Abstract
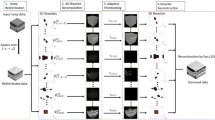
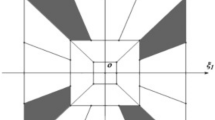
Image denoising is a fundamental preprocessing step of image processing in many applications developed for optical coherence tomography (OCT) retinal imaging—a high-resolution modality for evaluating disease in the eye. To make a homogeneity similarity-based image denoising method more suitable for OCT image removal, we improve it by considering the noise and retinal characteristics of OCT images in two respects: (1) median filtering preprocessing is used to make the noise distribution of OCT images more suitable for patch-based methods; (2) a rectangle neighborhood and region restriction are adopted to accommodate the horizontal stretching of retinal structures when observed in OCT images. As a performance measurement of the proposed technique, we tested the method on real and synthetic noisy retinal OCT images and compared the results with other well-known spatial denoising methods, including bilateral filtering, five partial differential equation (PDE)-based methods, and three patch-based methods. Our results indicate that our proposed method seems suitable for retinal OCT imaging denoising, and that, in general, patch-based methods can achieve better visual denoising results than point-based methods in this type of imaging, because the image patch can better represent the structured information in the images than a single pixel. However, the time complexity of the patch-based methods is substantially higher than that of the others.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang D, Swanson EA, Lin CP, Schumann JS, Stinson WG, Chang M, Hee MR, Flotte T, Gregory K, Puliafito CA, Fujimoto JG: Optical coherence tomography. Science 254:1178–1181, 1991
Bezerra HG, Costa MA, Guagliumi G, Rollins AM, Simon DI: Intracoronary optical coherence tomography: a comprehensive review. J Am Coll Cardiol Intv 2(11):1035–1046, 2009
Schmitt JM, Xiang SH, Yung KM: Speckle in optical coherence tomography. J Biomed Opt 4:95–105, 1999
Rogowska J, Brezinski ME: Evalutation of the adaptive speckle suppression filter for coronary optical coherence tomography imaging. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 19:1261–1266, 2000
Gargesha M, Jenkins MW, Rollins AM, Wilson DL: Denoising and 4D visualization of OCT images. Opt Express 16:12313–12333, 2008
Kobayashi M, Hanafusa H, Takada K, Noda J: Polarization-independent interferometric optical-time-domain reflectometer. J Lightwave Technol 9:623–628, 1991
Iftimia N, Bouma BE, Tearney GJ: Speckle reduction in optical coherence tomography by path length encoded angular compounding. J Biomed Opt 8:260–263, 2003
Hughes M, Spring M, Podoleanu A: Speckle noise reduction in optical coherence tomography of paint layers. Appl Opt 49:99–107, 2010
Pircher M, Gtzinger E, Leitgeb R, Fercher AF, Hitzenberger CK: Speckle reduction in optical coherence tomography by frequency compounding. J Biomed Opt 8:565–569, 2003
Bernstein R: Adaptive nonlinear filters for simultaneous removal of different kinds of noise in images. IEEE Trans Circ Syst 34:1275–1291, 1987
Rogowska J, Brezinski ME: Image processing techniques for noise removal, enhancement and segmentation of cartilage OCT images. Phys Med Biol 47:641–655, 2002
Marks DL, Ralston TS, Boppart SA: Speckle reduction by I-divergence regularization in optical coherence tomography. J Opt Soc Am A 22:2366–2371, 2005
Wong A, Mishra A, Bizheva K, Clausi DA: General Bayesian estimation for speckle noise reduction in optical coherence tomography retinal imagery. Opt Express 18:8338–8352, 2010
Chen Q, Sun QS, Xia DS: Homogeneity similarity based image denoising. Pattern Recogn 43:4089–4100, 2010
Bashkansky M, Reintjes J: Statistics and reduction of speckle in optical coherence tomography. Opt Lett 25:545–547, 2000
Salinas HM, Fernandez DC: Comparison of PDE-based nonlinear diffusion approaches for image enhancement and denoising in optical coherence tomography. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 26:761–771, 2007
Perona P, Malik J: Scale-space and edge detection using anisotropic diffusion. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal 12:629–639, 1990
Gilboa G, Sochen N, Zeevi YY: Image enhancement and denoising by complex diffusion processes. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 26:1020–1036, 2004
Fang L, Li S, Nie Q, Izatt JA, Toth CA, Farsiu S: Sparsity based denoising of spectral domain optical coherence tomography images. Biomed Opt Express 3:927–942, 2012
Tomasi C, Manduchi R: Bilateral filtering for gray and color images. Sixth International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Bombay, India, 1998, pp 839–846
Chen Q, Montesinos P, Sun QS, Heng PA, Xia DS: Adaptive total variation denoising based on difference curvature. Image Vis Comput 28:298–306, 2010
Chen Q, Montesinos P, Sun QS, Xia DS: Ramp preserving Perona-Malik model. Signal Process 90:1963–1975, 2010
Rudin LI, Osher S, Fatemi E: Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms. Physica D 60:259–268, 1992
Buades A, Coll B, Morel JM: A non-local algorithm for image denoising. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), San Diego, California, 2005, pp 60–65
Dabov K, Foi A, Katkovnik V, Egiazarian K: Image denoising by sparse 3-D transform-domain collaborative filtering. IEEE Trans Image Process 16:2080–2095, 2007
Huang Y, Gangaputra S, Lee KE, Narkar AR, Klein R, Klein BEK, Meuer SM, Danis RP: Signal quality assessment of retinal optical coherence tomography images. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci 53:2133–41, 2012
He L, Greenshields IR: A non-local maximum likelihood estimation method for Rician noise reduction in MR images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 28:165–172, 2009
Moreno-Montanes J, Olmo N, Alvarez A, Garcia N, Zarranz-Ventura J: Cirrus high-definition optical coherence tomography compared with stratus optical coherence tomography in glaucoma diagnosis. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci 51:335–343, 2010
Chiu SJ, Li XT, Nicholas P, Toth CA, Izatt JA, Farsiu S: Automatic segmentation of seven retinal layers in SDOCT images congruent with expert manual segmentation. Opt Express 18:19413–19428, 2010
Rubin DL, de Sisternes L, Kutzscher L, Chen Q, Leng T, Zheng LL: Improving drusen visualization in projection images in optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology 120:644–644e2, 2013
Chen Q, Leng T, Zheng LL, Kutzscher L, Ma J, de Sisternes L, Rubin DL: Automated drusen segmentation and quantification in SD-OCT images. Med Image Anal 17:1058–1072, 2013
Kierman DF, Mieler WF, Hariprasad SM: Spectral-domain optical coherence tomography: a comparison of modern high-resolution retinal imaging systems. Am J Ophthalmol 498:18–31, 2010
Wang Z, Bovik AC, Sheikh HR, Simoncelli EP, Simoncelli EP: Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans Image Process 13:600–612, 2004
Cincotti G, Loi G, Pappalardo M: Frequency decomposition and compounding of ultrasound medical images with wavelet packets. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 20:764–771, 2001
Bao P, Zhang L: Noise reduction for magnetic resonance images via adaptive multiscale products thresholding. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 22:1089–1099, 2003
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, grant no. 30920140111004, the Qing Lan Project, and the Bio-X Interdisciplinary Initiatives Program of Stanford University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Q., de Sisternes, L., Leng, T. et al. Application of Improved Homogeneity Similarity-Based Denoising in Optical Coherence Tomography Retinal Images. J Digit Imaging 28, 346–361 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-014-9742-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-014-9742-8