Abstract
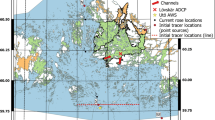
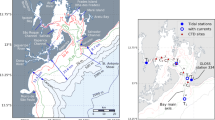
A hydrodynamic model of the Venice Lagoon and the Adriatic Sea has been developed in order to study the exchanges at the inlets of the Venice Lagoon, a complex morphological area connecting the sea and the lagoon. The model solves the shallow water equations on a spatial domain discretized by a staggered finite element grid. The grid represents the Adriatic Sea and the Venice Lagoon with different spatial resolutions varying from 30 m for the smallest channels of the lagoon to 30 km for the inner areas of the central Adriatic Sea. Data from more than ten tide gauges displaced in the Adriatic Sea have been used in the calibration of the simulated water levels. After the calibration, the tidal wave propagation in the North Adriatic and in the Venice Lagoon is well reproduced by the model. To validate the model results, empirical flux data measured by acoustic Doppler current profiler probes installed inside the inlets of Lido and Malamocco have been used and the exchanges through the three inlets of the Venice Lagoon have been analyzed. The comparison between modeled and measured fluxes at the inlets outlines the efficiency of the model to reproduce both tide- and wind-induced water exchanges between the sea and the lagoon. Even in complex areas, where highly varying resolution is needed, the model is suitable for the simulation of the dominating physical processes.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bajo M, Zampato L, Umgiesser G, Cucco A, Canestrelli P (2007) A finite element operational model for the storm surge prediction in Venice. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 75:236–249
Bergamasco A, Carniel S, Pastres R, Pecenik G (1998) A unified approach to the modelling of the Venice Lagoon–Adriatic Sea ecosystem. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 46:483–492
Bianchi F, Ravagnan E, Acri F, Bernardi-Aubry F, Boldrin A, Camatti E, Cassin D, Turchetto M (2004) Variability and fluxes of hydrology, nutrients and particulate matter between the Venice Lagoon and the Adriatic Sea. Preliminary results (years 2001–2002). J Mar Syst 51(v–vi):49–64
Blumberg AF, Mellor GL (1987) A description of a coastal ocean circulation model. In: Heaps NS (ed) Three dimensional ocean model. American Geophysical Union, Washington D.C., pp 1–16
Cavaleri L, Bertotti L (1996) In search for the correct wind and wave fields in a minor basin. Mon Weather Rev 125(8):1964–1975
Cucco A, Umgiesser G (2005) Modeling the tide induced water exchanges between the Venice Lagoon and the Adriatic Sea. In: Scientific research and safeguarding of Venice. Proceedings of the annual meeting of the CORILA research program, 2003 results, vol III. Venice, Italy, pp 385–402
Cushman-Roisin B, Naimie CE (2002) A 3D-finite element model for the Adriatic tides. J Mar Syst 37(4):279–297
Ferla M, Cordella M, Michielli L, Rusconi A (2007) Long-term variation on the sea level and the tidal regime in the lagoon of Venice. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 75:214–222
Foreman MGG (1978) Manual for tidal currents analysis and prediction. In: Pacific marine science report, vol 78, no 6. Institute of Ocean Sciences, Patricia Bay, p 57
Foreman MGG (1996) Manual for tidal heights analysis and prediction. Pac Mar Sci Rep 77(10):58
Gačić M, Kovačević V, Mazzoldi A, Paduan JD, Arena F, Mosquera IM, Gelsi G, Arcari G (2002) Measuring water exchange between the Venetian Lagoon and the open sea. EOS, Trans Am Geophys Union 83(20):217–222
Gačić M, Mosquera IM, Kovačević V, Mazzoldi A, Cardin V, Arena F, Gelsi G (2004) Temporal variations of water flow between the Venetian Lagoon and the open sea. J Mar Syst 51:33–47
Goldmann A, Rabagliati R, Sguazzero P (1975) Characteristics of the tidal wave in the lagoon of Venice. Technical Report 47, IBM, Venice Scientific Center
Melaku Canu D, Umgiesser G, Solidoro C (2001) Short term simulations under winter conditions in the lagoon of Venice: a contribution to the environmental impact assessment of a temporary closure of the inlets. Ecol Model 138(1–3):215–230
Mellor GL (1991) An equation of state for numerical models of ocean and estuaries. J Atmos Ocean Technol 8:609–611
Mosetti F (1987) Distibuzione delle maree nei mari italiani. Boll Oceanol Teor Appl 5(1):65–72
Orlić M, Gačić M, Violette PEL (1992) The currents and circulation of the Adriatic Sea. Oceanol Acta 15:109–124
Polli S (1960) La propagazione delle maree nellÁlto adriatico. Publications of the Istituto Sperimentale Talassografico—Trieste 370
Polli S (1961) La propagazione delle maree nel golfo di Venezia. Publications of the Istituto Sperimentale Talassografico—Trieste 385
Tomasin A (2005) The software Polifemo for tidal analysis. Technical Note 202, ISMAR-CNR Institute of Marine Science Venice
Tomasin A, Pirazzoli PA (1999) The seiches in the Adriatic Sea. Atti dell’Istituto Veneto di Scienze, Lettere ed Arti CLVII, pp 299–316
Umgiesser G (2000) Modeling residual currents in the Venice Lagoon. In: Yanagi T (ed) Interaction between estuaries, coastal seas and shelf seas. Terra Scientific Publishing Company (TERRAPUB), Tokyo, pp 107–124
Umgiesser G, Bergamasco A (1993) A staggered grid finite element model of the Venice Lagoon. In: Morgan K, Offiate E, Periaux J, Peraire J, Zienkiewicz OC (eds) Finite elements in fluids, proceedings of the VIII international conference, 20–23 September 1993, Barcelona. Pineridge Press, Barcelona, pp 659–668
Umgiesser G, Bergamasco A (1995) Outline of a primitive equation finite element model. In: Rapporto e Studi, vol XII. Istituto Veneto di Scienze, Lettere ed Arti, Venice, Italy, pp 291–320
Umgiesser G, Bergamasco A (1998) The spreading of the Po plume and the Italian coastal current. In: Dronkers J, Scheffers M (eds) Physics of estuaries and coastal seas. Rotterdam, pp 267–275
Umgiesser G, Canu DM, Cucco A, Solidoro C (2004) A finite element model for the Venice Lagoon. Development, set-up, calibration and validation. J Mar Syst 51:123–145
Zampato L, Canestrelli P, Tomasin A, Zecchetto S (2005) A comparison between modelled and observed atmospheric fields over the Adriatic and Tyrrhenian seas. Technical Report 263, ISMAR-CNR, Venezia, Italy
Zampato L, Umgiesser G, Zecchetto S (2007) Sea level forecasting in Venice through high resolution meteorological fields. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 75:223–235
Acknowledgements
The authors want to thank the CMCC Project for the financial support. This work has been also partially funded by the CORILA projects 3.2 Hydrodynamics and morphology of the Venice Lagoon and 3.5 Quantity and quality of exchanges between lagoon and sea which also provided the necessary flux data. The wind dataset of the CNR Platform has been provided by the Venice Municipality. Special thanks to Professor Tomasin for the precious help in dealing with the subject of tides and harmonic analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Pierre Lermusiaux
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bellafiore, D., Umgiesser, G. & Cucco, A. Modeling the water exchanges between the Venice Lagoon and the Adriatic Sea. Ocean Dynamics 58, 397–413 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10236-008-0152-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10236-008-0152-7