Abstract
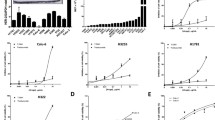
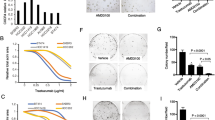
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death. For this reason, new therapies are needed for the treatment of this devastating disease. In this study, we investigated the effects of combining cetuximab and the trastuzumab on the growth of a model of human non-small cell lung carcinoma cell line (A549). The results were compared with those obtained from a human lung squamous carcinoma cell line (NCI-H226). Both cell lines were treated with cetuximab and trastuzumab, alone or in combination, at various concentrations, for 24, 48 and 72 h. Cell proliferation was measured by the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay. EGFR and HER-2 mRNA expression was detected by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, and the gene amplification status of receptors was evaluated by fluorescence in situ hybridisation. The colorimetric proliferation assay showed that trastuzumab combined with cetuximab significantly inhibited A549 cells at a dose of 40 μg/ml after 72 h of treatment (p < 0.05), while no time-dose dependent inhibition was observed in NCI-H226 cells. The combined treatment influenced both levels of EGFR and HER-2 mRNA in A549 cells and only EGFR mRNA levels in NCI-H226 cells. Fluorescence in situ hybridisation showed that both cell lines were aneuploid for the two genes with equally increased EGFR and CEN7 signals, as well as HER-2 and CEN17 signals, indicating a condition of polysomy without amplification. The preliminary results of this study encourage further investigations to elucidate the downstream events involved and to understand how these mechanisms influence non-small cell lung cancers growth.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Porter AC, Vaillancourt RR. Tyrosine Kinase receptor-activated signal transduction pathways which lead to oncogenesis. Oncogene. 1998;15:1343–52.
Altekruse SF, Kosary CL, Krapcho M, Neyman N, Aminou R, Waldron W, et al. In: SEER cancer statistics review, 1975–2008. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2008/.
Schottenfield D. Etiology and epidemiology of lung cancer. In: Pass HI, Michelle JB, Johnson DH, et al., editors. Lung cancer principles and practice. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Williams; 2000. p. 367–8.
Arteaga CL. Epidermal growth factor dependence in human tumours: more than just expression. Oncologist. 2002;7(4):31–39.
Salomon DS, Brndt R, Ciardello F, Normanno N. Epidermal growth factor-related peptides and their receptors in human malignancies. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 1995;19:183–232.
Graus-porta D, Beerli RR, Daly JM, Hynes NE. ErbB2, the preferred heterodimerization partner of all ErbB receptors, is a mediator of lateral signalling. Eur Mol Biol Org J. 1997;16:1647–59.
Karunagaran D, Tzahar E, Beerli RR. ErbB2 is a common auxiliary subunit of NDF and EGF receptors: implications for breast cancer. Eur mol Biol Org J. 1996;15:254–64.
Spencer KS, Graus-Porta D, Leng J. ErbB2 is necessary for induction of carcinoma cell invasion by erbB family receptor tyrosine kinases. J Cell Biol. 2000;148:385–97.
Woodburn JR. The epidermal growth factor receptor and its inhibition in cancer therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 1999;82:241–50.
Laskin JJ. Sandler Ab. Epidermal Growth factor receptor: a promising target in solid tumours. Cancer Treat Rev. 2004;30:1–17.
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, et al. Activating mutations in epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness if non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2129–39.
Costa DB, Kobayashi S, Tenen DG, Huberman MS. Pooled analysis of the prospective trials of gefitinib monotherapy for EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancers. Lung Cancer. 2007;58(1):95–103.
Giaccone G, Herbst RS, Manegold C, et al. Gefitinib in combination with gemcitabine and cisplatin in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. A phase III trial-INTACT 1. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22(5):777–84.
Asahina H, Yamazaki K, Kinoshita I, et al. A phase II trial of gefitinib as first-line therapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer with epidermal growth factor receptor mutations. Br J Cancer. 2006;95(8):998–1004.
Garassino MC, Martelli O, Broggini M, et al. TAILOR trialists. Erlotinib versus docetaxel as second-line treatment of patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer and wild-type EGFR tumours (TAILOR): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14(10):981–8.
Mendelsohn J, Baselga J. Status of epidermal growth factor receptor antagonists in the biology and treatment of cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:2787–99.
Pirker R, Pereira JR, Szczesna A, et al. Cetuximab plus chemotherapy in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (FLEX): an open-label randomised phase III trial. Lancet. 2009;373:1525–31.
Lynch TJ, Patel T, Dreisbach L, et al. Cetuximab and first-line taxane/carboplatin chemotherapy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: results of the randomized multicenter phase III trial BMS099. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:911–7.
