Abstract
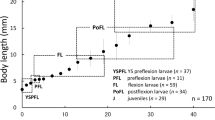
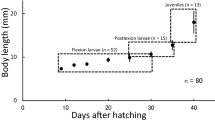
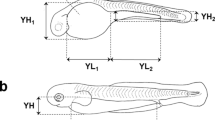
Morphological development in laboratory-reared larval and juvenile Hemibagrus filamentus, and behavioral features observed under rearing conditions are described. Body lengths (BL) of larvae and juveniles were 3.8 ± 0.2 (mean ± SD) mm just after hatching and 11.7 ± 1.6 mm on day 15, reaching 26.5 ± 5.4 mm on day 30 after hatching. Aggregate fin ray numbers (for caudal fin, except for procurrent rays) attained full complements in specimens larger than 12.9 mm BL. A maxillary barbel bud appeared on day 0, and all larvae initiated feeding on day 3 with the development of mandibular barbels and conical teeth. Pectoral fin buds and primordial nostrils were present on day 1. Notochord flexion began on day 3, and the yolk was completely absorbed by day 4. Melanophores were scarce at hatching, but increased with growth to cover almost the entire body except the ventral surface of the head and body. Body proportions became relatively constant in juveniles, excepting maxillary barbel length that continued to increase, reaching over 40% BL. Fish were negatively phototactic from day 1. Cannibalism was observed from day 6, continuing to the juvenile stage.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Silva SS, Nguyen TTT, Abery NW, Amarasinghe US (2006) An evaluation of the role and impacts of alien finfish in Asian inland aquaculture. Aquac Res 37:1–17
Ferraris CJ Jr (2007) Checklist of catfishes, recent and fossil (Osteichthyes: Siluriformes), and catalogue of siluriform primary types. Zootaxa 1418:1–628
Hecht T, Pienaar AG (1993) A review of cannibalism and its implications in fish larviculture. J World Aquac Soc 24:246–261
Hseu JR, Chang HF, Ting YY (2003) Morphometric prediction of cannibalism in larviculture of orange-spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides. Aquaculture 218:203–207
Kendall AW Jr, Ahlstrom EH, Moser HG (1984) Early life history stages of fishes and their characters. In: Moser HG, Richards WJ, Cohen DM, Fahay MP, Kendall AW Jr, Richardson SL (eds) Ontogeny and systematics of fishes, Am Soc Ichthyol Herpetol Spec Publ No 1. Allen Press, Lawrence, pp 11–22
Kohno H (1998) Early life history features influencing larval survival of cultivated tropical finfish. In: De Silva SS (ed) Tropical mariculture, Academic Press, London, pp 71–111
Kottelat M (2001a) Fish of Laos. Ganaratne Offset Ltd, Colombo
Kottelat M (2001b) Freshwater fishes of northern Vietnam. Environment and Social Development Sector Unit, East Asia and Pacific Region, The World Bank, Washington
Leis JM, Trnski T (1989) The larvae of Indo-Pacific shorefishes. NSW University Press, Kensington
Matsumoto S, Morioka S, Kumagai S (2001) Development of African catfish Clarias gariepinus larvae during the transitional phase between endogenous and exogenous energy intake. In: Weyl OLF, Weyl MV (eds) Proceedings of the Lake Malawi fisheries management symposium, Department of Fishery, Lilongwe, pp 227–232
Morioka S, Ito S, Kitamura S, Vongvichith B (2009a) Growth and morphological development of laboratory-reared larval and juvenile climbing perch Anabas testudineus. Ichthyol Res 56:162–171
Morioka S, Sakiyama K, Ito S, Vongvichith B (2009b) Technical report and manual of seed production of the climbing perch Anabas testudineus. JIRCAS working Report No 61, Japan International Research Center for Agricultural Sciences, Tsukuba
Morioka S, Ito S, Kitamura S (2009c) Growth and morphological development of laboratory-reared larval and juvenile snakeskin gourami Trichogaster pectoralis. Ichthyol Res 57:24–31
Morioka S, Sano K, Phommachan P, Vongvichith B (2010) Growth and morphological development of laboratory-reared larval and juvenile Pangasianodon hypophthalmus. Ichthyol Res 57:139–147
Moteki S, Yoseda K, Sahin T, Üstündağ C, Kohno H (2001) Transition from endogenous to exogenous nutritional sources in larval Black Sea turbot Psetta maxima. Fish Sci 67:571–578
Na-Nakorn U, Kamonrat W, Ngamsiri T (2004) Genetic diversity of walking catfish, Clarias macrocephalus, in Thailand and evidence of genetic introgression from introduced farmed C. gariepinus. Aquaculture 240:145–163
Nelson JS (2006) Fishes of the world, 4th edn. Wiley, Hoboken
Ng HH, Rainboth WJ (1999) The bagrid catfish genus Hemibagrus (Teleostei: Siluriformes) in central Indochina with a new species from the Mekong River. Raffles Bull Zool 47:555–576
Ng HH, Ferraris CJ Jr (2000) A review of the genus Hemibagrus in Southern Asia, with descriptions of two new species. Proc Cal Acad Sci 52:125–142
Nguyen TTT, De Silva SS (2006) Freshwater finfish biodiversity and conservation: an Asian perspective. Biodivers Conserv 15:3543–3568
Ogata Y, Morioka S, Sano K, Vongvichith B, Eda H, Kurokura H, Khonglaliane T (2010) Growth and morphological development of laboratory-reared larvae and juveniles of the Laotian indigenous cyprinid Hypsibarbus malcolmi. Ichthyol Res 57:389–397
Parazo MM, Avila EM, Reyes Jr DM (1991) Size- and weight-dependent cannibalism in hatchery-bred sea bass (Lates calcarifer Bloch). J Appl Ichthyol 7:1–7
Phillips MJ (2002) Fresh water aquaculture in the Lower Mekong Basin. MRC Technical Paper No 7, Mekong River Commission, Phnom Penh
Qin J, Fast AW (1996) Size and feed dependent cannibalism with juvenile snakehead Channa striatus. Aquaculture 144:313–320
Rainboth WJ (1996) Fishes of the Cambodian Mekong. FAO Species Identification Field Guide for Fishery Purposes. FAO, Rome
Senanan W, Kapuscinski AR, Na-Nakorn U, Miller LM (2004) Genetic impacts of hybrid catfish farming (Clarias macrocephalus × C. gariepinus) on native catfish populations in central Thailand. Aquaculture 235:167–184
Smith C, Reay P (1991) Cannibalism in teleost fish. Rev Fish Fish 1:41–64
Watanabe K (1994) Mating behavior and larval development of Pseudobagrus ichikawai (Siluriformes: Bagridae). Jpn J Ichthyol 41:243–251
Welcomme RL, Vidthayanon C (2003) The impact of introductions and stocking of exotic species in the Mekong basin and policies for their control. Technical Paper No 9, Mekong River Commission, Phnom Penh
Acknowledgments
We express our sincere gratitude to staff of the Seng Sa Vang Phan Pa Fish Farm, Vientiane, for technical assistance. Our thanks also go to G. Hardy for his constructive English revision.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Morioka, S., Vongvichith, B. Growth and morphological development of laboratory-reared larval and juvenile Hemibagrus filamentus (Siluriformes: Bagridae). Ichthyol Res 58, 245–254 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10228-011-0219-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10228-011-0219-1