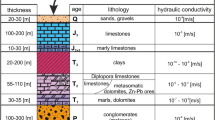
Abstract
Sedimentary phosphorites are being exploited in southern Togo. The ore is processed to high-grade purified commercial phosphorite by wet sieving, using water pumped directly from the sea. The resultant muddy tailings are dumped directly into the sea without any pretreatment. We have separated the solid and liquid phases of the muddy tailings and characterized their metal contents. Leaching tests were conducted with weak acid and saline water to evaluate the solubility and the potential bioavailability of various metals. The results show that the purification process leads to the enrichment of certain metals (Cr, Cu, Ni, V, Zn, Ba, Sr, Fe, and Al) in the tailings due to their association with the clay minerals, whereas Cd, Th, and U are enriched in the purified apatite-rich phase. The leaching tests showed that the solubility of metals generally increases when salinity increases or when pH decreases. Thus, the processing of phosphorites with sea water and the dumping of phosphorite tailings into the sea represent a serious potential risk for the marine ecosystem and for human health through the food chain.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abollino O, Aceto M, Malandrino M, Mentasti E, Sarzanini C, Petrella F (2002) Heavy metals in agricultural soil from Piedmont, Italy: distribution, speciation and chemometric data treatment. Chemosphere 49:545–557
Allan RJ (1995) Impact of mining activities on the terrestrial and aquatic environment. In: Salomons W, Förstner U, Mader P (eds) Heavy metals, problems and solutions. Springer, Berlin, p 412
Altschuler ZS (1980) The geochemistry of trace elements in marine phosphorites, Part I: characteristic abundances and enrichment. In: Bentor YK (ed) Marine phosphorites. Soc of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists Special Publ 575–B, pp 19–30
Bopp F, Biggs RB (1981) Metals in estuarine sediments, factor analysis and its environmental significance. Science 214:441
Cook PJ (1972) Petrology and geochemistry of the phosphorite deposits of Northwest Queensland, Australia. Econ Geol 67:1193–1213
Cook JM, Gardner MJ, Griffiths AH, Jessep MA, Ravenscroft JE, Yates R (1997) The comparability of sample digestion techniques for the determination of metals in sediments. Mar Pollut Bull 34:37–644
Deheyn DD, Gendreau P, Baldwin R, Latz MI (2005) Evidence for enhanced bioavailability of trace elements in the marine ecosystem of Deception Island, a volcano in Antarctica. Mar Environ Res 60:1–33
DIN (Deutsche Industrie Normen) 38414–Teil 4 (1984) Deutsche Einheitsverfahren zur Wasser-, Abwasser- und Schlammuntersuchung, Schlamm und Sediment Gruppe S. Beuth Verlag, Berlin, Germany
Garcı′a-Meza JV, Carrillo-Cha′vez A, Morton-Bermea O (2006) Sequential extractions on mine tailings samples after and before bioassays: implications on the speciation of metals during microbial re-colonization. Environ Geol 49:437–448
Gnandi K, Tobschall HJ (1999a) The pollution of marine sediments by trace elements in the coastal region of Togo caused by dumping of Cd rich phosphorite tailings into the sea. Environ Geol 38(1):13–24
Gnandi K, Tobschall HJ (1999b) Heavy metal release from phosphorite tailings into sea water: a simulated laboratory study. Sci Total Environ 236(1–3):181–190
Gnandi K, Tobschall HJ (2003) The distribution patterns of rare earth elements and uranium in Tertiary off/shore sedimentary phosphorite deposits of Hahotoé and Kpogamé (Togo). J Afr Earth Sci 37:1–10
Gnandi K, Tchangbedji G, Baba G, Killi K, Abbe K (2006) The impact of phosphate mine tailings on the bioaccumulation of heavy metals in marine fish and crustaceans from the coastal zone of Togo. Int J Mine Water Environ 25(1):56–62
