Abstract
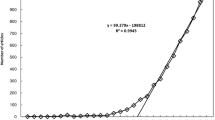
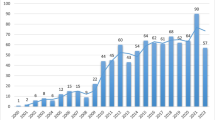
As a common chronic liver disease, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has attracted increasing attention in the past decade. Nevertheless, there are few bibliometric analyses that systematically study this field as a whole. This paper explores the latest research progress and future research trends of NAFLD through the method of bibliometric analysis. The articles related to NAFLD, published from 2012 to 2021 in the Web of Science Core Collections, were searched on February 21, 2022, using relevant keywords. Two different scientometrics software tools were used to conduct the knowledge maps of NAFLD research field. A total of 7975 articles on NAFLD research were included. From 2012 to 2021, the publications related to NAFLD increased by year. China ranked on the top of the list with 2043 publications, and the University of California System emerged as the premier institution in this field. PLOs One, Journal of Hepatology and Scientific Reports became the prolific journals in this research field. Co-cited reference analysis revealed the landmark literature in this research field. In terms of potential hotspots, the burst keywords analysis revealed that liver fibrosis stage, sarcopenia, and autophagy will become the focus of future NAFLD research. The annual output of the global publications in the field of NAFLD research showed a strong upward trend. Research in the field of NAFLD in China and America is more mature than in other countries. Classic literature lays the foundation for research, and multi-field studies provide the new development directions. And besides, fibrosis stage, sarcopenia and autophagy research are the hot spots and frontiers of this field.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Powell EE, Wong VW, Rinella M. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Lancet. 2021;397(10290):2212–24.
Targher G, Lonardo A, Byrne CD. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and chronic vascular complications of diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018;14(2):99–114.
Yki-Järvinen H. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease as a cause and a consequence of metabolic syndrome. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014;2(11):901–10.
Tilg H, Adolph TE, Dudek M, Knolle P. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: the interplay between metabolism, microbes and immunity. Nat Metab. 2021;3(12):1596–607.
Younossi ZM, Koenig AB, Abdelatif D, Fazel Y, Henry L, Wymer M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology. 2016;64(1):73–84.
Araújo AR, Rosso N, Bedogni G, Tiribelli C, Bellentani S. Global epidemiology of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease/non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: what we need in the future. Liver Int. 2018;38(Suppl 1):47–51.
Sheka AC, Adeyi O, Thompson J, Hameed B, Crawford PA, Ikramuddin S. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a review. JAMA. 2020;323(12):1175–83.
Zarei M, Aguilar-Recarte D, Palomer X, Vázquez-Carrera M. Revealing the role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor β/δ in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Metabolism. 2021;114:154342.
Santhekadur PK, Kumar DP, Sanyal AJ. Preclinical models of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 2018;68(2):230–7.
Friedman SL, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Rinella M, Sanyal AJ. Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies. Nat Med. 2018;24(7):908–22.
Ma D, Yang B, Guan B, et al. A bibliometric analysis of pyroptosis from 2001 to 2021. Front Immunol. 2021;12:731933.
Guo J, Gu D, Zhao T, et al. Trends in piezo channel research over the past decade: a bibliometric analysis. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:668714.
Xie L, Chen Z, Wang H, Zheng C, Jiang J. Bibliometric and visualized analysis of scientific publications on atlantoaxial spine surgery based on web of science and VOSviewer. World Neurosurg. 2020;137:435–42.
Huang X, Fan X, Ying J, Chen S. Emerging trends and research foci in gastrointestinal microbiome. J Transl Med. 2019;17(1):67.
Lu C, Liu M, Shang W, et al. Knowledge mapping of angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels (Danggui) research: a scientometric study. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:294.
Wu H, Tong L, Wang Y, Yan H, Sun Z. Bibliometric analysis of global research trends on ultrasound microbubble: a quickly developing field. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:646626.
Xu D, Wang YL, Wang KT, et al. A scientometrics analysis and visualization of depressive disorder. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021;19(6):766–86.
Chen C, Lou Y, Li XY, Lv ZT, Zhang LQ, Mao W. Mapping current research and identifying hotspots on mesenchymal stem cells in cardiovascular disease. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):498.
Zuanazzi NR, Ghisi NC, Oliveira EC. Analysis of global trends and gaps for studies about 2,4-D herbicide toxicity: a scientometric review. Chemosphere. 2020;241:125016.
Chen S, Lu Q, Bai J, Deng C, Wang Y, Zhao Y. Global publications on stigma between 1998–2018: a bibliometric analysis. J Affect Disord. 2020;274:363–71.
Martynov I, Klima-Frysch J, Schoenberger J. A scientometric analysis of neuroblastoma research. BMC Cancer. 2020;20(1):486.
Younossi Z, Tacke F, Arrese M, et al. Global perspectives on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 2019;69(6):2672–82.
Bauer KC, Littlejohn PT, Ayala V, Creus-Cuadros A, Finlay BB. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and the gut-liver axis: exploring an undernutrition perspective. Gastroenterology. 2022;162(7):1858–75.
Orci LA, Sanduzzi-Zamparelli M, Caballol B, et al. Incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20(2):283–92.
