Abstract
Rationale and Objectives
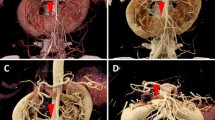
Rationale and Objectives: Three-dimensional (3D) real-time volume rendering has demonstrated improvements in clinical care for several areas of radiological imaging. We test whether advanced real-time rendering techniques combined with an effective user interface will allow radiologists and surgeons to improve their performance for cardiothoracic surgery planning and diagnostic evaluation.
Material and Methods
Materials and Methods: An interactive combination 3D and 2D visualization system developed at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill was compared against standard tiled 2D slice presentation on a viewbox. The system was evaluated for 23 complex cardiothoracic computed tomographic (CT) cases including heart–lung and lung transplantation, tumor resection, airway stent placement, repair of congenital heart defects, aortic aneurysm repair, and resection of pulmonary arteriovenous malformation. Radiologists and surgeons recorded their impressions with and without the use of the interactive visualization system.
Results
Results: The cardiothoracic surgeons reported positive benefits to using the 3D visualizations. The addition of the 3D visualization changed the surgical plan (65% of cases), increased the surgeon’s confidence (on average 40% per case), and correlated well with the anatomy found at surgery (95% of cases). The radiologists reported fewer and less major changes than the surgeons in their understanding of the case due to the 3D visualization. They found new findings or additional information about existing findings in 66% of the cases; however, they changed their radiology report in only 14% of the cases.
Conclusion
Conclusion: With the appropriate choice of 3D real-time volume rendering and a well-designed user interface, both surgeons and radiologists benefit from viewing an interactive 3D visualization in addition to 2D images for surgery planning and diagnostic evaluation of complex cardiothoracic cases. This study finds that 3D visualization is especially helpful to the surgeon in understanding the case, and in communicating and planning the surgery. These results suggest that including real-time 3D visualization would be of clinical benefit for complex cardiothoracic CT cases.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
JK Kim JH Ahn T Park HJ Ahn CS Kim KS Cho (September 2002) ArticleTitleVirtual cystoscopy of the contrast material-filled bladder in patients with gross hematuria Am J Roentgenol 179 IssueID(3): 763–768
Y Kato S Nair H Sano MS Sanjaykumar K Katada M Hayakawa T Kanno (Jul 2002) ArticleTitleMulti-slice 3D-CTA—an improvement over single slice helical CTA for cerebral aneurysms Acta Neurochir (Wien) 144 IssueID(7): 715–722 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00701-002-0932-7
JP Villablanca R Jahan P Hooshi S Lim G Duckwiler A Patel J Sayre N Martin J Frazee J Bentson F Vinuela (August 2002) ArticleTitleDetection and characterization of very small cerebral aneurysms by using 2D and 3D helical CT angiography Am J Neuroradiol 23 IssueID(7): 1187–1198
A Morra G Tirelli A Rimondini V Cioffi M Russolo V Giacomarra R Pozzi-Mucelli (Jun 2002) ArticleTitleUsefulness of virtual endoscopic three-dimensional reconstructions of the middle ear Acta Otolaryngol 122 IssueID(4): 382–385 Occurrence Handle10.1080/00016480260000058
EK Fishman KM Horton (2001) ArticleTitleImaging pancreatic cancer: the role of multidetector CT with three-dimensional CT angiography Pancreatology 1 IssueID(6): 610–624 Occurrence Handle10.1159/000055871 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD38znsVKhug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle12120244
