Abstract
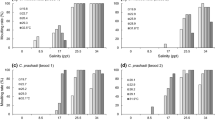
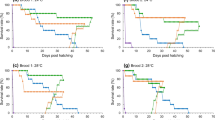
Organisms that migrate between rivers and the sea inevitably pass through estuarine habitats. Despite the potential importance of salinity and temperature fluctuations for metabolic adaptation, little is known about the impact of environmental changes in estuaries on the survival of residents. Ayu (Plecoglossus altivelis) is a migratory fish that inhabits estuarine brackish water in its early life stages. The recent decline in the abundance of populations ascending into rivers is of concern for local biodiversity. The present study aims to elucidate the ecological processes that determine the early success of Ayu larvae under variable environmental conditions. The effects of salinity and water temperature on the endogenous growth of newly hatched larvae from the same brood were examined experimentally based on morphological and metabolic characteristics. High salinity and high water temperature together appeared to require more energy for larval osmoregulation, resulting in the acceleration of yolk depletion and reduced growth of the notochord. Increasing the osmoregulative cost during the yolk-sac stage resulted in the faster induction of a state of starvation. Seawater is considered to have an adverse effect on the survival of newly hatched larvae, as it lowers the efficiency of foraging and predator avoidance due to an energetic tradeoff. More attention should be paid to the significance of estuarine environments involving brackish waters to ensure the early survival of amphidromous fish such as Ayu.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azuma K, Horiki N, Taniguchi N (2003) Annual stock fluctuation of ayu, Plecoglossus altivelis altivelis, in the coastal waters of the central Wakayama Prefecture, Japan. Suisanzoshoku 51:263–271
Blaxter JHS (1992) The effect of temperature on larval fishes. Neth J Zool 42:336–357
Blaxter JHS, Hempel G (1963) The influence of size on herring larvae (Clupea harrengus L.). J Cons Perm Int Explor Mer 28:211–240
Devreker D, Souissi S, Seuront L (2004) Development and mortality of the first naupliar stage of Eurytemora affinis (Copepoda, Calanoida) under different conditions of salinity and temperature. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 303:31–46
Epelbaum A, Herborg LM, Therriault TW, Pearce CM (2009) Temperature and salinity effects on growth, survival, reproduction, and potential distribution of two non-indigenous botryllid ascudians in British Columbia. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 369:43–52
Evans DH (1993) Osmotic and ionic regulation. In: Evans DH (ed) The physiology of fishes. CRC Press, Boca Ranton, pp 315–341
Fukuhara O, Fushimi T (1986) Development and early life history of the ayu reared in the laboratory. Bull Jpn Soc Sci Fish 52:75–80
Horiki N (1991) Annual changes in the catch of marine juvenile ayu in Wakayama Prefecture, with special reference to sharp decrease in the catch in recent years. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 57:1065–1070
Iguchi K (2007) Limitation of early seaward migration success in amphidromous fishes. In: Evenhuis NL, Fitzsimons JM (eds) Bishop Museum Bulletin in Cultural and Environmental Studies 3, Honolulu, pp 75–85
Iguchi K, Mizuno N (1990) Diel changes of larval drift among amphidromous gobies in Japan, especially Rhinogobius brunneus. J Fish Biol 37:255–264
Iguchi K, Mizuno N (1991) Mechanisms of embryonic drift in the amphidromous goby, Rhinogobius brunneus. Environ Biol Fish 31:295–300
Iguchi K, Mizuno N (1999) Early starvation limits survival in amphidromous fishes. J Fish Biol 54:705–712
Kashiwagi M, Iwai T, Yamamoto H, Sokabe Y (1986) Effects of temperature and salinity on egg hatch of the ayu Plecoglossus altivelis. Bull Fac Fish Mie Univ 13:17–24
Mamboya F, Lyimo TJ, Landberg T, Björk M (2009) Influence of combined changes is salinity and copper modulation on growth and copper uptake in the tropical green macroalga Ulva reticulate. Estuar Coas Shelf Sci 84:326–330
McDowall RM (1992) Diadromy: origins and definitions of terminology. Copeia 1992:248–251
Morgan JD, Iwama GK (1991) Effects of salinity on growth, metabolism, and ion regulation in juvenile rainbow and steelhead trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and fall chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha). Can J Fish Aquat Sci 48:2083–2094
Morgan JD, Iwama GK, (1998) Salinity effects on oxygen consumption, gill NA+, K+-ATPase and ion regulation in juvenile coho salmon. J Fish Biol 53:1110–1119
Myers GS (1949) Usage of anadromous, catadromous and allied terms for migratory fishes. Copeia 1949:89–97
Saruwatari T (1995) Temporal utilization of a brackish water lake, Lake Hinuma, as a nursery ground by amphidromous ayu, Plecoglossus altivelis (Plecoglossidae) larvae. Environ Biol Fish 43:371–380
Tago Y (2002) Larval distribution of ayu Plecoglossus altivelis in the surface layer of estuary regions in Toyama Bay. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 68:61–71
Tsukamoto K (1991) Age and growth of ayu larvae Plecoglossus altivelis collected in the Nagara, Kiso and Tone River during the downstream migration. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 57:2013–2022
Tsukamoto K, Kajihara T (1984) On the relation between yolk absorption and swimming activity in the ayu larvae Plecoglossus altivelis. Bull Jpn Soc Sci Fish 50:59–61
Tsukamoto K, Kajihara T, Nishiwaki M (1975) Swimming ability of fish. Bull Jpn Soc Sci Fish 42:167–174
Yagi Y, Bito C, Funakoshi, Kinoshita I, Takahashi I (2006) Distribution and feeding habits of ayu Plecoglossus altivelis altivelis larvae in coastal waters of Tosa Bay. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 72:1057–1067
Yoshimoto Y, Takahashi Y (2006) Factors for catch fluctuation of juvenile ayu in eastern coastal waters facing Kii Channel. Aquacul Sci 54:89–94
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Japan. We would like to address special thanks to Dr. Hiroyuki Sakano, Mrs. Yoko Kurashima and Mrs. Taeko Hazama for their help in collecting and measuring the Ayu larvae.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Iguchi, K., Takeshima, H. Effect of saline water on early success of amphidromous fish. Ichthyol Res 58, 33–37 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10228-010-0191-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10228-010-0191-1