Smith GI, Shankaran M, Yoshino M, et al. Insulin resistance drives hepatic de novo lipogenesis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Invest. 2020;130(3):1453–60.
Harrison SA, Alkhouri N, Davison BA, et al. Insulin sensitizer MSDC-0602K in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase IIb study. J Hepatol. 2020;72(4):613–26.
Simon TG, Roelstraete B, Khalili H, Hagström H, Ludvigsson JF. Mortality in biopsy-confirmed nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: results from a nationwide cohort. Gut. 2021;70(7):1375–82.
Liu XL, Pan Q, Cao HX, et al. Lipotoxic hepatocyte-derived exosomal MicroRNA 192–5p activates macrophages through rictor/akt/forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2020;72(2):454–69.
Fei N, Bruneau A, Zhang X, et al. Endotoxin producers overgrowing in human gut microbiota as the causative agents for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Mbio. 2020;11(1)
Henao-Mejia J, Elinav E, Jin C, et al. Inflammasome-mediated dysbiosis regulates progression of NAFLD and obesity. Nature. 2012;482(7384):179–85.
Shen F, Zheng RD, Sun XQ, Ding WJ, Wang XY, Fan JG. Gut microbiota dysbiosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2017;16(4):375–81.
Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, Van Natta M, et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2005;41(6):1313–21.
Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, et al. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: practice guidance from the American Association for the study of liver diseases. Hepatology. 2018;67(1):328–57.
Vernon G, Baranova A, Younossi ZM. Systematic review: the epidemiology and natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in adults. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2011;34(3):274–85.
Angulo P, Hui JM, Marchesini G, et al. The NAFLD fibrosis score: a noninvasive system that identifies liver fibrosis in patients with NAFLD. Hepatology. 2007;45(4):846–54.
Targher G, Corey KE, Byrne CD, Roden M. The complex link between NAFLD and type 2 diabetes mellitus—mechanisms and treatments. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;18(9):599–612.
Stefan N, Cusi K. A global view of the interplay between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022;10(4):284–96.
Mantovani A, Petracca G, Beatrice G, Tilg H, Byrne CD, Targher G. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and risk of incident diabetes mellitus: an updated meta-analysis of 501 022 adult individuals. Gut. 2021;70(5):962–9.
Distefano JK. Fructose-mediated effects on gene expression and epigenetic mechanisms associated with NAFLD pathogenesis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020;77(11):2079–90.
Yu Y, Cai J, She Z, Li H. Insights into the epidemiology, pathogenesis, and therapeutics of nonalcoholic fatty liver diseases. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2019;6(4):1801585.
Tacke F, Trautwein C. Mechanisms of liver fibrosis resolution. J Hepatol. 2015;63(4):1038–9.
Johnson ND, Wu X, Still CD, et al. Differential DNA methylation and changing cell-type proportions as fibrotic stage progresses in NAFLD. Clin Epigenetics. 2021;13(1):152.
Xu Y, Guo W, Zhang C, et al. Herbal medicine in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases-efficacy, action mechanism, and clinical application. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:601.
Zhao YW, Yang J, Niu J, et al. Pharmacodynamic evaluation of the gexia zhuyu decoction in the treatment of NAFLD and the molecular mechanism underlying the TRPM4 pathway regulation. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021;2021:3364579.
Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Bahat G, Bauer J, et al. Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing. 2019;48:16–31.
Pacifico L, Perla FM, Chiesa C. Sarcopenia and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a causal relationship. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2019;8(2):144–7.
Hong HC, Hwang SY, Choi HY, et al. Relationship between sarcopenia and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: the Korean sarcopenic obesity study. Hepatology. 2014;59(5):1772–8.
Lee YH, Jung KS, Kim SU, et al. Sarcopaenia is associated with NAFLD independently of obesity and insulin resistance: nationwide surveys (KNHANES 2008–2011). J Hepatol. 2015;63(2):486–93.
Lee YH, Kim SU, Song K, et al. Sarcopenia is associated with significant liver fibrosis independently of obesity and insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: nationwide surveys (KNHANES 2008–2011). Hepatology. 2016;63(3):776–86.
Gao Y, Zhang W, Zeng LQ, et al. Exercise and dietary intervention ameliorate high-fat diet-induced NAFLD and liver aging by inducing lipophagy. Redox Biol. 2020;36:101635.
Singh R, Kaushik S, Wang Y, et al. Autophagy regulates lipid metabolism. Nature. 2009;458(7242):1131–5.
Zhao J, Hu Y, Peng J. Targeting programmed cell death in metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD): a promising new therapy. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2021;26(1):17.
Eslam M, Sanyal AJ, George J. International consensus Panel. MAFLD: a consensus-driven proposed nomenclature for metabolic associated fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2020;158(7):1999–2014.
Funding
This work was supported by the State Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82030116) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81703376).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZL was responsible for methodology and writing. SC and SZ contributed to the data analysis and draft writing. NK designed and supervised the study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Cao, S., Zhao, S. et al. A bibliometric analysis and visualization of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease from 2012 to 2021. Clin Exp Med 23, 1961–1971 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-023-01023-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-023-01023-2