Abstract
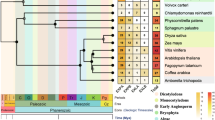
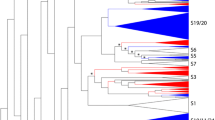
Expansins form a superfamily of plant proteins that assist in cell wall loosening during growth and development. The superfamily is divided into four families: EXPA, EXPB, EXLA, and EXLB (Sampedro and Cosgrove in Genome Biol 6:242, 2005. doi:10.1186/gb-2005-6-12-242). Previous studies on Arabidopsis, rice, and Populus trichocarpa have clarified the evolutionary history of expansins in angiosperms (Sampedro et al. in Plant J 44:409–419, 2005. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02540.x). Amborella trichopoda is a flowering plant that diverged very early. Thus, it is a sister lineage to all other extant angiosperms (Amborella Genome Project in 342:1241089, 2013. doi:10.1126/science.1241089). Because of this relationship, comparing the A. trichopoda expansin superfamily with those of other flowering plants may indicate which expansin genes were present in the last common ancestor of all angiosperms. The A. trichopoda expansin superfamily was assembled using BLAST searches with angiosperm expansin queries. The search results were analyzed and annotated to isolate the complete A. trichopoda expansin superfamily. This superfamily is similar to other angiosperm expansin superfamilies, but is somewhat smaller. This is likely because of a lack of genome duplication events (Amborella Genome Project 2013). Phylogenetic and syntenic analyses of A. trichopoda expansins have improved our understanding of the evolutionary history of expansins in angiosperms. Nearly all of the A. trichopoda expansins were placed into an existing Arabidopsis-rice expansin clade. Based on the results of phylogenetic and syntenic analyses, we estimate there were 12–13 EXPA genes, 2 EXPB genes, 1 EXLA gene, and 2 EXLB genes in the last common ancestor of all angiosperms.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amborella Genome Project (2013) The Amborella genome and the evolution of flowering plants. Science 342:1241089. doi:10.1126/science.1241089
Bae JM, Kwak MS, Noh SA, Oh MJ, Kim YS, Shin JS (2014) Overexpression of sweetpotato expansin cDNA (IbEXP1) increases seed yield in Arabidopsis. Transgenic Res 23:657–667. doi:10.1007/s11248-014-9804-1
Banks JA, Nishiyama T, Hasebe M et al (2011) The Selaginella genome identifies genetic changes associated with the evolution of vascular plants. Science 332:960–963. doi:10.1126/science.1203810
Boron AK, Van Loock B, Suslov D, Markakis MN, Verbelen JP, Vissenberg K (2015) Over-expression of AtEXLA2 alters etiolated arabidopsis hypocotyl growth. Ann Bot 115:67–80. doi:10.1093/aob/mcu221
Carey RE, Cosgrove DJ (2007) Portrait of the expansin superfamily in Physcomitrella patens: comparisons with angiosperm expansins. Ann Bot 99:1131–1141. doi:10.1093/aob/mcm044
Carey RE, Hepler NK, Cosgrove DJ (2013) Selaginella moellendorffii has a reduced and highly conserved expansin superfamily with genes more closely related to angiosperms than to bryophytes. BMC Plant Biol 13:4. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-13-4
Cosgrove DJ (2000) Loosening of plant cell walls by expansins. Nature 407:321–326. doi:10.1038/35030000
Cosgrove DJ (2015) Plant expansins: diversity and interactions with plant cell walls. Curr Opin Plant Biol 25:162–172. doi:10.1016/j.pbi.2015.5.014
Dal Santo S, Vannozzi A, Tornielli GB, Fasoli M, Venturini L, Pezzotti M, Zenoni S (2013) Genome-wide analysis of the expansin gene superfamily reveals grapevine-specific structural and functional characteristics. PLoS ONE 8:e62206. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0062206
Gaete-Eastman C, Morales-Quintana L, Herrera R, Moya-Leon MA (2015) In-silico analysis of the structure and binding site features of an α-expansin protein from mountain papaya fruit (VpEXPA2), through molecular modeling, docking, and dynamics simulation studies. J Mol Model 21:115. doi:10.1007/s00894-015-2656-7
Georgelis N, Nikolaidis N, Cosgrove DJ (2015) Bacterial expansins and related proteins from the world of microbes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:3807–3823. doi:10.1007/s00253-015-6534-0
Huelsenbeck JP, Ronquist F, Nielsen R, Bollback JP (2001) Bayesian inference of phylogeny and its impact on evolutionary biology. Science 294:2310–2314. doi:10.1126/science.1065889
Jung J, O’Donoghue EM, Dijkwel PP, Brummell DA (2010) Expression of multiple expansin genes is associated with cell expansion in potato organs. Plant Sci 179:77–85. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2010.04.007
