Abstract
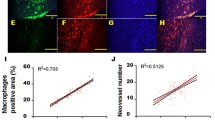
Intra-plaque angiogenesis plays an important role in the development of atherosclerotic plaque. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a major initiating factor in this pathologic progress. One selective and specific inhibitor of VEGF is soluble VEGF receptor-1 (sFlt-1). The anti-angiogenic utilization of sFlt-1 in treatment of atherosclerotic plaque has not been fully confirmed yet. Our study was designed to construct eukaryotic expression recombinant pEGFP-N1-sFlt-1, evaluate sFlt-1 recombinant’s effects on endothelial cells proliferation and tube formation in vitro, and investigate effects of local high-expressed sFlt-1 on atherosclerotic plaque in vivo. Rabbit models of atherosclerotic plaque were established by high-lipid diet combined with injury induced by balloon catheter on iliac artery intima. Animals were divided into four groups randomly: control group (C), atherosclerotic plaque group (AP), atherosclerotic plaque with blank vector pEGFP-N1 transfection group (APV), and atherosclerotic plaque with pEGFP-N1-sFlt-1 transfection group (APsFlt-1). The local expression of sFlt-1 protein in target artery was detected by western blotting. The plaque area (PA), plaque circumference (PC), and maximum plaque thickness (MPT) were measured via HE staining. Degree of intra-plaque angiogenesis was evaluated by CD34+ cells immunohistochemistry. As results, we observed that pEGFP-N1-sFlt-1 transfection suppressed the HUVECs proliferation and ability of tube formation, against the effect of VEGF. We obtained higher local expression of sFlt-1 protein in Group APsFlt-1 than that in other groups (P < 0.05). PA, PC, and MPT of plaque in group APsFlt-1 were significantly decreased when compared with other groups (P < 0.05). Amount of annulations surrounded by CD34-positive cells was significantly decreased in pEGFP-N1-sFlt-1 transfection group, which represented decreased level of intra-plaque neovessels formation. The present study confirmed that local gene delivery of sFlt-1 can suppress plaque formation, as one of possible mechanisms, via inhibitive effect on intra atherosclerotic plaque angiogenesis, which hints at the clinical utility of sFlt-1 in atherosclerosis therapy.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Virmani R, Kolodgie FD, Burke AP, Finn AV, Gold HK, Tulenko TN, Wrenn SP, Narula J (2005) Atherosclerotic plaque progression and vulnerability to rupture: angiogenesis as a source of intraplaque hemorrhage. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25:2054–2061
Sluimer JC, Daemen MJ (2009) Novel concepts in atherogenesis: angiogenesis and hypoxia in atherosclerosis. J Pathol 218:7–29
Burchardt P, Nowak W, Gozdzicka-Jozefiak A, Link R, Grotowski T, Wisniecka A, Siminiak T (2009) Presence of irregularity in region between −1115 and −784 nt in P1 promoter of insulin-like growth factor-1 gene may indicate beneficial effect on coronary arteries in a group of patients with stable angina: preliminary data. Heart Vessels 24:254–259
Petrovan RJ, Kaplan CD, Reisfeld RA, Curtiss LK (2007) DNA vaccination against VEGF receptor 2 reduces atherosclerosis in LDL receptor-deficient mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27:1095–1100
Holm PW, Slart RH, Zeebregts CJ, Hillebrands JL, Tio RA (2009) Atherosclerotic plaque development and instability: a dual role for VEGF. Ann Med 41:257–264
Eubank TD, Roberts R, Galloway M, Wang Y, Cohn DE, Marsh CB (2004) GM-CSF induces expression of soluble VEGF receptor-1 from human monocytes and inhibits angiogenesis in mice. Immunity 21:831–842
Ramachandra S, D’Souza SS, Gururaj AE, Shaila MS, Salimath BP (2009) Paracrine action of sFlt-1 secreted by stably-transfected Ehrlich ascites tumor cells and therapy using sFlt-1 inhibits ascites tumor growth in vivo. J Gene Med 11:422–434
Arat S, Gibbons J, Rzucidlo SJ, Respess DS, Tumlin M, Stice SL (2002) In vitro development of bovine nuclear transfer embryos from transgenic clonal lines of adult and fetal fibroblast cells of the same genotype. Biol Reprod 66:1768–1774
Daly C, Pasnikowski E, Burova E, Wong V, Aldrich TH, Griffiths J, Ioffe E, Daly TJ, Fandl JP, Papadopoulos N, McDonald DM, Thurston G, Yancopoulos GD, Rudge JS (2006) Angiopoietin-2 functions as an autocrine protective factor in stressed endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:15491–15496
Lovren F, Pan Y, Quan A, Teoh H, Wang G, Shukla PC, Levitt KS, Oudit GY, Al-Omran M, Stewart DJ, Slutsky AS, Peterson MD, Backx PH, Penninger JM, Verma S (2008) Angiotensin converting enzyme-2 confers endothelial protection and attenuates atherosclerosis. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 295:H1377–H1384
Celletti FL, Hilfiker PR, Ghafouri P, Dake MD (2001) Effect of human recombinant vascular endothelial growth factor165 on progression of atherosclerotic plaque. J Am Coll Cardiol 37:2126–2130
