Abstract
Exosomes, a subset of vesicles generated from cell membranes, are crucial for cellular communication. Exosomes' innate qualities have been used in recent studies to create nanocarriers for various purposes, including medication delivery and immunotherapy. As a result, a wide range of approaches has been designed to utilize their non-immunogenic nature, drug-loading capacity, or targeting ability. In this study, we aimed to review the novel methods and approaches in exosome engineering for encapsulation and targeting in regenerative medicine. We have assessed and evaluated each method's efficacy, advantages, and disadvantages and discussed the results of related studies. Even though the therapeutic role of non-allogenic exosomes has been demonstrated in several studies, their application has certain limitations as these particles are neither fully specific to target tissue nor tissue retainable. Hence, there is a strong demand for developing more efficient encapsulation methods along with more accurate and precise targeting methods, such as 3D printing and magnetic nanoparticle loading in exosomes, respectively.
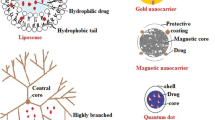
Graphical abstract



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data available on request due to privacy/ethical restrictions.
References
Shi Y, Hu G, Su J, Li W, Chen Q, Shou P, Xu C, Chen X, Huang Y, Zhu Z. Mesenchymal stem cells: a new strategy for immunosuppression and tissue repair. Cell Res. 2010;20(5):510–8.
Vlassov AV, Magdaleno S, Setterquist R, Conrad R. Exosomes: current knowledge of their composition, biological functions, and diagnostic and therapeutic potentials. Biochim et Biophys Acta (BBA) Gen Subj. 2012;1820(7):940–8.
Théry C, Amigorena S, Raposo G, Clayton A. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. 2006;30(1):3–22.
Iero M, Valenti R, Huber V, Filipazzi P, Parmiani G, Fais S, Rivoltini L. Tumour-released exosomes and their implications in cancer immunity. Cell Death Differ. 2008;15(1):80–8.
Keshtkar S, Azarpira N, Ghahremani MH. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: novel frontiers in regenerative medicine. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):1–9.
Toh WS, Lai RC, Hui JHP, Lim SK: MSC exosome as a cell-free MSC therapy for cartilage regeneration: Implications for osteoarthritis treatment. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017;67:56–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2016.11.008
Sukma Dewi I, Celik S, Karlsson A, Hollander Z, Lam K, McManus J-W, Tebbutt S, Ng R, Keown P, McMaster R. Exosomal miR-142-3p is increased during cardiac allograft rejection and augments vascular permeability through down-regulation of endothelial RAB11FIP2 expression. Cardiovasc Res. 2017;113(5):440–52.
Jing H, He X, Zheng J. Exosomes and regenerative medicine: state of the art and perspectives. Transl Res. 2018;196:1–16.
Moghadasi S, Elveny M, Rahman HS, Suksatan W, Jalil AT, Abdelbasset WK, Yumashev AV, Shariatzadeh S, Motavalli R, Behzad F. A paradigm shift in cell-free approach: the emerging role of MSCs-derived exosomes in regenerative medicine. J Transl Med. 2021;19(1):1–21.
Sun D, Zhuang X, Xiang X, Liu Y, Zhang S, Liu C, Barnes S, Grizzle W, Miller D, Zhang H-G. A novel nanoparticle drug delivery system: the anti-inflammatory activity of curcumin is enhanced when encapsulated in exosomes. Mol Ther. 2010;18(9):1606–14.
Wang J, Chen D, Ho EA. Challenges in the development and establishment of exosome-based drug delivery systems. J Control Release. 2021;329:894–906.
Elliott RO, He M. Unlocking the power of exosomes for crossing biological barriers in drug delivery. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13(1):122.
Khayambashi P, Iyer J, Pillai S, Upadhyay A, Zhang Y, Tran SD. Hydrogel encapsulation of mesenchymal stem cells and their derived exosomes for tissue engineering. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(2):684.
Shafiei M, Ansari MNM, Razak SIA, Khan MUA. A comprehensive review on the applications of exosomes and liposomes in regenerative medicine and tissue engineering. Polymers. 2021;13(15):2529.
Bai Q, Han K, Dong K, Zheng C, Zhang Y, Long Q, Lu T. Potential applications of nanomaterials and technology for diabetic wound healing. Int J Nanomed. 2020;15:9717.
Huang J, Xiong J, Yang L, Zhang J, Sun S, Liang Y. Cell-free exosome-laden scaffolds for tissue repair. Nanoscale. 2021;13(19):8740–50.
Foyt DA, Norman MD, Yu TT, Gentleman E. Exploiting advanced hydrogel technologies to address key challenges in regenerative medicine. Adv Healthcare Mater. 2018;7(8):1700939.
