Abstract
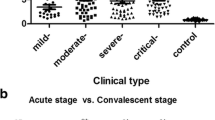
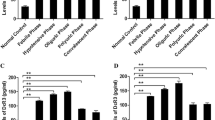
β3 integrin has been identified as a cellular receptor for Hantaan virus which causes hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS). As one of the ligands of β3 integrin, vitronectin (VN) may be altered in HFRS. In this study, changes of serum VN levels were determined in 112 patients with HFRS and 30 age- and sex-matched healthy controls by quantitative sandwich enzyme immunoassay. The levels of serum VN were analyzed in patients at various phases of HFRS and with different severity of clinical types. Serum VN levels in patients with HFRS, at all clinical phases except the convalescent phase, were significantly decreased compared with those in the controls (P < 0.01). The serum levels of VN decreased at febrile phase, maintained at the lowest status during hypotensive and oliguric phases, started to increase from polyuric phase and reached almost normal condition till convalescent phase. The levels of serum VN between patients with milder and more severe clinical types showed no significant difference at each phase (P > 0.05). These results suggest that VN level was altered during the course of HFRS and chronological changes of serum levels of VN may correlate with the evolution of the disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee HW (1982) Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS). Scand J Infect Dis 36:S82–S85
World Health Organization (1983) Haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome: memorandum from a WHO meeting. Bull WHO 61:269–275
Faulde M, Sobe D, Kimmig P, Scharninghausen J (2000) Renal failure and hantavirus infection in Europe. Nephrol Dial Transplant 15:751–753
Cosgriff TM (1991) Mechanisms of disease in Hantavirus infection: pathophysiology of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. Rev Infect Dis 13:97–107
Schmaljohn C, Hjelle B (1997) Hantaviruses: a global disease problem. Emerg Infect Dis 3:95–104
Reynolds LE, Wyder L, Lively JC et al (2002) Enhanced pathological angiogenesis in mice lacking beta3 integrin or beta3 and beta5 integrins. Nat Med 8:27–34
Martinez-Lemus LA, Wu X, Wilson E et al (2003) Integrins as unique receptors for vascular control. J Vasc Res 40:211–233
Sonnenberg A (1993) Integrin and their ligands. Curr Top Microbiol Immun 184:7–35
Gavrilovskaya IN, Brown EJ, Ginsberg MH, Mackow ER (1999) Cellular entry of hantaviruses which cause hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome is mediated by beta3 integrins. J Virol 73:3951–3959
Geimonen E, Neff S, Raymond T, Kocer SS, Gavrilovskaya IN, Mackow ER (2002) Pathogenic and nonpathogenic hantaviruses differentially regulate endothelial cell responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:13837–13842
Mackow ER, Gavrilovskaya IN (2001) Cellular receptors and hantavirus pathogenesis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 256:91–115
Liu Z, Gao M, Han Q, Fang J, Zhao Q, Zhang N (2008) Intensity of platelet β3 integrin in patients with hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome and its correlation with disease severity. Viral Immunol 21:255–261
Liang M, Li D, Xiao SY, Hang C, Rossi CA, Schmaljohn CS (1994) Antigenic and molecular characterization of hantavirus isolates from China. Virus Res 31:219–233
Liu Z, Zhao Q, Han Q, Gao M, Zhang N (2008) Serum thrombospondin-1 is altered in patients with hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. J Med Virol 80:1799–1803
Lee HW, Lee PW, Johnson KM (1978) Isolation of the etiologic agent of Korean Hemorrhagic fever. J Infect Dis 137:298–308
Seiffert D, Schleef RR (1996) Two functionally distinct pools of vitronectin (Vn) in the blood circulation: identification of a heparin-binding competent population of Vn within platelet alpha-granules. Blood 88:552–560
Takala A, Lähdevirta J, Jansson SE et al (2000) Systemic inflammation in hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome correlates with hypotension and thrombocytopenia but not with renal injury. J Infect Dis 181:1964–1970
Høgåsen K, Mollnes TE, Brandtzaeg P (1994) Low levels of vitronectin and clusterin in acute meningococcal disease are closely associated with formation of the terminal-complement complex and the vitronectin-thrombin-antithrombin complex. Infect Immun 62:4874–4880
Korc-Grodzicki B, Tauber-Finkelstein M, Chain D, Shaltiel S (1988) Vitronectin is phosphorylated by a cAMP-dependent protein kinase released by activation of human platelets with thrombin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 157:1131–1138
Preissner KT, Anders E, Grulich-Henn J, Müller-Berghaus G (1988) Attachment of cultured human endothelial cells is promoted by specific association with S protein (vitronectin) as well as with the ternary S protein-thrombin-antithrombin III complex. Blood 71:1581–1589
de Boer HC, Preissner KT, Bouma BN, de Groot PG (1992) Binding of vitronectin-thrombin-antithrombin III complex to human endothelial cells is mediated by the heparin binding site of vitronectin. J Biol Chem 267:2264–2268
Sirotin BZ, Fedorchenko YL (1996) Visualization of microcirculatory disorders in haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. Nephrol Dial Transplant 11:721–722
Hjelle B, Jenison SA, Goade DE, Green WB, Feddersen RM, Scott AA (1995) Hantaviruses: clinical, microbiologic, and epidemiologic aspects. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 32:469–508
Reheman A, Gross P, Yang H et al (2005) Vitronectin stabilizes thrombi and vessel occlusion but plays a dual role in platelet aggregation. J Thromb Haemost 3:875–883
Conlan MG, Tomasini BR, Schultz RL, Mosher DF (1988) Plasma vitronectin polymorphism in normal subjects and patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation. Blood 72:185–190
Kemkes-Matthes B, Preissner KT, Langenscheidt F, Matthes KJ, Müller-Berghaus G (1987) S protein/vitronectin in chronic liver diseases: correlations with serum cholinesterase, coagulation factor X and complement component C3. Eur J Haematol 39:161–165
Kobayashi J, Yamada S, Kawasaki H (1994) Distribution of vitronectin in plasma and liver tissue: relationship to chronic liver disease. Hepatology 20:1412–1417
Inuzuka S, Ueno T, Torimura T et al (1992) Vitronectin in liver disorders: biochemical and immunohistochemical studies. Hepatology 15:629–636
Yamada S, Suou T, Kawasaki H (1997) Plasma vitronectin concentrations in patients with chronic hepatitis C treated with interferon alpha. Clin Chim Acta 261:81–90
Sun HC, Deng PF, Wang CJ et al (1997) Liver involvement in epidemic haemorrhagic fever: in situ hybridization, immunohistochemical and pathological studies. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 12:540–546
Elisaf M, Stefanaki S, Repanti M, Korakis H, Tsianos E, Siamopoulos KC (1993) Liver involvement in hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. J Clin Gastroenterol 17:33–37
Morioka S, Makino H, Shikata K, Ota Z (1994) Changes in plasma concentrations of vitronectin in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Acta Med Okayama 48:137–142
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of the People’s Republic of China (No. 30271176), and Provincial Science and Technological Program of Shaanxi Province, China (2004K172G8). We are indebted to Miss Jian Chen in the Department of Medical Affairs, First Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Xi’an Jiaotong University, for her helpful work in the manuscript preparation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest related to the publication of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Han, Q., Zhang, L. et al. Low levels of serum vitronectin associated with clinical phases in patients with hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. Clin Exp Med 9, 297–301 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-009-0050-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-009-0050-4