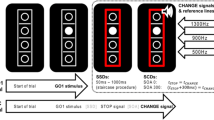
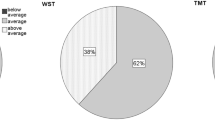
Abstract
The aim of this study is to investigate the effects of exposure to aluminium on the cognitive sphere in a group of welders. Given the intrinsic complexity of the neurocognitive sphere, three different psychomotor variables were used for its investigation allowing the resulting problem to be naturally modelized into a multivariate framework and solved by a nonparametric combination of permutation tests (NPC test). In order to make the treated and control groups comparable, we also stratified the samples on the basis of a risk index that estimates the combined action of biological age and exposure time. Despite the fact that studies in the literature have reached conflicting results, our study highlights a significant drop in attention and memory performances in individuals exposed to aluminium. Finally, we identify a global criterion that summarises the information on the neurocognitive state by applying the nonparametric combination of dependent rankings method (NPC ranking).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbate C, Micali E, Giorgianni C, Munaò F, Brecciaroli R, Salmaso L, Germanò D (2004) Affective correlates of occupational exposure to whole-body vibration. Psychother Psychosom 73:375–379
Akila R, Stollery BT, Riihimäki V (1999) Decrements in cognitive performance in metal inert gas welders exposed to aluminium. J Occup Environ Med 56:632–639
Alfrey AC, LeGrende GR, Kaehny WD (1976) The dialysis encephalopathy syndrome. Possible aluminum intoxication. N Engl J med 294:184–188
Bast-Pettersen R, Drablos PA, Goffeng LO, Thomassen Y, Torres CG (1994) Neuropsychological deficit among elderly workers in aluminum production. Am J Ind Med 25:649–662
Bast-Pettersen R, Skaug V, Ellingsen D, Thomassen Y (2000) Neurobehavioral performance in aluminum welders. Am J Ind Med 37:184–192
Bolla KI, Briefel G, Spector D, Schwartz BS, Wieler L, Herron J, Gimenez L (1992) Neurocognitive effects of aluminum. Arch neurol 49:1021–1026
Bowler RM, Gysens S, Diamond E, Booty A, Hartney C, Roels HA (2003) Neuropsychological sequelae of exposure to welding fumes in a group of occupationally exposed men. Int J Hyg Environ Health 206:517–529
Buchta M, Kiesswetter E, Otto A, Schaller KH, Seeber A, Hilla W, Windorfer K, Stork J, Kuhlmann A, Gefeller O, Letzel S (2003) Longitudinal study examining the neurotoxicity of occupational exposure to aluminium-containing welding fumes. International Arch Occupa Environ Health 76:539–548
Guo-Ross SX, Yang EY, Walsh TJ, Bondy SC (1999) Decrease of glial fibrillary acidic protein in rat frontal cortex following aluminum treatment. J Neurochem 73:1609–1614
Hänninen H, Matikainen E, Kovala T, Valkonen S, Riihimäki V (1994) Internal load of aluminum and the central nervous system function of aluminium welders. Scand J Work Environ Health 20:279–285
He SC, Qiao N, Sheng W (2003) Neurobehavioral, autonomic nervous function and lymphocyte subsets among aluminum electrolytic workers. Int J Immunipathol Pharmacol 16:139–144
Hošovski E, Mastelica Z, Šunderić D, Radulovic D (1990) Mental abilities of workers exposed to aluminium. La Medicina del lavoro 81:119–123
Iregren A (1999) Manganese neurotoxicity in industrial exposures: proof of effects, critical exposure level, and sensitive tests. Neurotoxicology 20:315–323
Iregren A, Sjögren B, Gustafsson K, Hagman M, Nylén L, Frech W, Andersson M, Ljunggren KG, Wennberg A (2001) Effects on the nervous system in different groups of workers exposed to aluminium. Occupa Environ Med 58:453–460
Lago A, Pesarin F (2000) Nonparametric combination of dependent rankings with application to the quality assessment of industrial products. Metron LVIII, 39–52
Lang C, Letzel S (1995) Neurotoxicity of aluminum. Study of a long-term exposed sample of workers of an aluminum powder industry. Fortschritte der Medizin 113:30–31
Letzel S, Lang CJ, Schaller KH, Angerer J, Fuchs S, Neundorfer B, Lehnert G (2000) Longitudinal study of neurotoxicity with occupational exposure to aluminum dust. Neurology 54:997–1000
Pesarin F (2001) Multivariate permutation tests with application in biostatistics. Wiley, Chichester
Pliskin NH, Yurk HM, Ho LT, Umans JG (1996) Neurocognitive function in chronic hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int 49:1435–1440
Polizzi S, Pira E, Ferrara M, Bugiani M, Papaleo A, Albera R, Palmi S (2002) Neurotoxic effects of aluminium among foundry workers and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurotoxicology 23:761–774
Riihimäki V, Hänninen H, Akila R, Kovala T, Kuosma E, Paakkulainen H, Valkonen S, Engstrom B (2000) Body burden of aluminum in relation to central nervous system function among metal inert-gas welders. Scand J Work Environ Health 26:118–130
SIEMENS ARISTO 50080 515 User’s Guide (2003)
Sinczuk-Walczak H, Szymczak M, Razniewska G, Matczak W, Szymczak W (2003) Effects of occupational exposure to aluminum on nervous system: clinical and electroencephalographic findings. Int J Occup Med Environ Health 16:301–310
Sjögren B, Gustavsson P, Hogstedt C (1990) Neuropsychiatric symptoms among welders exposed to neurotoxic metals. Br J Ind Med 47:704–707
Sjögren B, Iregren A, Frech W, Hagman M, Johansson L, Tesarz M, Wennberg A (1996) Effects on the nervous system among welders exposed to aluminium and manganese. J Occup Environ Med 53:32–40
Stroop S R (1983) Color–word test. O.S. Organizzazioni Speciali, Firenze
Wechsler D (1963) Wechsler memory scale. O.S. Organizzazioni Speciali, Firenze, Edizione italiana: E. Cimino
White DM, Longstreth WT Jr, Rosenstock L, Claypoole KH, Brodkin CA, Townes BD (1992) Neurologic syndrome in 25 workers from an aluminum smelting plant. Arch Intern Med 152:1443–1448. Erratum (1993) 153:2796
Yokel RA (2000) The toxicology of aluminum in the brain: a review. Neurotoxicology 21:813–828
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bonnini, S., Corain, L., Munaò, F. et al. Neurocognitive Effects in Welders Exposed to Aluminium: An Application of the NPC Test and NPC Ranking Methods. Stat. Meth. & Appl. 15, 191–208 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10260-006-0019-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10260-006-0019-3