Saunderson SC, Dunn AC, Crocker PR, McLellan AD. CD169 mediates the capture of exosomes in spleen and lymph node. Blood. 2014;123(2):208–16.
Takahashi Y, Nishikawa M, Shinotsuka H, Matsui Y, Ohara S, Imai T, Takakura Y. Visualization and in vivo tracking of the exosomes of murine melanoma B16-BL6 cells in mice after intravenous injection. J Biotechnol. 2013;165(2):77–84.
György B, Hung ME, Breakefield XO, Leonard JN. Therapeutic applications of extracellular vesicles: clinical promise and open questions. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2015;55:439–64.
Ahmed EM. Hydrogel: preparation, characterization, and applications: a review. J Adv Res. 2015;6(2):105–21.
Elkhoury K, Koçak P, Kang A, Arab-Tehrany E, Ellis Ward J, Shin SR. Engineering smart targeting nanovesicles and their combination with hydrogels for controlled drug delivery. Pharmaceutics. 2020;12(9):849.
Tao SC, Guo SC, Li M, Ke QF, Guo YP, Zhang CQ. Chitosan wound dressings incorporating exosomes derived from MicroRNA-126-overexpressing synovium mesenchymal stem cells provide sustained release of exosomes and heal full-thickness skin defects in a diabetic rat model. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(3):736–47.
Wang M, Wang C, Chen M, Xi Y, Cheng W, Mao C, Xu T, Zhang X, Lin C, Gao W. Efficient angiogenesis-based diabetic wound healing/skin reconstruction through bioactive antibacterial adhesive ultraviolet shielding nanodressing with exosome release. ACS Nano. 2019;13(9):10279–93.
Sun M, Li Q, Yu H, Cheng J, Wu N, Shi W, Zhao F, Shao Z, Meng Q, Chen H. Cryo-self-assembled silk fibroin sponge as a biodegradable platform for enzyme-responsive delivery of exosomes. Bioact Mater. 2022;8:505–14.
Zhao D, Yu Z, Li Y, Wang Y, Li Q, Han D. GelMA combined with sustained release of HUVECs derived exosomes for promoting cutaneous wound healing and facilitating skin regeneration. J Mol Histol. 2020;51(3):251–63.
Fan J, Lee C-S, Kim S, Chen C, Aghaloo T, Lee M. Generation of small RNA-modulated exosome mimetics for bone regeneration. ACS Nano. 2020;14(9):11973–84.
Derkus B. Human cardiomyocyte-derived exosomes induce cardiac gene expressions in mesenchymal stromal cells within 3D hyaluronic acid hydrogels and in dose-dependent manner. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2021;32(1):1–11.
Han C, Zhou J, Liang C, Liu B, Pan X, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Yan B, Xie W, Liu F. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell derived exosomes encapsulated in functional peptide hydrogels promote cardiac repair. Biomater Sci. 2019;7(7):2920–33.
Chen CW, Wang LL, Zaman S, Gordon J, Arisi MF, Venkataraman CM, Chung JJ, Hung G, Gaffey AC, Spruce LA. Sustained release of endothelial progenitor cell-derived extracellular vesicles from shear-thinning hydrogels improves angiogenesis and promotes function after myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res. 2018;114(7):1029–40.
Liu X, Yang Y, Li Y, Niu X, Zhao B, Wang Y, Bao C, Xie Z, Lin Q, Zhu L. Integration of stem cell-derived exosomes with in situ hydrogel glue as a promising tissue patch for articular cartilage regeneration. Nanoscale. 2017;9(13):4430–8.
Wang C, Wang M, Xu T, Zhang X, Lin C, Gao W, Xu H, Lei B, Mao C. Engineering bioactive self-healing antibacterial exosomes hydrogel for promoting chronic diabetic wound healing and complete skin regeneration. Theranostics. 2019;9(1):65–76.
Yang J, Chen Z, Pan D, Li H, Shen J. Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes combined pluronic F127 hydrogel promote chronic diabetic wound healing and complete skin regeneration. Int J Nanomed. 2020;15:5911.
Li M, Ke Q-F, Tao S-C, Guo S-C, Rui B-Y, Guo Y-P. Fabrication of hydroxyapatite/chitosan composite hydrogels loaded with exosomes derived from miR-126-3p overexpressed synovial mesenchymal stem cells for diabetic chronic wound healing. J Mater Chem B. 2016;4(42):6830–41.
Wu N, Zhang X, Li J, Gan Y. Targeting exosomal miRNA with pH-sensitive liposome coated chitosan-siRNA nanoparticles for inhibition of hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis. J Control Release Off J Control Release Soc. 2015;213: e82.
