Abstract
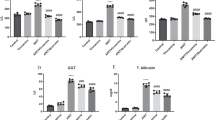
Edaravone (EDA), a newly synthesized free radical scavenger, has shown excellent results in the treatment of stroke. An overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS) causing oxidative DNA damage has been accounted as a major factor causing liver injury and fibrosis. Therefore, we examined its effect of EDA in rat model of liver cirrhosis induced by dimethylnitrosamine (DMN). Ten rats (DMN-group) were injected intraperitoneally with DMN (10 μg/g body weight) alone and another ten rats (EDA-group) were injected intraperitoneally with EDA (10 mg/kg body weight) 2 h after being injected with DMN. Both groups underwent their injection regimen three times a week for 4 weeks, after which the rats were sacrificed and their liver tissue sections were stained with Azan–Mallory for quantitative analyses of fibrosis development, using soft imaging and a previously published scoring system. Additionally, these sections were immunohistochemically stained using an antibody against α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA). The total-bililubin in the EDA-group was found to be lower than that in the DMN-group. Quantitive analysis of liver fibrosis showed that the fibrotic area of the EDA-group was significantly smaller than that of the DMN-group. Additionally, the number of α-SMA positive cells in the EDA-group were significantly lower than that in the DMN-group. This study showed that EDA reduces liver fibrosis in a rat of cirrhosis induced by DMN. These data suggest that the reduction of liver fibrosis by EDA may be induced by the suppression of activated hepatic stellate cells.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Olaso E, Friedman SL (1998) Molecular regulation of hepatic fibrogenesis. J Hepatol 29:836–847
Romero MJ, Bosch-Morell F, Romero B, Rodrigo JM, Serra MA, Romero J (1998) Serum malondialdehyde: posible use for the clinical management of chronic hepatitis C patients. Free Rad Biol Med 25:993–997
Higueras V, Raya A, Rodrigo JM, Serra MA, Roma J, Romero FJ (1994) Interferon decreases serum lipid peroxidation products of hepatitis C patients. Free Rad Biol Med 16:131–133
James OFL, Day CP (1998) Non-alcholic steatohepatitis (NASH): a disease of emerging identity and importance. J Hepatol 29:495–501
Sanyal AJ, Campbell-Sargent C, Mirshahi F, Rizzo WB, Contos MJ, Sterling RK, Luketic VA, Shiffman ML, Clore JN (2001) Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: association of insulin resistance and mitochondrial abnormalities. Gastroenterology 120:1183–1192
Cheeseman KH, Saalter TF (1993) An introduction to free radical biochemistry. Br Med Bull 49:481–493
Watanabe T, Yuki S, Egawa M, Nishi H (1994) Protective effects of MCI–186 on cerebral ischemia: possible involvement of free radical scavenging and antioxidant actions. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 268:1597–1604
Watanabe T, Morita I, Nishi H, Murota S (1989) Preventive effect of MCI-186 on 15-PETE induced vascular endothelial cell injury in vitro. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 33:81–87
Abe K, Yuki S, Kogure K (1988) Strong attenuation of ischemic and postischemic brain edema in rats by a novel free radical scavenger. Stroke 19:480–485
Nishi H, Watanabe T, Sakurai H, Yuki S, Ishibashi A (1989) Effect of MCI-186 on brain edema in rats. Stroke 20:1236–1240
Oishi T, Itoh Y, Nishibori M, Watanabe T, Nishi H, Saeki K (1989) Effect of MCI-186 on ischemia-induced changes in monoamine metabolism in rat brain. Stroke 20:1557–1564
Minhaz U, Tanaka M, Tswukamoto H, Watanabe K, Koide S, Shohtsu A, Nakazawa H (1996) Effect of MCI-186 on postischemic reperfusion injury in isolated rat heart. Free Radic Res 24:361–367
Ninomiya M, Shimada M, Harada N, Shiotani S, Hirosige S, Soejima Y, Suehiro T, Sugimachi K (2002) Beneficial effect of MCI-186 on hepatic warm ischemia-reperfusion in the rat. Transplantation 74:1470–1476
Okatani Y, Wakatsuki A, Enzan H, Miyahara Y (2003) Edaravone protects against ischemia/reperfusion-induced oxidative damage to mitochondria in rat liver. Eur j Pharm 465:163–170
Kono H, Asakawa M, Fujii H, Maki A, Amemiya H, Yamamoto M, Matsuda M, Matsumoto Y (2003) Edaravone, a novel free radical scavenger, prevents liver injury and mortality in rats administered endotoxin. J Pharm Experi Ther 307:74–82
Tada S, Nakamoto N, Kameyama K, Tsunematsu S, Kumagai N, Saito H, Ishii H (2003) Clinical usefulness of edaravone for acute injury. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 18:851–857
Jenkins SA, Grandison A, Bazter JN, Day DW, Taylor I, Shields R (1985) A dimethylnitrosamine-induced model of cirrhosis and portal hypertension in the rat. J Hepatol 1:489–499
Jezequel AM, Mancini R, Rinaldesi ML, Macarri G, Venturini C, Orlandi F (1987) A morphological study of the early stages of hepatic fibrosis induced by low doses of dimethylnitrosamine in the rat. J Hepatol 5:174–181
Ishak K, Baptista A, Bianchi L, Callea F, De Groote J, Gudat F, Denk H, Desmet V, Korb G, MacSween RN et al (1995) Histological grading and staging of chronic hepatitis. J Hepatol 22:696–699
Bedossa P, Houglum K, Trautwein C, Holstege A, Chojkier M (1994) Stimulation of collagen α(I) gene expression is associated with lipid peroxidation in hepatocellular injury: a link to tissue fibrosis. Hepatology 19:1262–1271
Parola M, Robino G (2001) Oxidative stress-related molecules and liver fibrosis. J Hepatol 35:297–306
Poli G, Parola M (1997) Oxidative damage and fibrogenesis. Free Radic Biol Med 22:287–305
Yamamoto Y, Kuwahara T, Watanabe K (1996) Antioxidation activity of 3-methyl-1-phenyl-pyrazolin-5-one. Redox Rep 2:333–338
Friedman SL (2000) Molecular regulation of hepatic fibrosis: an integrated cellular response to injury. J Biol Chem 275:2247–2250
Bissell DM, Arenson DM, Maher JJ, Roll FJ (1987) Support of cultured hepatocytes by a laminin-rich gel: evidence for functionally significant subendothelial matrix in normal rat liver. J Clin Invest 79:801–812
Maher JJ, Bissell DM, Friedman SL, Roll FJ (1988) Collagen measured in primary cultures of normal rat hepatocytes derives from lipocytes within the monolayer. J Clin Invest 82:450–459
Svegliati Baroni G, D’Ambrosio L, Ferreti G, Casini A, Di Sario A, Salzano JR, Ridolfi F, Saccomanno S, Jezequel AM, Benedetti A (1998) Fibrogenic effect of oxidative stress on rat hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology 27:720–726
Svegliati Baroni G, Di Sario A, Casini A, Ferreti G, D’Ambrosio L, Ridolfi F, Bolognini L, Salzano R, Orlandi F, Benedeti A (1999) The Na+/H+ exchanger modulates the fibrogenic effect of oxidative stress in hepatic stellate cells. J Hepatol 30:868–875
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest related to the publication of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanaka, H., Ueda, H., Fukuchi, H. et al. Antifibrotic effect of edaravone in rat liver cirrhosis induced by dimethylnitrosamine. Clin Exp Med 9, 229–233 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-009-0034-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-009-0034-4