SA Pelizzari R Grzeszczuk GT Chen R Heimann DJ Haraf DJ Vijayakumar MJ Ryan (January 1996) ArticleTitleVolumetric visualization of anatomy for treatment planning Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 34 IssueID(1): 205–211 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0360-3016(95)00272-3
B Pflesser A Petersik U Tiede KH Hohne R Leuwer (2002) ArticleTitleVolume cutting for virtual petrous bone surgery Comput Aided Surg 7 IssueID(2): 74–83 Occurrence Handle10.1002/igs.10036 Occurrence Handle12112716
T Rodt S Bartling AM Schmidt BP Weber T Lenarz H Becker (July 2002) ArticleTitleVirtual endoscopy of the middle ear: experimental and clinical results of a standardised approach using multi-slice helical computed tomography Eur Radiol 12 IssueID(7): 1684–1692 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00330-002-1313-6
MG Cavalcanti A Ruprecht MW Vannier (July 2002) ArticleTitle3D volume rendering using multislice CT for dental implants Dentomaxillofacial Radiol 31 IssueID4 218–223 Occurrence Handle10.1038/sj.dmfr.4600701
K Imai K Tsujiguchi C Toda E Enoki KC Sung H Sakamoto S Kitano M Hatoko S Tajima (Jun 1999) ArticleTitleReduction of operating time and blood transfusion for craniosynostosis by simulated surgery using three-dimensional solid models Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 39 IssueID(6): 423–426 Occurrence Handle10.2176/nmc.39.423
MW Vannier JL Marsh (May 1996) ArticleTitleThree-dimensional imaging, surgical planning, and image-guided therapy Radiol Clin North Am 34 IssueID(3): 545–563 Occurrence Handle8657871
MG Cavalcanti MW Vannier (November 1998) ArticleTitleQuantitative analysis of spiral computed tomography for craniofacial clinical applications Dentomaxillofacial Radiol 27 IssueID(6): 344–350 Occurrence Handle10.1038/sj.dmfr.4600389
JM Abrahams PK Saha RW Hurst PD LeRoux JK Udupa (July 2002) ArticleTitleThree-dimensional bone-free rendering of the cerebral circulation by use of computed tomographic angiography and fuzzy connectedness Neurosurgery 51 IssueID(1): 264–268 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006123-200207000-00044
T Lei JK Udupa PK Saha D Odhner R Baum SK Tadikonda EK Yucel (May 2002) ArticleTitle3D MRA visualization and artery–vein separation using blood-pool contrast agent MS-325 Acad Radiol 9 IssueID(suppl 1): S127–S133 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1076-6332(03)80417-8 Occurrence Handle12019847
GD Rubin CF Beaulieu V Argiro H Ringl AM Norbash AM Feller MD Dake RB Jeffrey S Napel (May 1996) ArticleTitlePerspective volume rendering of CT and MR images: applications for endoscopic imaging Radiology 199 IssueID2 321–330 Occurrence Handle8668772
CF Beaulieu RB Jeffrey SuffixJr. C Karadi DS Paik S Napel (July 1999) ArticleTitleDisplay modes for CT colonography: Part II. Blinded comparison of axial CT and virtual endoscopic and panoramic endoscopic volume-rendered studies Radiology 212 IssueID1 203–212
BC Pineau ED Paskett GJ Chen MA Espeland K Phillips JP Han C Mikulaninec DJ Vining (August 2003) ArticleTitleVirtual colonoscopy using oral contrast compared with colonoscopy for the detection of patients with colorectal polyps Gastroenterology 125 IssueID2 304–310 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0016-5085(03)00885-0
AJ Burke DJ Vining WF McGuirt SuffixJr G Postma JD Browne (January 2000) ArticleTitleEvaluation of airway obstruction using virtual endoscopy Laryngoscope 110 IssueID1 23–29 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00005537-200001000-00005
DJ Vining K Liu RH Choplin EF Haponik (February 1996) ArticleTitleVirtual bronchoscopy. Relationships of virtual reality endobronchial simulations to actual bronchoscopic findings Chest 109 IssueID2 549–553
JC Carr AA Nemcek SuffixJr M Abecassis A Blei L Clarke FS Pereles R McCarthy JP Finn (April 2003) ArticleTitlePreoperative evaluation of the entire hepatic vasculature in living liver donors with use of contrast-enhanced MR angiography and true fast imaging with steady-state precession J Vasc Interv Radiol 14 IssueID4 441–449