Yuan H, Li K, Li B, Lou X, Zhao Q, Zhang Y. Development of a novel elastic and macroporous chitosan hydrogel for wound healing application. J Control Release. 2015;100(213):e43–4.
Shi Q, Qian Z, Liu D, Sun J, Wang X, Liu H, Xu J, Guo X. GMSC-derived exosomes combined with a chitosan/silk hydrogel sponge accelerates wound healing in a diabetic rat skin defect model. Front Physiol. 2017;8:904.
Nooshabadi VT, Khanmohamadi M, Valipour E, Mahdipour S, Salati A, Malekshahi ZV, Shafei S, Amini E, Farzamfar S, Ai J. Impact of exosome-loaded chitosan hydrogel in wound repair and layered dermal reconstitution in mice animal model. J Biomed Mater Res Part A. 2020;108(11):2138–49.
Li Q, Gong S, Yao W, Yang Z, Wang R, Yu Z, Wei M. Exosome loaded genipin crosslinked hydrogel facilitates full thickness cutaneous wound healing in rat animal model. Drug Deliv. 2021;28(1):884–93.
Yang S, Zhu B, Yin P, Zhao L, Wang Y, Fu Z, Dang R, Xu J, Zhang J, Wen N. Integration of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes with hydroxyapatite-embedded hyaluronic acid-alginate hydrogel for bone regeneration. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(3):1590–602.
Shafei S, Khanmohammadi M, Heidari R, Ghanbari H, Taghdiri Nooshabadi V, Farzamfar S, Akbariqomi M, Sanikhani NS, Absalan M, Tavoosidana G. Exosome loaded alginate hydrogel promotes tissue regeneration in full-thickness skin wounds: an in vivo study. J Biomed Mater Res Part A. 2020;108(3):545–56.
Wang C, Liang C, Wang R, Yao X, Guo P, Yuan W, Liu Y, Song Y, Li Z, Xie X. The fabrication of a highly efficient self-healing hydrogel from natural biopolymers loaded with exosomes for the synergistic promotion of severe wound healing. Biomater Sci. 2020;8(1):313–24.
Hajishengallis G. Immunomicrobial pathogenesis of periodontitis: keystones, pathobionts, and host response. Trends Immunol. 2014;35(1):3–11.
Grauballe MB, Østergaard JA, Schou S, Flyvbjerg A, Holmstrup P. Effects of TNF-α blocking on experimental periodontitis and type 2 diabetes in obese diabetic Z ucker rats. J Clin Periodontol. 2015;42(9):807–16.
Zhang K, Zhao X, Chen X, Wei Y, Du W, Wang Y, Liu L, Zhao W, Han Z, Kong D, et al. Enhanced therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes with an injectable hydrogel for hindlimb ischemia treatment. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(36):30081–91.
Shen Z, Kuang S, Zhang Y, Yang M, Qin W, Shi X, Lin Z. Chitosan hydrogel incorporated with dental pulp stem cell-derived exosomes alleviates periodontitis in mice via a macrophage-dependent mechanism. Bioact Mater. 2020;5(4):1113–26.
Liu W-z, Ma Z-j, Li J-r, Kang X-w. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: therapeutic opportunities and challenges for spinal cord injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):1–15.
Wyndaele J-J. The management of neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction after spinal cord injury. Nat Rev Urol. 2016;13(12):705–14.
Li L, Zhang Y, Mu J, Chen J, Zhang C, Cao H, Gao J. Transplantation of human mesenchymal stem-cell-derived exosomes immobilized in an adhesive hydrogel for effective treatment of spinal cord injury. Nano Lett. 2020;20(6):4298–305.
Zhang K, Li J, Jin J, Dong J, Li L, Xue B, Wang W, Jiang Q, Cao Y. Injectable, anti-inflammatory and conductive hydrogels based on graphene oxide and diacerein-terminated four-armed polyethylene glycol for spinal cord injury repair. Mater Des. 2020;196: 109092.
Liu X, Kim JC, Miller AL, Waletzki BE, Lu L. Electrically conductive nanocomposite hydrogels embedded with functionalized carbon nanotubes for spinal cord injury. New J Chem. 2018;42(21):17671–81.
Fan L, Liu C, Chen X, Zou Y, Wen H, Lu F, Luo Y, Tan G, Yu P, Chen D: Exosome-loaded conductive hydrogel with immune-modulating and neurogenesis-enhancing properties for synergistic spinal cord injury repair. 2020.
Zhao J, Li X, Hu J, Chen F, Qiao S, Sun X, Gao L, Xie J, Xu B. Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes attenuate myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury through miR-182-regulated macrophage polarization. Cardiovasc Res. 2019;115(7):1205–16.