Fleiner M, Kummer M, Mirlacher M, Sauter G, Cathomas G, Krapf R, Biedermann BC (2004) Arterial angiogenesis and inflammation in vulnerable patients: early and late signs of symptomatic atherosclerosis. Circulation 110:2843–2850
Dunmore BJ, McCarthy MJ, Naylor AR, Brindle NP (2007) Carotid plaque instability and ischemic symptoms are linked to immaturity of microvessels within plaques. J Vasc Surg 45:155–159
Skålén K, Gustafsson M, Rydberg EK, Hultén LM, Wiklund O, Innerarity TL, Borén J (2002) Subendothelial retention of atherogenic lipoproteins in early atherosclerosis. Nature 417:750–754
Sluimer JC, Kolodgie FD, Bijnens AP, Maxfield K, Pacheco E, Kutys B, Duimel H, Frederik PM, van Hinsbergh VW, Virmani R, Daemen MJ (2009) Thin-walled microvessels in human coronary atherosclerotic plaques show incomplete endothelial junctions relevance of compromised structural integrity for intraplaque microvascular leakage. J Am Coll Cardiol 53:1517–1527
Doyle B, Caplice N (2007) Plaque angiogenesis and antiangiogenic therapy for atherosclerosis. J Am Coll Cardiol 49:2073–2080
Naldini A, Carraro F (2005) Role of inflammatory mediators in angiogenesis. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy 4:3–8
Gössl M, Beighley PE, Malyar NM, Ritman EL (2004) Role of vasa vasorum in transendothelial solute transport in the coronary vessel wall: a study with cryostatic micro-CT. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 287:H2346–H2351
De Haro J, Acin F, Lopez-Quintana A, Florez A, Martinez-Aguilar E, Varela C (2009) Meta-analysis of randomized, controlled clinical trials in angiogenesis: gene and cell therapy in peripheral arterial disease. Heart Vessels 24:321–328
Chaturvedi S, Yadav JS (2006) The role of antiplatelet therapy in carotid stenting for ischemic stroke prevention. Stroke 37:1572–1577
Higo T, Ueda Y, Oyabu J, Okada K, Nishio M, Hirata A, Kashiwase K, Ogasawara N, Hirotani S, Kodama K (2009) Atherosclerotic and thrombogenic neointima formed over sirolimus drug-eluting stent: an angioscopic study. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2:616–624
Zhao Q, Egashira K, Inoue S, Usui M, Kitamoto S, Ni W, Ishibashi M, Hiasa Ki K, Ichiki T, Shibuya M, Takeshita A (2002) Vascular endothelial growth factor is necessary in the development of arteriosclerosis by recruiting/activating monocytes in a rat model of long-term inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis. Circulation 105:1110–1115
Belgore F, Blann A, Neil D, Ahmed AS, Lip GY (2004) Localisation of members of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) family and their receptors in human atherosclerotic arteries. J Clin Pathol 57:266–272
Inoue M, Itoh H, Ueda M, Naruko T, Kojima A, Komatsu R, Doi K, Ogawa Y, Tamura N, Takaya K, Igaki T, Yamashita J, Chun TH, Masatsugu K, Becker AE, Nakao K (1998) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression in human coronary atherosclerotic lesions: possible pathophysiological significance of VEGF in progression of atherosclerosis. Circulation 98:2108–2116
Moulton KS (2002) Plaque angiogenesis: its functions and regulation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 67:471–482
Ambati BK, Nozaki M, Singh N, Takeda A, Jani PD, Suthar T, Albuquerque RJ, Richter E, Sakurai E, Newcomb MT, Kleinman ME, Caldwell RB, Lin Q, Ogura Y, Orecchia A, Samuelson DA, Agnew DW, St Leger J, Green WR, Mahasreshti PJ, Curiel DT, Kwan D, Marsh H, Ikeda S, Leiper LJ, Collinson JM, Bogdanovich S, Khurana TS, Shibuya M, Baldwin ME, Ferrara N, Gerber HP, De Falco S, Witta J, Baffi JZ, Raisler BJ, Ambati J (2006) Corneal avascularity is due to soluble VEGF receptor-1. Nature 443:993–997
Ponticelli S, Marasco D, Tarallo V, Albuquerque RJ, Mitola S, Takeda A, Stassen JM, Presta M, Ambati J, Ruvo M, De Falco S (2008) Modulation of angiogenesis by a tetrameric tripeptide that antagonizes vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1. J Biol Chem 283:34250–34259
Malecki M, Trembacz H, Szaniawska B, Przybyszewska M, Janik P (2005) Vascular endothelial growth factor and soluble FLT-1 receptor interactions and biological implications. Oncol Rep 14:1565–1569
Takahashi H, Shibuya M (2005) The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)/VEGF receptor system and its role under physiological and pathological conditions. Clin Sci (Lond) 109:227–241
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support awarded by National Key Technology R&D Program (No.2008BA168B00) and support from Health Department of Jiangxi Province Government, P.R. China. We thank for the advices in manuscript writing given by Dr. Shuhong Li from Toronto General Hospital (Ontario, Canada).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Zhou, Y., He, L. et al. Gene delivery of soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 (sFlt-1) inhibits intra-plaque angiogenesis and suppresses development of atherosclerotic plaque. Clin Exp Med 11, 113–121 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-010-0112-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-010-0112-7