Jarvis I, Burnett WC, Nathan J, Almbaydin FSM, Attia AKM, Castro LN, Flicoteau R, Hilmy ME, Husain V, Quitwanah AA, Serjani A, Zanin Y (1994) Phosphorite geochemistry: state-of-the-art and environmental concerns. Ecol Geol Helv 87(3):643–700
Johnson AKC (1987) Le bassin côtier à phosphates du Togo: Thèse de doctorat, université de Dijon. France, unpubl 360 pp
Katz A, Kaplan IR (1981) Heavy metal behavior in coastal sediments of southern California: a critical review and synthesis. Mar Chem 10:261–299
Killinc M, Cotillon P (1977) Le gisement d’Hahotoé/Kpogamé (Terciaire du Sud Togo), exemple de piège sédimentaire à sables phosphatés. Bull BRGM, Section II, 1, pp 43–63
Kunkel H (1990) Über die Cadmiumverteilung in den Phosphoritlagerstätten von Kpogamé/Hahotoé: Dissertation/Universtät/Erlangen, unpubl, 149 p
Luoma SN (1989) Can we determine the biological availability of sediment-bound trace elements? Hydrobiologia 176:379–396
McArthur JM (1990) Fluorine-deficient apatite. Min Mag 54:508–510
McClellan GH (1980) Mineralogy of carbonate fluorapatite. J Geol Soc Lond 137:675–681
McClellan GH, Van Kauwenbergh SJ (1990) Mineralogy of sedimentary apatite. In: Notholt AJG, Jarvis I (eds) Phosphorite research and development. Geol Soc Spec Publ, vol 52, pp 23–31
McConnell GH, Lehr JR (1969) Crystal chemical investigations of natural apatites. Am Mineral 54:1374–1391
Morgan JJ, Stumm W (1995) Chemical processes in the environment, relevance of chemical speciation. In: Merian E (ed) Metals and their compounds in the environment. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 67–103
Nathan Y (1984) The mineralogy and geochemistry of phosphorite. In: Nriagu JO, Moore PB (eds) Phosphate minerals, Chap. 8, Springer, Berlin, pp 275–291
Petit CJ (2006) spéciation et biogéochimie des métaux dans les milieux estuariens (estuaire de l’Escaut). Synthèse bibliographique, Université Libre de Bruxelles, 17 pp
Piper DZ (1994) Seawater as the source of minor elements in black shales, phosphorites and other sedimentary rocks. Chem Geol 114:95–114
Salomons W, Förstner U (1980) Trace metal analysis on polluted sediments. II. Evaluation of environmental impact. Environ Technol Lett 1:506–517
Salomons W, Förstner U (1984) Metals in the hydrocycle. Springer, Berlin, 349 p
Snape I, Scouller RC, Stark SC, Stark J, Riddle MJ, Gore DB (2004) Characterization of the dilute HCl extraction method for the identification of metal contamination in Antarctic marine sediments. Chemosphere 57:491–504
Van Kauwenbergh SJ, McClellan GH (1990) Comparative geology and mineralogy of southern United States and Togo phosphorites. In: Notholt AJG, Jarvis I (eds) Phosphorite research and development. Geological Society Special Publication No. 52, pp 139-155
Wedepohl KH (1991) The composition of the upper earth’s crust and the natural cycles of selected metals. In: Merian E (ed) Metals and their compounds in the environment. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp p1–p10
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express sincere thanks to the Geosciences Institute (Geochemistry Laboratory) of the University of Mainz (Germany) for laboratory facilities and the German Academic Exchange Service (DAAD) for the financial support. The authors acknowledge the critical reading of the manuscript by the referees of the journal and the language improvements made by an anonymous reviewer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gnandi, K., Rezaie Boroon, M.H. & Edorh, P. The Geochemical Characterization of Mine Effluents from the Phosphorite Processing Plant of Kpémé (Southern Togo). Mine Water Environ 28, 65–73 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-008-0058-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-008-0058-0