Chen P, Zheng L, Wang Y, Tao M, Xie Z, Xia C, Gu C, Chen J, Qiu P, Mei S. Desktop-stereolithography 3D printing of a radially oriented extracellular matrix/mesenchymal stem cell exosome bioink for osteochondral defect regeneration. Theranostics. 2019;9(9):2439.
Xiong Y-Y, Gong Z-T, Tang R-J, Yang Y-J. The pivotal roles of exosomes derived from endogenous immune cells and exogenous stem cells in myocardial repair after acute myocardial infarction. Theranostics. 2021;11(3):1046–58.
Lv K, Li Q, Zhang L, Wang Y, Zhong Z, Zhao J, Lin X, Wang J, Zhu K, Xiao C. Incorporation of small extracellular vesicles in sodium alginate hydrogel as a novel therapeutic strategy for myocardial infarction. Theranostics. 2019;9(24):7403.
Han C, Zhou J, Liu B, Liang C, Pan X, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Shao L, Zhu B. Delivery of miR-675 by stem cell-derived exosomes encapsulated in silk fibroin hydrogel prevents aging-induced vascular dysfunction in mouse hindlimb. Mater Sci Eng C. 2019;99:322–32.
Li Z, Zhang K, Zhao X, Kong D, Zhao Q, Liu N, Ma F. Enhanced therapeutic effects of MSC-derived exosomes with an injectable hydrogel for hindlimb ischemia treatment. Circ Res. 2018;123(Suppl_1):A490–A490.
Epple C, Haumer A, Ismail T, Lunger A, Scherberich A, Schaefer DJ, Martin I. Prefabrication of a large pedicled bone graft by engineering the germ for de novo vascularization and osteoinduction. Biomaterials. 2019;192:118–27.
Filipowska J, Tomaszewski KA, Niedźwiedzki Ł, Walocha JA, Niedźwiedzki T. The role of vasculature in bone development, regeneration and proper systemic functioning. Angiogenesis. 2017;20(3):291–302.
Liu Y, Ma Y, Zhang J, Yuan Y, Wang J. Exosomes: a novel therapeutic agent for cartilage and bone tissue regeneration. Dose-Response. 2019;17(4):1559325819892702.
Zhou J, Liu H, Li S, Gong Y, Zhou M, Zhang J, Zhu G. Effects of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes on fracture healing in rats through the Wnt signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(11):4954–60.
Shi Y, Kang X, Wang Y, Bian X, He G, Zhou M, Tang K. Exosomes derived from bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs) enhance tendon-bone healing by regulating macrophage polarization. Med Sci Monitor Int Med J Exp Clin Res. 2020;26:e923328–e923321.
Wang L, Wang J, Zhou X, Sun J, Zhu B, Duan C, Chen P, Guo X, Zhang T, Guo H. A new self-healing hydrogel containing hucMSC-derived exosomes promotes bone regeneration. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:564731.
Ayhan E, Kesmezacar H, Akgun I. Intraarticular injections (corticosteroid, hyaluronic acid, platelet rich plasma) for the knee osteoarthritis. World J Orthoped. 2014;5(3):351.
Hoeeg C, Dolatshahi-Pirouz A, Follin B. Injectable hydrogels for improving cardiac cell therapy—in vivo evidence and translational challenges. Gels. 2021;7(1):7.
Riau AK, Ong HS, Yam GH, Mehta JS. Sustained delivery system for stem cell-derived exosomes. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:1368.
Wang L, Wang J, Zhou X, Sun J, Zhu B, Duan C, Chen P, Guo X, Zhang T, Guo H: A new self-healing hydrogel containing hucMSC-derived exosomes promotes bone regeneration. Frontiers in bioengineering and biotechnology. 2020:1047.
Hu J, Hou Y, Park H, Choi B, Hou S, Chung A, Lee M. Visible light crosslinkable chitosan hydrogels for tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2012;8(5):1730–8.
Axpe E, Oyen ML. Applications of alginate-based bioinks in 3D bioprinting. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(12):1976.
Ji S, Guvendiren M. Complex 3D bioprinting methods. APL Bioeng. 2021;5(1): 011508.
Rider P, Kačarević ŽP, Alkildani S, Retnasingh S, Barbeck M. Bioprinting of tissue engineering scaffolds. J Tissue Eng. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1177/2041731418802090
Hu Y, Wu B, Xiong Y, Tao R, Panayi AC, Chen L, Tian W, Xue H, Shi L, Zhang X. Cryogenic 3D printed hydrogel scaffolds loading exosomes accelerate diabetic wound healing. Chem Eng J. 2021;426:130634.
Chin SY, Dikshit V, Meera Priyadarshini B, Zhang Y. Powder-Based 3D Printing for the Fabrication of Device with Micro and Mesoscale Features. Micromachines (Basel). 2020;3011(7):658. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11070658.
