Abstract
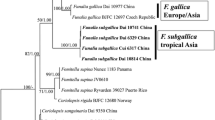
The taxonomic positions of three intraspecific groups of Umbelopsis ramanniana in the genus Umbelopsis were analyzed based on the nucleotide sequences of their nuclear large subunit ribosomal DNA (nLSU rDNA) D1/D2 region. The examined members of the genus Umbelopsis were resolved into two major clades, Clades I and II. The intraspecific groups of U. ramanniana were nested within Clade II together with U. westeae, U. swartii, U. autotrophica, U. gibberisopra, U. angularis, and U. fusiformis. In this major clade, the intraspecific groups of U. ramanniana were split into three polyphyletic subclades. This suggests that U. ramanniana is an assemblage of several genetically distinct species. Interestingly, in spite of the diverse sporangiospore shapes of the members of Clade II, the genetic variation among them was small. It is considered that their flexible sporangia membranes make it possible for them to develop various sporangiospore shapes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berbee ML, Yoshimura A, Sugiyama J, Taylor JW (1995) Is Penicillium monophyletic? An evaluation of phylogeny in the family Trichocomaceae from 18S, 5.8S and ITS ribosomal DNA sequence data. Mycologia 87:210–222
Cantrell SA, Hanlin RT (1997) Phylogenetic relationships in the family Hyaloscyphaceae inferred from sequences of ITS regions, 5.8S ribosomal DNA and morphological characters. Mycologia 89:745–755
Hasegawa M, Kishino H, Yano T (1985) Dating of the human-ape splitting by a molecular clock of mitochondria DNA. J Mol Evol 22:160–174
Ko KS, Hong SG, Jung HS (1997) Phylogenetic analysis of Trichaptum based on nuclear 18S 5.8S and ITS ribosomal DNA sequences. Mycologia 89:727–734
Meyer W, Gams W (2003) Delimitation of Umbelopsis (Mucorales, Umbelopsidaceae fam. nov.) based on ITS sequence and RFLP data. Mycol Res 107:339–350
Miura K, Kudo MY (1970) An agar medium for aquatic hyphomycetes (in Japanese). Trans Mycol Soc Japan 11:116–118
O’Donnell K (1993) Fusarium and its near relatives. In: Reynolds DR, Taylor JW (eds) The fungal holomorph: mitotic meiotic and pleomorphic speciation in fungal systematics. CAB International, Wallingford, pp 224–233
Ogawa Y, Suda A, Kusama-Eguchi K, Watanabe K, Tokumasu S (2005) Intraspecific groups of Umbelopsis ramanniana inferred from nucleotide sequences of nuclear rDNA internal transcribed spacer regions and sporangiospore morphology. Mycoscience 46:343–351
Okada G, Takematus A, Takamura Y (1997) Phylogenetic relationships of the hyphomycete genera Chaetopsina and Kionochaeta based on 18S rDNA sequences. Mycoscience 38:409–420
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sugiyama M, Tokumasu S, Gams W (2003) Umbelopsis gibberispora sp. nov. from Japanese leaf litter and a clarification of Micromucor ramannianus var. angulisporus. Mycoscience 44:217–226
Suyama Y, Kawamuro K, Kinoshita I, Yoshimura K, Tsumura Y, Takahara H (1996) DNA sequence from a fossil pollen of Abies spp. from Pleistocene peat. Genes Genet Syst 71:145–149
Swofford DL (2001) PAUP*: phylogenetic analysis using parsimony and other methods (PAUP* version 4.0 beta 10). Sinauer, Sunderland
Taylor JW, Jacobson DJ, Kroken S, Kasuga T, Geiser DM, Hibbett DS, Fisher MC (2000) Phylogenetic species recognition and species concept in fungi. Fungal Genet Biol 31:31–32
Thompson JD, Gibson F, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The Clustal X-Windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Tokumasu S, Sugiyama M, Tubaki K (1990) Taxonomy of Mortierella ramanniana and related species. In: 4th international mycological congress (IMC 4), Regensburg, August 28–September 3, p 58 (IA-58/3)
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by the “Academic Frontier” Project for Private Universities: a matching fund subsidy from MEXT (Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan) 2007–2009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Ogawa, Y., Sugiyama, M., Hirose, D. et al. Polyphyly of intraspecific groups of Umbelopsis ramanniana and their genetic and morphological variation. Mycoscience 52, 91–98 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10267-010-0074-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10267-010-0074-3