F Fraioli M Francone C Catalano A Napoli M Danti M Rossi F Pediconi R Rassariello (May–June 2003) ArticleTitleMultislice computed tomography in the preoperative assessment of adult-to-adult living donor liver transplantation: personal results Radiol Med (Torino) 105 IssueID5–6 436–444
GD Rubin MD Dake SA Napel CH McDonnell RB Jeffrey (1993) ArticleTitleThree-dimensional spiral CT angiography of the abdomen: initial clinical experience Radiology 186 147–152 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByyC3c7nvVI%3D Occurrence Handle8416556
DR Ney KF Elliot D Magid DD Robertson A Kawashima (1992) ArticleTitleThree-dimensional volumetric display of CT data: effect of scan parameters upon image quality J Comput Assist Tomogr 15 5
S Napel MP Marks GD Rubin MD Dake CH McDonnell CH Song DR Enzmann RB Jeffrey SuffixJr (1992) ArticleTitleCT angiography with spiral CT and maximum intensity projection Radiology 185 IssueID2 607–610 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByyD38bjsFw%3D Occurrence Handle1410382
Cabral B, Cam N, Foran F: Accelerated volume rendering and tomographic reconstruction using texture mapping hardware. Proceedings of Volume Visualization (Baltimore), October
Hemminger BM, Cullip T, North MJ: Interactive visualization of 3D medical image data. Computer applications to assist radiology, S/CAR 94. In: Boehme JM, Rowberg AH, Wolfman NT eds Symposia Foundation 1994, pp 127–135
Hemminger BM: Real-time 3D visualization for medical image display. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Department of Computer Science, Technical Report TR94-027, 1994
GS Hubona GW Shirah DG Fout (November 1997) ArticleTitleThe effects of motion and stereopsis on three-dimensional visualization Int J Hum Comput Stud 47 IssueID5 609–627 Occurrence Handle10.1006/ijhc.1997.0154
Hemminger BM, Molina PL, Braeuning PM, Detterbeck FC, Egan TM, Pisano ED, Beard DV, Clinical applications of real-time volume rendering. SPIE Med Imaging. 2431, February 1995
Brauening MP, Hemminger BM, Pisano ED, et al. 3D MRI of the breast. Roetgen Ray (conference abstract), 1995.
WE Lorensen HE Cline (1987) ArticleTitleMarching cubes: high resolution 3-D surface construction algorithm Comp Graph 21 IssueID3 163–169
GD Rubin MD Dake S Napel RB Jeffrey SuffixJr. CH McDonnell FG Sommer L Wexler DM Williams (January 1994) ArticleTitleSpiral CT of renal artery stenosis: comparison of three-dimensional rendering techniques Radiology 190 IssueID1 181–189
S Iwanaga T Yoshiura DA Shrier Y Numaguchi (May 2000) ArticleTitleEfficacy of targeted CT angiography in evaluation of intracranial internal carotid artery disease Acad Radiol 7 IssueID5 325–334 Occurrence Handle10803612
Symmetric Multiprocessing Systems Technical Report, Silicon Graphics Inc., 1993.
C Ware G Franck (April 1996) ArticleTitleEvaluating stereo and motion cues for visualizing information nets in three dimensions ACM Trans Graph 15 IssueID2 121–140 Occurrence Handle10.1145/234972.234975
NL Johnson S Kotz N Balakrishnan (1997) Discrete multivariate distributions Wiley New York
Lehman EL, D’Abrera HJM: Nonparametrics: statistical methods based on ranks. California: Holden-Day, 1975, pp 182–193
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by NIH R01 CA 44060, NIH P01 47982, and NIH R01-CA60193.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported in part by NIH RO1-CA 44060, NIH PO1-CA 47982, and NIH RO1-CA 60193.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hemminger, B.M., Molina, P.L., Egan, T.M. et al. Assessment of Real-Time 3D Visualization for Cardiothoracic Diagnostic Evaluation and Surgery Planning. J Digit Imaging 18, 145–153 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-004-1909-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-004-1909-2