Zhai M, Zhu Y, Yang M, Mao C. Human mesenchymal stem cell derived exosomes enhance cell-free bone regeneration by altering their miRNAs profiles. Advanced Science. 2020;7(19):2001334.
Stegen S, Carmeliet G. The skeletal vascular system–breathing life into bone tissue. Bone. 2018;115:50–8.
Ahn SH, Montero M, Odell D, Roundy S, Wright PK: Anisotropic material properties of fused deposition modeling ABS. Rapid Prototyp J. 2002.
Dudek P. FDM 3D printing technology in manufacturing composite elements. Arch Metall Mater. 2013;58(4):1415–8.
Zha Y, Li Y, Lin T, Chen J, Zhang S, Wang J. Progenitor cell-derived exosomes endowed with VEGF plasmids enhance osteogenic induction and vascular remodeling in large segmental bone defects. Theranostics. 2021;11(1):397.
Yan Y, Chen H, Zhang H, Guo C, Yang K, Chen K, Cheng R, Qian N, Sandler N, Zhang YS. Vascularized 3D printed scaffolds for promoting bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2019;190:97–110.
Phinney DG, Pittenger MF. Concise review: MSC-derived exosomes for cell-free therapy. Stem cells. 2017;35(4):851–8.
Chamberlain CS, Clements AE, Kink JA, Choi U, Baer GS, Halanski MA, Hematti P, Vanderby R. Extracellular vesicle-educated macrophages promote early achilles tendon healing. Stem Cells. 2019;37(5):652–62.
Song H, Li X, Zhao Z, Qian J, Wang Y, Cui J, Weng W, Cao L, Chen X, Hu Y. Reversal of osteoporotic activity by endothelial cell-secreted bone targeting and biocompatible exosomes. Nano Lett. 2019;19(5):3040–8.
De Luca L, Trino S, Laurenzana I, Lamorte D, Caivano A, Del Vecchio L, Musto P. Mesenchymal stem cell derived extracellular vesicles: A role in hematopoietic transplantation? Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(5):1022.
Sharifzadeh G, Hosseinkhani H. Biomolecule-responsive hydrogels in medicine. Adv Healthcare Mater. 2017;6(24):1700801.
Trevisan F, Calignano F, Aversa A, Marchese G, Lombardi M, Biamino S, Ugues D, Manfredi D. Additive manufacturing of titanium alloys in the biomedical field: processes, properties and applications. J Appl Biomater Funct Mater. 2018;16(2):57–67.
Mello DCR, de Oliveira JR, Cairo CAA, de Brito Ramos LS, da Cruz Vegian MR, de Vasconcellos LGO, de Oliveira FE, de Oliveira LD, de Vasconcellos LMR. Titanium alloys: in vitro biological analyzes on biofilm formation, biocompatibility, cell differentiation to induce bone formation, and immunological response. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2019;30(9):1–12.
Li Y, Yang W, Li X, Zhang X, Wang C, Meng X, Pei Y, Fan X, Lan P, Wang C. Improving osteointegration and osteogenesis of three-dimensional porous Ti6Al4V scaffolds by polydopamine-assisted biomimetic hydroxyapatite coating. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7(10):5715–24.
Murr LE, Gaytan SM, Ramirez DA, Martinez E, Hernandez J, Amato KN, Shindo PW, Medina FR, Wicker RB. Metal fabrication by additive manufacturing using laser and electron beam melting technologies. J Mater Sci Technol. 2012;28(1):1–14.
Wu Z, Pu P, Su Z, Zhang X, Nie L, Chang Y. Schwann cell-derived exosomes promote bone regeneration and repair by enhancing the biological activity of porous Ti6Al4V scaffolds. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;531(4):559–65.
Bashyal S, Thapa C, Lee S. Recent progresses in exosome-based systems for targeted drug delivery to the brain. J Control Release. 2022;348:723–44.
Kosaka N, Iguchi H, Yoshioka Y, Hagiwara K, Takeshita F, Ochiya T. Competitive interactions of cancer cells and normal cells via secretory microRNAs. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(2):1397–405.
Liang Y, Duan L, Lu J, Xia J. Engineering exosomes for targeted drug delivery. Theranostics. 2021;11(7):3183.
Chen H, Wang L, Zeng X, Schwarz H, Nanda HS, Peng X, Zhou Y: Exosomes, a new star for targeted delivery. Front Cell Develop Biol. 2021:2827.
Donoso-Quezada J, Ayala-Mar S, González-Valdez J. State-of-the-art exosome loading and functionalization techniques for enhanced therapeutics: a review. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2020;40(6):804–20.
Lin Y, Lu Y, Li X. Biological characteristics of exosomes and genetically engineered exosomes for the targeted delivery of therapeutic agents. J Drug Target. 2020;28(2):129–41.
