Abstract
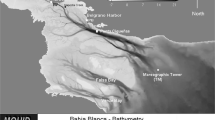
A hydrodynamic model of the Bay of Toulon has been developed for use as a post-accident radionuclide dispersion simulation tool. Located in a Mediterranean urban area, the Bay of Toulon is separated into two basins by a 1.4-km long seawall. The Little Bay is semi-enclosed and connected to the Large Bay by a fairway channel. This channel is the site of significant water mass exchange as a result of both wind-driven currents and bathymetry. It is therefore a focal point for marine contamination. As part of the model calibration and validation process, the first step consisted of studying the water mass exchange between the two basins. An Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler was moored in the channel for 1 year. The present study analyses in situ data to determine the current intensity and direction, and also to better understand the vertical current profile, which is highly correlated with meteorological forcing. Comparisons of model-generated and measured data are presented, and various atmospheric forcing datasets are used to enhance computed results. It appears that accurate meteorological forcing data is needed to enhance the accuracy of the hydrodynamic model. This channel is an important location for water mass renewal in the Bay of Toulon, and model results are used to quantify these exchanges. The mean calculated annual water exchange time is approximately 3.4 days. However, this duration is strongly wind dependent and shortens during windy winter months. It ranges from 1.5 days during strong wind periods to 7.5 days during calm weather. Residence time values calculated through tracer dispersion modelling after release at the back of the Little Bay are found to be comparable to the mean exchange time values, especially for windy conditions.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albérola C, Rousseau S, Millot C, Astraldi M, Font J, Garcia-Lafuente J, Gasparini GP, Send U, Vangriesheim A (1995) Tidal currents in the Western Mediterranean Sea. Oceanol Acta 18:273–284
André G, Garreau P, Fraunié P (2009) Mesoscale slope current variability in the Gulf of Lions. Interpretation of in-situ measurements using a three-dimensional model. Cont Shelf Res 29:407–423
Delhez EJM, Heemink AW, Deleersnijder E (2004) Residence time in a semi-enclosed domain from the solution of an adjoint problem. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 61:691–702
Duffa C, Dufois F, Coudray S (2011) An operational model to simulate post-accidental radionuclide transfers in Toulon marine area: preliminary development. Ocean Dyn 61(11):1811–1821
Estournel C, Bosc E, Bocquet M, Ulses C, Marsaleix P, Winiarek V, Osvath I, Nguyen C, Duhaut T, Lyard F, Michaud H, Auclair F (2012) Assessment of the amount of cesium-137 released into the Pacific Ocean after the Fukushima accident and analysis of its dispersion in Japanese coastal waters. J Geophys Res: Oceans 117(C11):C11014
Gaspar P, Gregoris Y, Lefevre JM (1990) A simple eddy-kinetic-energy model for simulations of the oceanic vertical mixing: tests at station Papa and long-term upper ocean study site. J Geophys Res 95:16179–16193
Geernaert GL, Larsen SE, Hansen F (1987) Measurements of the wind stress, heat flux, and turbulence intensity during storm conditions over the North Sea. J Geophys Res 92:13127–13139
Holzer M, Hall TM (2000) Transit-time and tracer-age distributions in geophysical flows. J Atmos Sci 57(21):3539–3558
Jouon A, Douillet P, Ouillon S, Fraunié P (2006) Calculations of hydrodynamic time parameters in a semi-opened coastal zone using a 3D hydrodynamic model. Cont Shelf Res 26:1395–1415
Large WG, Pond S (1981) Open ocean momentum flux measurement in moderate to strong winds. J Phys Oceanogr 11:324–336
Lazure P, Dumas F (2008) An external-internal mode coupling for a 3D hydrodynamical model for applications at regional scale (MARS). Adv Water Resour 31(2):233–250
Millot C, Broyard R, Metais O, Tine J (1981) Les oscillations propres de la rade de Toulon. Oceanol Acta 4(3):259–262
Monte L, Boyer P, Brittain JE, Goutal N, Heling R, Kryshev A, Kryshev I, Laptev G, Luck M, Periañez R, Siclet FO, Zheleznyak M (2008) Testing models for predicting the behaviour of radionuclides in aquatic systems. Appl Radiat Isot 66:1736–1740
Monte L, Periañez R, Boyer P, Smith JT, Brittain JE (2009) The role of physical processes controlling the behaviour of radionuclide contaminants in the aquatic environment: a review of state-of-the-art modelling approaches. J Environ Radioact 100(9):779–784
Nicolau R, Lucas Y, Merdy P, Raynaud M (2012) Base flow and stormwater net fluxes of carbon and trace metals to the Mediterranean Sea by an urbanized small river. Water Res 46(20):6625–6637
Nicolle A, Garreau P, Liorzou B (2009) Modelling for anchovy recruitment studies in the Gulf of Lions (western Mediterranean Sea). Ocean Dyn 59(6):953–968
Pairaud IL, Gatti J, Bensoussan N, Verney R, Garreau P (2011) Hydrology and circulation in a coastal area off Marseille: validation of a nested 3D model with observations. J Mar Syst 88:20–33
Periañez R (2005) Modelling the dispersion of radionuclides by a river plume: Application to the Rhone river. Cont Shelf Res 25:1583–1603
Periañez R, Hierro A, Bolívarb JP, Vaca F (2012) The geochemical behavior of natural radionuclides in coastal waters: a modeling study for the Huelva estuary. J Mar Syst. doi:10.1016/j.jmarsys.2012.08.001
Pirovano G, Coll I, Bedogni M, Alessandrini S, Costa MP, Gabusi V, Lasry F, Menut L, Vautard R (2007) On the influence of meteorological input on photochemical modelling of a severe episode over a coastal area. Atmos Environ Harbours Air Qual 41(30):6445–6464
Schaeffer A (2011) Impact du vent sur la circulation hydrodynamique dans le Golfe du Lion : modélisation haute résolution. Ph.D. thesis. Université Sud Toulon Var 245
Smagorinsky J (1963) General circulation experiments with the primitive equation, I. The basic experiment. Mon Weather Rev 91:99–164
Smith SD, Banke EG (1975) Variation of the sea surface drag coefficient with wind speed. Q J Roy Meteorol Soc 101:665–673
Tessier E, Garnier C, Mullot JU, Lenoble V, Arnaud M, Raynaud M, Mounier S (2011) Study of the spatial and historical distribution of sediment inorganic contamination in the. Toulon bay (France) Mar Pollut Bull 62(10):2075–2086
Tiné J, Martano G, Cabilic J, Jeudy de Grissac, A (1981) Hydrodynamisme en Rade Abri de Toulon. Ministère de la Défense—Marine Nationale
Acknowledgements
IRSN (Institut de Radioprotection et de Sûreté Nucléaire) and Region PACA (Provence Alpes Côte d’Azur) are acknowledged for their financial support for the Ph-D thesis of Christiane Dufresne.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Martin Verlaan
This article is part of the Topical Collection on the 16th biennial workshop of the Joint Numerical Sea Modelling Group (JONSMOD) in Brest, France 21-23 May 2012
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dufresne, C., Duffa, C. & Rey, V. Wind-forced circulation model and water exchanges through the channel in the Bay of Toulon. Ocean Dynamics 64, 209–224 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10236-013-0676-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10236-013-0676-3