Abstract
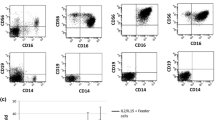
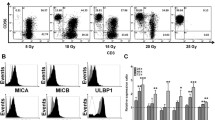
We characterised the expansion, phenotype and functional activity of natural killer (NK) cells obtained for a clinical trial. Nineteen expansion procedures were performed to obtain NK cell products for 16 patients. NK cells were expanded ex vivo from haploidentical donor peripheral blood mononuclear cells in the presence of the locally generated feeder cell line K-562 with ectopic expression of 4-1BBL and mbIL-21. The median duration of expansion was 18 days (interquartile range 15–19). The median number of live cells yielded was 2.26 × 109 (range 1.6–3.4 × 109) with an NK content of 96.6% (range 95.1–97.9%). The median NK cell fold expansion was 171 (range 124–275). NK cell fold expansion depended on the number of seeded NK cells, the initial level of C-myc expression and the initial number of mature and immature NK cells. The majority of expanded NK cells had the phenotype of immature activated cells (NKG2A + , double bright CD56 + + CD16 + + , CD57-) expressing NKp30, NKp44, NKp46, NKG2D, CD69, HLA-DR and CD96. Despite the expression of exhaustion markers, expanded NK cells exhibited high cytolytic activity against leukaemia cell lines, high degranulation activity and cytokine production. There was a noted decrease in the functional activity of NK cells in tests against the patient’s blasts.
In conclusion, NK cells obtained by ex vivo expansion with locally generated K562-41BBL-mbIL21 cells had a relatively undifferentiated phenotype and enhanced cytolytic activity against cancer cell lines. Expansion of NK cells with feeder cells yielded a sufficient quantity of the NK cell product to reach high cell doses or increase the frequency of cell infusions for adoptive immunotherapy. Registered at clinicaltrials.gov as NCT04327037.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kiessling R, Klein E, Pross H, Wigzell H. “Natural” killer cells in the mouse. II. Cytotoxic cells with specificity for mouse moloney leukemia cells. characteristics of the killer cell. Eur J Immunol. 1975;5(2):117. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.1830050209.
Suen WC, Lee WY, Leung KT, Pan XH, Li G. Natural killer cell-based cancer immunotherapy: A review on 10 years completed clinical trials. Cancer Invest. 2018;36(8):431–57. https://doi.org/10.1080/07357907.2018.1515315.
Choucair K, Duff JR, Cassidy CS, Albrethsen MT, Kelso JD, Lenhard A, Staats H, Patel R, Brunicardi FC, Dworkin L, Nemunaitis J. Natural killer cells: A review of biology, therapeutic potential and challenges in treatment of solid tumors. Future Oncol. 2019;15:3053–69. https://doi.org/10.2217/fon-2019-0116.
Liu S, Galat V, Galat Y, Lee YKA, Wainwright D, Wu J. NK cell-based cancer immunotherapy: from basic biology to clinical development. J Hematol Oncol. 2021;14:7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-020-01014-w.
Ragoonanan D, Khazal SJ, Abdel-Azim H, McCall D, Cuglievan B, Tambaro FP, Ahmad AH, Rowan CM, Gutierrez C, Schadler K, Li S, Di Nardo M, Chi L, Gulbis AM, Shoberu B, Mireles ME, McArthur J, Kapoor N, Miller J, Fitzgerald JC, Tewari P, Petropoulos D, Gill JB, Duncan CN, Lehmann LE, Hingorani S, Angelo JR, Swinford RD, Steiner ME, Hernandez Tejada FN, Martin PL, Auletta J, Choi SW, Bajwa R, Dailey Garnes N, Kebriaei P, Rezvani K, Wierda WG, Neelapu SS, Shpall EJ, Corbacioglu S, Mahadeo KM. Diagnosis, grading and management of toxicities from immunotherapies in children, adolescents and young adults with cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2021;18:435–53. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41571-021-00474-4.
Parisi S, Lecciso M, Ocadlikova D, Salvestrini V, Ciciarello M, Forte D, Corradi G, Cavo M, Curti A. The more, the better: “Do the right thing” for natural killer immunotherapy in acute myeloid leukemia. Front Immunol. 2017;8:1330. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.01330.
Shimasaki N, Jain A, Campana D. NK cells for cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2020;19:200–18. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41573-019-0052-1.
Lee DA. Cellular therapy: Adoptive immunotherapy with expanded natural killer cells. Immunol Rev. 2019;290:85–99. https://doi.org/10.1111/imr.12793.
Denman CJ, Senyukov VV, Somanchi SS, Phatarpekar PV, Kopp LM, Johnson JL, Singh H, Hurton L, Maiti SN, Huls MH, Champlin RE, Cooper LJ, Lee DA. Membrane-bound IL-21 promotes sustained ex vivo proliferation of human natural killer cells. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e30264. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0030264.