Kim H, Yun N, Mun D, Kang J-Y, Lee S-H, Park H, Park H, Joung B. Cardiac-specific delivery by cardiac tissue-targeting peptide-expressing exosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;499(4):803–8.
Wang X, Chen Y, Zhao Z, Meng Q, Yu Y, Sun J, Yang Z, Chen Y, Li J, Ma T. Engineered exosomes with ischemic myocardium-targeting peptide for targeted therapy in myocardial infarction. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018;7(15): e008737.
Bellavia D, Raimondo S, Calabrese G, Forte S, Cristaldi M, Patinella A, Memeo L, Manno M, Raccosta S, Diana P. Interleukin 3-receptor targeted exosomes inhibit in vitro and in vivo chronic myelogenous leukemia cell growth. Theranostics. 2017;7(5):1333.
Limoni SK, Moghadam MF, Moazzeni SM, Gomari H, Salimi F. Engineered exosomes for targeted transfer of siRNA to HER2 positive breast cancer cells. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2019;187(1):352–64.
Peng H, Ji W, Zhao R, Yang J, Lu Z, Li Y, Zhang X. Exosome: a significant nano-scale drug delivery carrier. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(34):7591–608.
Choi H, Choi Y, Yim HY, Mirzaaghasi A, Yoo JK, Choi C. Biodistribution of exosomes and engineering strategies for targeted delivery of therapeutic exosomes. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2021;18(4):1–13.
Ramasubramanian L, Kumar P, Wang A. Engineering extracellular vesicles as nanotherapeutics for regenerative medicine. Biomolecules. 2020;10(1):48.
Salunkhe S, Basak M, Chitkara D, Mittal A. Surface functionalization of exosomes for target-specific delivery and in vivo imaging & tracking: strategies and significance. J Control Release. 2020;326:599–614.
Jia G, Han Y, An Y, Ding Y, He C, Wang X, Tang Q. NRP-1 targeted and cargo-loaded exosomes facilitate simultaneous imaging and therapy of glioma in vitro and in vivo. Biomaterials. 2018;178:302–16.
Tian T, Zhang H-X, He C-P, Fan S, Zhu Y-L, Qi C, Huang N-P, Xiao Z-D, Lu Z-H, Tannous BA. Surface functionalized exosomes as targeted drug delivery vehicles for cerebral ischemia therapy. Biomaterials. 2018;150:137–49.
Qi H, Liu C, Long L, Ren Y, Zhang S, Chang X, Qian X, Jia H, Zhao J, Sun J. Blood exosomes endowed with magnetic and targeting properties for cancer therapy. ACS Nano. 2016;10(3):3323–33.
Wang J, Li W, Zhang L, Ban L, Chen P, Du W, Feng X, Liu B-F. Chemically edited exosomes with dual ligand purified by microfluidic device for active targeted drug delivery to tumor cells. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(33):27441–52.
Kumar S, Michael IJ, Park J, Granick S, Cho YK. Cloaked exosomes: biocompatible, durable, and degradable encapsulation. Small. 2018;14(34):1802052.
Shin M, Lee H, Lee M, Shin Y, Song J-J, Kang S-W, Nam D-H, Jeon EJ, Cho M, Do M. Targeting protein and peptide therapeutics to the heart via tannic acid modification. Nat Biomed Eng. 2018;2(5):304–17.
Lin Y, Zhang K, Zhang R, She Z, Tan R, Fan Y, Li X. Magnetic nanoparticles applied in targeted therapy and magnetic resonance imaging: crucial preparation parameters, indispensable pre-treatments, updated research advancements and future perspectives. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(28):5973–91.
Xiao Y, Du J. Superparamagnetic nanoparticles for biomedical applications. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(3):354–67.
Oh JK, Park JM. Iron oxide-based superparamagnetic polymeric nanomaterials: design, preparation, and biomedical application. Prog Polym Sci. 2011;36(1):168–89.
Barjesteh T, Mansur S, Bao Y. Inorganic nanoparticle-loaded exosomes for biomedical applications. Molecules. 2021;26(4):1135.
Lee J-R, Park B-W, Kim J, Choo YW, Kim HY, Yoon J-K, Kim H, Hwang J-W, Kang M, Kwon SP. Nanovesicles derived from iron oxide nanoparticles–incorporated mesenchymal stem cells for cardiac repair. Sci Adv. 2020;6(18):eaaz0952.
Li X, Wang Y, Shi L, Li B, Li J, Wei Z, Lv H, Wu L, Zhang H, Yang B. Magnetic targeting enhances the cutaneous wound healing effects of human mesenchymal stem cell-derived iron oxide exosomes. J Nanobiotechnol. 2020;18(1):1–14.