Krishnamurthy P, Hong JK, Kim JA, Jeong MJ, Lee YH, Lee SI (2015) Genome-wide analysis of the expansin gene superfamily reveals Brassica rapa-specific evolutionary dynamics upon whole genome triplication. Mol Genet Genomics 290:521–530. doi:10.1007/s00438-014-0935-0
Lyons E, Pedersen B, Kane J, Alam M, Ming R, Tang H, Wang X, Bowers J, Paterson A, Lisch D, Freeling M (2008) Finding and comparing syntenic regions among Arabidopsis and the outgroups papaya, poplar, and grape: CoGe with rosids. Plant Physiol 148:1772–1781. doi:10.1104/pp.108.124867
McQueen-Mason S, Durachko DM, Cosgrove DJ (1992) Two endogenous proteins that induce cell wall extension in plants. Plant Cell 4:1425–1433
Nikolaidis N, Doran N, Cosgrove DJ (2014) Plant expansins in bacteria and fungi: evolution by horizontal gene transfer and independent domain fusion. Mol Biol Evol 31:376–386. doi:10.1093/molbev/mst206
Palapol Y, Kunyamee S, Thongkhum M, Ketsa S, Ferguson IB, van Doorn WG (2015) Expression of expansin genes in the pulp and the dehiscence zone of ripening durian (Durio zibethinus) fruit. J Plant Physiol 182:33–39. doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2015.04.005
Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck JP (2003) MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 19:1572–1574. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btg180
Saito T, Tuan PA, Katsumi-Horigane A, Bai S, Ito A, Sekiyama Y, Ono H, Moriguchi T (2015) Development of flower buds in the Japanese pear (Pyrus pyrifolia) from late autumn to early spring. Tree Physiol 35:653–662. doi:10.1093/treephys/tpv043
Sampedro J, Cosgrove DJ (2005) The expansin superfamily. Genome Biol 6:242. doi:10.1186/gb-2005-6-12-242
Sampedro J, Lee Y, Carey RE, dePamphilis C, Cosgrove DJ (2005) Use of genomic history to improve phylogeny and understanding of births and deaths in a gene family. Plant J 44:409–419. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02540.x
Sampedro J, Carey RE, Cosgrove DJ (2006) Genome histories clarify evolution of the expansin superfamily: new insights from the poplar genome and pine ESTs. J Plant Res 119:11–21. doi:10.1007/s10265-005-0253-z
Stover BC, Muller KF (2010) TreeGraph 2: combining and visualizing evidence from different phylogenetic analyses. BMC Bioinformatics 11:7. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-11-7
Tabuchi A, Li LC, Cosgrove DJ (2011) Matrix solubilization and cell wall weakening by β-expansin (group-1 allergen) from maize pollen. Plant J 68:546–559. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04705.x
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729. doi:10.1093/molbev/mst197
Tovar-Herrera OE, Batista-Garcia RA, Sanchez-Carbente Mdel R, Iracheta-Cardenas MM, Arevalo-Nino K, Folch-Mallol JL (2015) A novel expansin protein from the white-rot fungus Schizophyllum commune. PLoS ONE 10:e0122296. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0122296
Vannerum K, Huysman MJ, De Rycke R, Vuylsteke M, Leliaert F, Pollier J, Lutz-Meindl U, Gillard J, De Veylder L, Goossens A, Inze D, Vyverman W (2011) Transcriptional analysis of cell growth and morphogenesis in the unicellular green alga Micrasterias (Streptophyta), with emphasis on the role of expansin. BMC Plant Biol 11:128. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-11-128
Wang T, Park YB, Caporini MA, Rosay M, Zhong L, Cosgrove DJ, Hong M (2013) Sensitivity-enhanced solid-state NMR detection of expansin’s target in plant cell walls. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:16444–16449. doi:10.1073/pnas.1316290110
Yan A, Wu M, Yan L, Hu R, Ali I, Gan Y (2014) AtEXP2 is involved in seed germination and abiotic stress response in Arabidopsis. PLoS ONE 9:e85208. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0085208
Zhang S, Xu R, Gao Z, Chen C, Jiang Z, Shu H (2013) A genome-wide analysis of the expansin genes in Malus × Domestica. Mol Genet Genomics 289:225–236. doi:10.1007/s00438-013-0796-y
Zhou S, Han YY, Chen Y, Kong X, Wang W (2015) The involvement of expansins in response to water stress during leaf development in wheat. J Plant Physiol 183:64–74. doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2015.05.012
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by Lebanon Valley College through an Arnold Student-Faculty Research Grant and the Wolf Fund. The sequence data were produced by the Amborella Genome Project in collaboration with the user community.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seader, V.H., Thornsberry, J.M. & Carey, R.E. Utility of the Amborella trichopoda expansin superfamily in elucidating the history of angiosperm expansins. J Plant Res 129, 199–207 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-015-0772-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-015-0772-1