Vashkevich EP, Migas AA, Meleshko AN, Matveenko MA, Strushkevich NV, Shman TV. Expansion and activation of human natural killer cells ex vivo in the presence of transgenic feeder cells. Cell Tiss Biol. 2020;14:365–71. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990519X20050090.
Uphoff CC, Drexler HG. Detecting mycoplasma contamination in cell cultures by polymerase chain reaction. In: Cree I, editor. Cancer cell culture methods in molecular biology. Humana Press; 2011. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-080-5_8.
Miller JS, Soignier Y, Panoskaltsis-Mortari A, McNearney SA, Yun GH, Fautsch SK, McKenna D, Le C, Defor TE, Burns LJ, Orchard PJ, Blazar BR, Wagner JE, Slungaard A, Weisdorf DJ, Okazaki IJ, McGlave PB. Successful adoptive transfer and in vivo expansion of human haploidentical NK cells in patients with cancer. Blood. 2005;105:3051–7. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2004-07-2974.
Bachanova V, Burns LJ, McKenna DH, Curtsinger J, Panoskaltsis-Mortari A, Lindgren BR, Cooley S, Weisdorf D, Miller JS. Allogeneic natural killer cells for refractory lymphoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2010;59:1739–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-010-0896-z.
Choi I, Yoon SR, Park SY, Kim H, Jung SJ, Jang YJ, Kang M, Yeom YI, Lee JL, Kim DY, Lee YS, Kang YA, Jeon M, Seol M, Lee JH, Lee JH, Kim HJ, Yun SC, Lee KH. Donor-derived natural killer cells infused after human leukocyte antigen-haploidentical hematopoietic cell transplantation: A dose-escalation study. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014;20:696–704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2014.01.031.
Curti A, Ruggeri L, Parisi S, Bontadini A, Dan E, Motta MR, Rizzi S, Trabanelli S, Ocadlikova D, Lecciso M, Giudice V, Fruet F, Urbani E, Papayannidis C, Martinelli G, Bandini G, Bonifazi F, Lewis RE, Cavo M, Velardi A, Lemoli RM. Larger size of donor alloreactive nk cell repertoire correlates with better response to NK cell immunotherapy in elderly acute myeloid leukemia patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22:1914–21. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-1604.
Silla L, Valim V, Pezzi A, da Silva M, Wilke I, Nobrega J, Vargas A, Amorin B, Correa B, Zambonato B, Scherer F, Merzoni J, Sekine L, Huls H, Cooper LJ, Paz A, Lee DA. Adoptive immunotherapy with double-bright (CD56bright /CD16bright) expanded natural killer cells in patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukaemia: A proof-of-concept study. Br J Haematol. 2021;195:710–21. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.17751.
Liu Y, Wu HW, Sheard MA, Sposto R, Somanchi SS, Cooper LJ, Lee DA, Seeger RC. Growth and activation of natural killer cells ex vivo from children with neuroblastoma for adoptive cell therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19:2132–1243. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-1243.
Shenouda MM, Gillgrass A, Nham T, Hogg R, Lee AJ, Chew MV, Shafaei M, Aarts C, Lee DA, Hassell J, Bane A, Dhesy-Thind S, Ashkar AA. Ex vivo expanded natural killer cells from breast cancer patients and healthy donors are highly cytotoxic against breast cancer cell lines and patient-derived tumours. Breast Cancer Res. 2017;19:76. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13058-017-0867-9.
Shah N, Li L, McCarty J, Kaur I, Yvon E, Shaim H, Muftuoglu M, Liu E, Orlowski RZ, Cooper L, Lee D, Parmar S, Cao K, Sobieiski C, Saliba R, Hosing C, Ahmed S, Nieto Y, Bashir Q, Patel K, Bollard C, Qazilbash M, Champlin R, Rezvani K, Shpall EJ. Phase I study of cord blood-derived natural killer cells combined with autologous stem cell transplantation in multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol. 2017;177:457–66. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.14570.
Ciurea SO, Kongtim P, Soebbing D, Trikha P, Behbehani G, Rondon G, Olson A, Bashir Q, Gulbis AM, Indreshpal K, Rezvani K, Shpall EJ, Bassett R, Cao K, Martin AS, Devine S, Horowitz M, Pasquini M, Lee DA, Champlin RE. Decrease post-transplant relapse using donor-derived expanded NK-cells. Leukemia. 2022;36:155–64. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-021-01349-4.
Ojo EO, Sharma AA, Liu R, Moreton S, Checkley-Luttge MA, Gupta K, Lee G, Lee DA, Otegbeye F, Sekaly RP, de Lima M, Wald DN. Membrane bound IL-21 based NK cell feeder cells drive robust expansion and metabolic activation of NK cells. Sci Rep. 2019;9:14916. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-51287-6.
Yang Y, Badeti S, Tseng HC, Ma MT, Liu T, Jiang JG, Liu C, Liu D. Superior expansion and cytotoxicity of human primary NK and CAR-NK cells from various sources via enriched metabolic pathways. Mol Ther Method Clin Dev. 2020;18:428–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtm.2020.06.014.