Di H, Zeng E, Zhang P, Liu X, Zhang C, Yang J, Liu D. General approach to engineering extracellular vesicles for biomedical analysis. Anal Chem. 2019;91(20):12752–9.
Zhang M, Vojtech L, Ye Z, Hladik F, Nance E. Quantum dot labeling and visualization of extracellular vesicles. ACS Appl Nano Mater. 2020;3(7):7211–22.
Zhuang M, Chen X, Du D, Shi J, Deng M, Long Q, Yin X, Wang Y, Rao L. SPION decorated exosome delivery of TNF-α to cancer cell membranes through magnetism. Nanoscale. 2020;12(1):173–88.
Zhuang M, Du D, Pu L, Song H, Deng M, Long Q, Yin X, Wang Y, Rao L. SPION-decorated exosome delivered BAY55-9837 targeting the pancreas through magnetism to improve the blood GLC response. Small. 2019;15(52):1903135.
Wang J, Chen P, Dong Y, Xie H, Wang Y, Soto F, Ma P, Feng X, Du W, Liu B-F. Designer exosomes enabling tumor targeted efficient chemo/gene/photothermal therapy. Biomaterials. 2021;276:121056.
Liu S, Chen X, Bao L, Liu T, Yuan P, Yang X, Qiu X, Gooding JJ, Bai Y, Xiao J. Treatment of infarcted heart tissue via the capture and local delivery of circulating exosomes through antibody-conjugated magnetic nanoparticles. Nat Biomed Eng. 2020;4(11):1063–75.
Betzer O, Perets N, Angel A, Motiei M, Sadan T, Yadid G, Offen D, Popovtzer R. In vivo neuroimaging of exosomes using gold nanoparticles. ACS Nano. 2017;11(11):10883–93.
Khongkow M, Yata T, Boonrungsiman S, Ruktanonchai UR, Graham D, Namdee K. Surface modification of gold nanoparticles with neuron-targeted exosome for enhanced blood–brain barrier penetration. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):1–9.
Sancho-Albero M, del Mar E-B, Beltran-Visiedo M, Fernández-Messina L, Sebastián V, Sánchez-Madrid F, Arruebo M, Santamaria J, Martin-Duque P. Efficient encapsulation of theranostic nanoparticles in cell-derived exosomes: leveraging the exosomal biogenesis pathway to obtain hollow gold nanoparticle-hybrids. Nanoscale. 2019;11(40):18825–36.
Fuhrmann G, Serio A, Mazo M, Nair R, Stevens MM. Active loading into extracellular vesicles significantly improves the cellular uptake and photodynamic effect of porphyrins. J Control Release. 2015;205:35–44.
Haney MJ, Zhao Y, Jin YS, Li SM, Bago JR, Klyachko NL, Kabanov AV, Batrakova EV. Macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles as drug delivery systems for triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) therapy. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2020;15(3):487–500.
Li Y-J, Wu J-Y, Wang J-M, Hu X-B, Cai J-X, Xiang D-X. Gemcitabine loaded autologous exosomes for effective and safe chemotherapy of pancreatic cancer. Acta Biomater. 2020;101:519–30.
Haney MJ, Klyachko NL, Zhao Y, Gupta R, Plotnikova EG, He Z, Patel T, Piroyan A, Sokolsky M, Kabanov AV. Exosomes as drug delivery vehicles for Parkinson’s disease therapy. J Control Release. 2015;207:18–30.
Liang G, Zhu Y, Ali DJ, Tian T, Xu H, Si K, Sun B, Chen B, Xiao Z. Engineered exosomes for targeted co-delivery of miR-21 inhibitor and chemotherapeutics to reverse drug resistance in colon cancer. J Nanobiotechnol. 2020;18(1):1–15.
Oskouie MN, Aghili Moghaddam NS, Butler AE, Zamani P, Sahebkar A. Therapeutic use of curcumin-encapsulated and curcumin-primed exosomes. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(6):8182–91.
Trivedi M, Talekar M, Shah P, Ouyang Q, Amiji M. Modification of tumor cell exosome content by transfection with wt-p53 and microRNA-125b expressing plasmid DNA and its effect on macrophage polarization. Oncogenesis. 2016;5(8):e250–e250.
Yamashita T, Takahashi Y, Takakura Y. Possibility of exosome-based therapeutics and challenges in production of exosomes eligible for therapeutic application. Biol Pharm Bull. 2018;41(6):835–42.
Witwer KW, Buzás EI, Bemis LT, Bora A, Lässer C, Lötvall J, Nolte-‘t Hoen EN, Piper MG, Sivaraman S, Skog J. Standardization of sample collection, isolation and analysis methods in extracellular vesicle research. J Extracel Vesicles. 2013;2(1):20360.
