina images. Pattern Recognit Image Anal 16(4):671–676, 2006
Narasimha-Iyer H, Can A, Roysam B, Stewart V, Tanenbaum HL, Majerovics A, Singh H: Robust detection and classification of longitudinal changes in color retinal fundus images for monitoring diabetic retinopathy. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 53(6):1084–1098, 2006
Zheng Y, Vanderbeek B, Xiao R, Daniel E, Stambolian D, Maguire M, O'Brien J, Gee J: Retrospective illumination correction of retinal fundus images from gradient distribution sparsity. 9th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI): 972–975, 2012
Fairchild MD. Color appearance models, Second Edition, John Wiley & Sons, 2005.
Smith AR: Colour gamut transform pairs. ACM Siggraph. Comput Graph 12(3):12–19, 1978
Cantrell K et al.: Use of the hue parameter of the hue, saturation, value colour space as a quantitative analytical parameter for bitonal optical sensors. Anal Chem 82(2):531–542, 2009
John CR: The image processing handbook, Fifth edition. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2006
Viola P, Jones M: Rapid object detection using a boosted cascade of simple features. Proceedings of the 2001 I.E. Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2001) 1: I-I, 2001
Saha S, Démoulin V: ALOHA: an efficient binary descriptor based on Haar features. IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP): 2345–2348, 2012
Saha SK, Fernando B, Xiao D, Tay-Kearney ML, Kanagasingam Y: Deep learning for automatic detection and classification of microaneurysms, hard and soft exudates, and hemorrhages for diabetic retinopathy diagnosis. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci 57(12):5962–5962, 2016
Zhu X, Rangayyan RM: Detection of the optic disc in images of the retina using the Hough transform. 30th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBS 2008): 3546–3549, 2008
LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G: Deep learning. Nature 521(7553):436–444, 2015
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saha, S.K., Xiao, D. & Kanagasingam, Y. A Novel Method for Correcting Non-uniform/Poor Illumination of Color Fundus Photographs. J Digit Imaging 31, 553–561 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-017-0040-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-017-0040-0