Fernández A, Navarro-Zapata A, Escudero A, Matamala N, Ruz-Caracuel B, Mirones I, Pernas A, Cobo M, Casado G, Lanzarot D, Rodríguez-Antolín C, Vela M, Ferreras C, Mestre C, Viejo A, Leivas A, Martínez J, Fernández L, Pérez-Martínez A. Optimizing the procedure to manufacture clinical-grade NK cells for adoptive immunotherapy. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13:577. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13030577.
Lapteva N, Durett AG, Sun J, Rollins LA, Huye LL, Fang J, Dandekar V, Mei Z, Jackson K, Vera J, Ando J, Ngo MC, Coustan-Smith E, Campana D, Szmania S, Garg T, Moreno-Bost A, Vanrhee F, Gee AP, Rooney CM. Large-scale ex vivo expansion and characterization of natural killer cells for clinical applications. Cytotherapy. 2012;14:1131–43. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13030577.
Moseman JE, Foltz JA, Sorathia K, Heipertz EL, Lee DA. Evaluation of serum-free media formulations in feeder cell-stimulated expansion of natural killer cells. Cytotherapy. 2020;22:322–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcyt.2020.02.002.
Vela M, Corral D, Carrasco P, Fernández L, Valentín J, González B, Escudero A, Balas A, de Paz R, Torres J, Leivas A, Martinez-Lopez J, Pérez-Martínez A. Haploidentical IL-15/41BBL activated and expanded natural killer cell infusion therapy after salvage chemotherapy in children with relapsed and refractory leukemia. Cancer Lett. 2018;422:107–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2018.02.033.
Lopez-Vergès S, Milush JM, Pandey S, York VA, Arakawa-Hoyt J, Pircher H, Norris PJ, Nixon DF, Lanier LL. CD57 defines a functionally distinct population of mature NK cells in the human CD56dimCD16+ NK-cell subset. Blood. 2010;116:3865–74. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2010-04-282301.
Streltsova MA, Erokhina SA, Kanevskiy LM, Lee DA, Telford WG, Sapozhnikov AM, Kovalenko EI. Analysis of NK cell clones obtained using interleukin-2 and gene-modified K562 cells revealed the ability of “senescent” NK cells to lose CD57 expression and start expressing NKG2A. PLoS ONE. 2018;13:e0208469. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0208469.
Takahashi E, Kuranaga N, Satoh K, Habu Y, Shinomiya N, Asano T, Seki S, Hayakawa M. Induction of CD16+CD56bright NK cells with antitumour cytotoxicity not only from CD16- CD56bright NK cells but also from CD16-CD56dim NK cells. Scand J Immunol. 2007;65:126–38. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3083.2006.01883.x.
Lieberman NAP, DeGolier K, Haberthur K, Chinn H, Moyes KW, Bouchlaka MN, Walker KL, Capitini CM, Crane CA. An uncoupling of canonical phenotypic markers and functional potency of ex vivo-expanded natural killer cells. Front Immunol. 2018;9:150. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.00150.
Buckle I, Guillerey C. Inhibitory receptors and immune checkpoints regulating natural killer cell responses to cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13:4263. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174263.
Laskowski TJ, Biederstädt A, Rezvani K. Natural killer cells in antitumour adoptive cell immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2022;22(10):557–75. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-022-00491-0.
Liu E, Marin D, Banerjee P, Macapinlac HA, Thompson P, Basar R, Nassif Kerbauy L, Overman B, Thall P, Kaplan M, Nandivada V, Kaur I, Nunez Cortes A, Cao K, Daher M, Hosing C, Cohen EN, Kebriaei P, Mehta R, Neelapu S, Nieto Y, Wang M, Wierda W, Keating M, Champlin R, Shpall EJ, Rezvani K. Use of CAR-transduced natural killer cells in CD19-positive lymphoid tumors. N Engl J Med. 2018;6(382):6. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1910607.
Colamartino ABL, Lemieux W, Bifsha P, Nicoletti S, Chakravarti N, Sanz J, Roméro H, Selleri S, Béland K, Guiot M, Tremblay-Laganière C, Dicaire R, Barreiro L, Lee DA, Verhoeyen E, Haddad E. Efficient and robust NK-cell transduction with baboon envelope pseudotyped lentivector. Front Immunol. 2019;16(10):2873. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.02873.
Funding
This work was supported by the Belarus government program ‘Knowledge-intensive technologies and technics’ (contract № 2/2017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
T.Sh. designed the study and wrote the manuscript. A.M. engineered the feeder cell line. K.V., M.M. expanded NK cells. Y.L., N.M. and K.H. analyzed expanded NK cells. O.A. recruited the patients and supervised the clinical study. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shman, T.V., Vashkevich, K.P., Migas, A.A. et al. Phenotypic and functional characterisation of locally produced natural killer cells ex vivo expanded with the K562-41BBL-mbIL21 cell line. Clin Exp Med 23, 2551–2560 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-022-00974-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-022-00974-2