Abstract
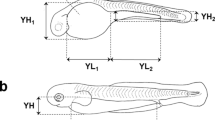
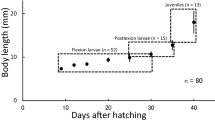
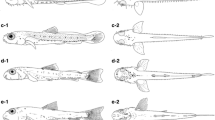
The morphological development, including the pigmentation, body proportions, fins, and survival rate for 30 days after hatching, of laboratory-reared larval and juvenile Hypsibarbus malcolmi is described. Body lengths (BL) of larvae and juveniles were 2.0 ± 0.2 (mean ± SD) mm at 1 h after hatching (day 0) and 9.2 ± 0.6 mm on day 16, reaching 12.1 ± 0.9 mm on day 30. Yolk volume decreased linearly, with the yolk being completely absorbed by day 3 in all preflexion larvae (all specimens >3.2 mm BL). Feeding was observed on day 2 in fish which had rapidly undergone complete yolk absorption following mouth and anus opening on day 1, and on day 3 in all remaining fish. Myomere numbers were 20–21 + 11–12 = 31–33, although they were not clearly visible in juveniles. Melanophores were few on the body during days 0–2, but increased with growth and covered the entire upper dorsal body surface during the juvenile stage. Body proportions tended to become constant in juveniles. Notochord flexion began in larvae >5.2 mm BL on day 8, and was completed in larvae >8.4 mm BL on day 14. Specimens with full fin ray complements were initially observed on day 22 (10.4 mm BL in juveniles). All specimens >11.5 mm BL had attained the juvenile stage. A high survival rate of 92.7% was estimated on day 30.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baird IG, Phylavanh B (1999) Observations of the vocalizations of spawning Mekong River Goldfin Tinfoil barb Hypsibarbus malcolmi (Smith 1945) in southern Lao PDR below the Khone Falls (Technical Report for Environmental Protection and Community Development in Siphandone Wetland, Champasak Province, CESVI Project). Agriculture and Forestry Division (Champasak Province), Pakse
Baird IG, Inthaphaisy V, Kisouvannalath P, Phylavanh B, Mounsouphom B (1999) The fishes of southern Lao (Lao Community Fisheries and Dolphin Protection Project). Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry of Lao PDR, Vientiane
Bardach J (1959) Report on fisheries in Cambodia. The United States Operations Mission, Phnom Penh
Bremigan MT, Stein RA (1994) Gape-dependent larval foraging and zooplankton size: implications for fish recruitment across systems. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 51:913–922
Cooper JE (1980) Egg, larval and juvenile development of Longnose Dace, Rhinichthys cataractae, and River Chub, Nocomis micropogon, with notes on their hybridization. Copeia 3:469–478
De Silva SS, Nguyen TTT, Abery NW, Amarasinghe US (2006) An evaluation of the role and impacts of alien finfish in Asian inland aquaculture. Aquacul Res 37:1–17
Doi A (1997) A review of taxonomic studies of cypriniform fishes in Southeast Asia. Jpn J Ichthyol 44:1–33
Herre AWCT, Myers GS (1937) A contribution to the ichthyology of the Malay Peninsula. Bull Raffles Mus 13:5–75
Kendall AW Jr, Ahlstrom EH, Moser HG (1984) Early life history stages of fishes and their characters. In: Moser HG, Richards WJ, Cohen DM, Fahay MP, Kendall AW Jr, Richardson SL (eds) Ontogeny and systematics of fishes (Am Soc Ichthyol Herpetol Spec Publ No 1). Allen, Lawrence, pp 11–22
Kohno H (1998) Early life history features influencing larval survival of cultivated tropical finfish. In: De Silva SS (ed) Tropical mariculture. Academic, London, pp 71–111
Kottelat M (2001) Fish of Laos. Ganaratne Offset Ltd., Colombo
Leis JM, Trnski T (1989) The larvae of Indo-Pacific shorefishes. NSW University Press, Kensington