Pirker R, Pereira JR, von Pawel J, et al. EGFR expression as a predictor of survival for first-line chemotherapy plus cetuximab in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: analysis of data from the phase 3 FLEX study. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:33–42.
Langer CJ, Stephenson P, Thor A, Vangel M, Johnson DH. Trastuzumab in the treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: is there a role? Focus on eastern co-operative oncology group study 2598. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:1180–7.
Atzemeier U, Groth G, Butts C, et al. Randomized phase II trial of gemcitabine-cisplatin with or without trastuzumab in HER2-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. 2004;15:19–27.
Cavazzoni A, Alfieri RR, Cretella D, et al. Combined use of anti-ErbB monoclonal antibodies and erlotinib enhances antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity of wild-type erlotinib-sensitive NSCLC cell lines. Mol Cancer. 2012;11:91.
Hirsch FR, Varella-Garcia M, Bunn PA Jr, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor in non-small-cell lung carcinomas: correlation between gene copy number and protein expression and impact on prognosis. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:3798–807.
Cappuzzo F, Hirsch FR, Rossi E, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor gene and protein and gefitinib sensitivity in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005;97:643–55.
Paez JG, Jänne PA, Lee JC, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004;304:1497–500.
Arteaga CL, Sliwkowski MX, Osborne CK, et al. Treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer: current status and future perspectives. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2012;9:16–32.
Rouquette I, Lauwers-Cances V, Allera C, et al. Characteristics of lung cancer in women: importance of hormonal and growth factors. Lung Cancer. 2012;76:280–5.
Pellegrini C, Falleni M, Marchetti A, et al. HER-2/Neu alterations in non-small cell lung cancer: a comprehensive evaluation by real time reverse transcription-PCR, fluorescence in situ hybridization, and immunohistochemistry. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:3645–52.
Arcila ME, Chaft JE, Nafa K, et al. Prevalence, clinicopathologic associations and molecular spectrum of ERBB2 (HER2) tyrosine kinase mutations in lung adenocarcinomas. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18:4910–8.
Tomizawa K, Suda K, Onozato R, et al. Prognostic and predictive implications of HER2/ERBB2/neu gene mutations in lung cancers. Lung Cancer. 2011;74:139–44.
Li S, Schmitz KR, Jeffrey PD, Wiltzius JJ, Kussie P, Ferguson KM. Structural basis for inhibition of the epidermal growth factor receptor by cetuximab. Cancer Cell. 2005;7:301–11.
Altundag K, Esteva FJ, Arun B. Monoclonal antibody-based targeted therapy in breast cancer. Curr Med Chem Anti Cancer Agents. 2005;5:99–106.
Roh H, Pippin J, Drebin JA. Down-regulation of HER2/neu expression induces apoptosis in human cancer cells that overexpress Her2/neu. Cancer Res. 2000;60(3):560–5.
Simpson BJ, Phillips HA, Lessels AM, Langdon SP, Miller WR. c-erbB growth-factor-receptor proteins in ovarian tumours. Int J Cancer. 1995;64:202–6.
Kawaguchi Y, Kono K, Mimura K, et al. Targeting EGFR and HER-2 with cetuximab- and trastuzumab-mediated immunotherapy in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2007;97(4):494–501.
Li S, Schmitz KR, Jeffrey PD, Wiltzius JJ, Kussie P, Ferguson KM. Structural basis for inhibition of the epidermal growth factor by cetuximab. Cancer Cell. 2005;7:301–11.
Putnam EA, Yen N, Gallick GE, et al. Autocrine growth stimulation by transforming growth factor-alpha in human non-small cell lung cancer. Surg Oncol. 1992;1(1):49–60.
Anaka S, Mori M, Akiyoshi T, Tanaka Y, Mafune K, et al. A novel variant of human Grb7 is associated with invasive esophageal carcinoma. J Clin Invest. 1998;102(4):821–7.
Pero SC, Daly RJ, Krag DN. Grb7-based molecular therapeutics in cancer. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2003;5(14):1–11.
Dong Cho Han. Tang-Long Shen, Jun-Lin Guan. The Grb7 family proteins: structure, interactions with other signaling molecules and potential cellular functions. Oncogene. 2001;20(44):6315–21.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Privitera, G., Luca, T., Musso, N. et al. In vitro antiproliferative effect of trastuzumab (Herceptin®) combined with cetuximab (Erbitux®) in a model of human non-small cell lung cancer expressing EGFR and HER2. Clin Exp Med 16, 161–168 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-015-0343-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-015-0343-8