Popowski KD, Moatti A, Scull G, Silkstone D, Lutz H, de Juan Abad BL, George A, Belcher E, Zhu D, Mei X. Inhalable dry powder mRNA vaccines based on extracellular vesicles. Matter. 2022;5(9):2960–74.
Willis GR, Kourembanas S, Mitsialis SA. Toward exosome-based therapeutics: isolation, heterogeneity, and fit-for-purpose potency. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2017;4:63.
Mendt M, Rezvani K, Shpall E. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for clinical use. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2019;54(2):789–92.
Squillaro T, Peluso G, Galderisi U. Clinical trials with mesenchymal stem cells: an update. Cell Transpl. 2016;25(5):829–48.
Skuratovskaia D, Vulf M, Khaziakhmatova O, Malashchenko V, Komar A, Shunkin E, Gazatova N, Litvinova L. Exosome limitations in the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Curr Pharm Des. 2021;27(28):3105–21.
Umezu T, Imanishi S, Azuma K, Kobayashi C, Yoshizawa S, Ohyashiki K, Ohyashiki JH. Replenishing exosomes from older bone marrow stromal cells with miR-340 inhibits myeloma-related angiogenesis. Blood Adv. 2017;1(13):812–23.
Patel DB, Gray KM, Santharam Y, Lamichhane TN, Stroka KM, Jay SM. Impact of cell culture parameters on production and vascularization bioactivity of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles. Bioeng Transl Med. 2017;2(2):170–9.
Li M, Li S, Du C, Zhang Y, Li Y, Chu L, Han X, Galons H, Zhang Y, Sun H. Exosomes from different cells: characteristics, modifications, and therapeutic applications. Eur J Med Chem. 2020;207: 112784.
Sun Z, Shi K, Yang S, Liu J, Zhou Q, Wang G, Song J, Li Z, Zhang Z, Yuan W. Effect of exosomal miRNA on cancer biology and clinical applications. Mol Cancer. 2018;17(1):1–19.
Chen H, Xue R, Huang P, Wu Y, Fan W, He X, Dong Y, Liu C. Modified exosomes: a good transporter for miRNAs within stem cells to treat ischemic heart disease. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2022;28:1–10.
Manca S, Upadhyaya B, Mutai E, Desaulniers AT, Cederberg RA, White BR, Zempleni J. Milk exosomes are bioavailable and distinct microRNA cargos have unique tissue distribution patterns. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):1–11.
Ju S, Mu J, Dokland T, Zhuang X, Wang Q, Jiang H, Xiang X, Deng Z-B, Wang B, Zhang L. Grape exosome-like nanoparticles induce intestinal stem cells and protect mice from DSS-induced colitis. Mol Ther. 2013;21(7):1345–57.
Zhou X, Li Z, Sun W, Yang G, Xing C, Yuan L. Delivery efficacy differences of intravenous and intraperitoneal injection of exosomes: Perspectives from tracking dye labeled and MiRNA encapsulated exosomes. Curr Drug Deliv. 2020;17(3):186–94.
Mizrak A, Bolukbasi MF, Ozdener GB, Brenner GJ, Madlener S, Erkan EP, Ströbel T, Breakefield XO, Saydam O. Genetically engineered microvesicles carrying suicide mRNA/protein inhibit schwannoma tumor growth. Mol Ther. 2013;21(1):101–8.
Hwang DW, Jo MJ, Lee JH, Kang H, Bao K, Hu S, Baek Y, Moon HG, Lee DS, Kashiwagi S. Chemical modulation of bioengineered exosomes for tissue-specific biodistribution. Adv Therap. 2019;2(11):1900111.
Popowski KD, Dinh PUC, George A, Lutz H, Cheng K. Exosome therapeutics for COVID-19 and respiratory viruses. View. 2021;2(3):20200186.
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge all the contributions from the Research Center for Advanced Technologies in Cardiovascular Medicine, Cardiovascular Diseases Research Institute, Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Funding
This study was carried out in authors own capacity, and this study was not funded by any governmental organization and the authors themselves financed this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HTG did manuscript composure, conceptualization, and visualization. SPB done manuscript composure and visualization. AA provided manuscript composure, revision and editing. ZKZ, AH-T, and KH were involved in manuscript composure. AH revised and edited the manuscript. HAT contributed to editing, revision, scientific supervision, and conceptualization. SD and MAT edited and revised the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Consent for publication
All authors have consent for publication of the article.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tashak Golroudbari, H., Banikarimi, S.P., Ayati, A. et al. Advanced micro-/nanotechnologies for exosome encapsulation and targeting in regenerative medicine. Clin Exp Med 23, 1845–1866 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-023-00993-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-023-00993-7