Matsumoto S, Morioka S, Kumagai S (2001) Development of African catfish Clarias gariepinus larvae during the transitional phase between endogenous and exogenous energy intake. In: Weyl OLF, Weyl MV (eds) Proceedings of the Lake Malawi Fisheries Management Symposium. Department of Fishery, Lilongwe, pp 227–232
Morioka S, Ito S, Kitamura S, Vongvichith B (2009a) Growth and morphological development of laboratory-reared larval and juvenile climbing perch Anabas testudineus. Ichthyol Res 56:162–171
Morioka S, Sakiyama K, Ito S, Vongvichith B (2009b) Technical report and manual of seed production of the climbing perch Anabas testudineus (JIRCAS Working Report 61). Japan International Research Center for Agricultural Sciences, Tsukuba
Morioka S, Ito S, Kitamura S (2010a) Growth and morphological development of laboratory-reared larval and juvenile snakeskin gourami Trichogaster pectoralis. Ichthyol Res 57:24–31
Morioka S, Sano K, Phommachan P, Vongvichith B (2010b) Growth and morphological development of laboratory-reared larval and juvenile Pangasianodon hypophthalmus. Ichthyol Res 57:139–147
Moteki S, Yoseda K, Sahin T, Üstündağ C, Kohno H (2001) Transition from endogenous to exogenous nutritional sources in larval Black Sea turbot Psetta maxima. Fish Sci 67:571–578
Na-Nakorn U, Kamonrat W, Ngamsiri T (2004) Genetic diversity of walking catfish, Clarias macrocephalus, in Thailand and evidence of genetic introgression from introduced farmed C. gariepinus. Aquaculture 240:145–163
Nguyen TTT, De Silva SS (2006) Freshwater finfish biodiversity and conservation: an Asian perspective. Biodivers Conserv 15:3543–3568
Poulsen A, Poeu O, Viravong S, Suntornratana U, Tung NT (2002) Deep pools as dry season fish habitats in the Mekong Basin (MRC Technical Paper 4). Mekong River Commission, Phnom Penh
Rainboth WJ (1996a) The taxonomy, systematics, and zoogeography of Hypsibarbus, a new genus of large barb (Pisces: Cyprinidae) from the rivers of southeastern Asia (Univ Calif Publ Zool 129). University of California Press, Los Angeles
Rainboth WJ (1996b) Fishes of the Cambodian Mekong. FAO species identification field guide for fishery purposes. FAO, Rome
Sado T, Kimura S (2002a) Descriptive morphology of the eggs, larvae, and juveniles of two cyprinid fishes belonging to the Zacco temminckii species’ group. Ichthyol Res 49:245–252
Sado T, Kimura S (2002b) Developmental morphology of the cyprinid fish, Candidia barbatus. Ichthyol Res 49:350–354
Sado T, Kimura S (2005a) Developmental morphology of the cyprinid fish Horadandia atukorali. Ichthyol Res 52:152–157
Sado T, Kimura S (2005b) Developmental morphology of the Indian cyprinid fish Barilius canarensis. Ichthyol Res 52:360–363
Sado T, Kimura S (2005c) Developmental morphology of the cyprinid fish Tanichthys albonubes. Ichthyol Res 52:386–391
Sado T, Kimura S (2006) Developmental morphology of the cyprinid fish Inlecypris auropurpureus. Ichthyol Res 53:34–40
Senanan W, Kapuscinski AR, Na-Nakorn U, Miller LM (2004) Genetic impacts of hybrid catfish farming (Clarias macrocephalus × C. gariepinus) on native catfish populations in central Thailand. Aquaculture 235:167–184
Smith HM (1945) The fresh-water fishes of Siam, or Thailand. Bull US Natn Mus 188:xi + 622
Sverdrup-Jensen S (2002) Fisheries in the lower Mekong basin: status and perspectives. MRC Tech Paper 6, Mekong River Commission, Phnom Penh
Vidthayanon C (2001) Aquaculture of indigenous Mekong fish species. Mekong River Commission Component Rep 7, Mekong River Commission, Bangkok
Welcomme RL, Vidthayanon C (2003) The impact of introductions and stocking of exotic species in the Mekong basin and policies for their control. Tech Paper 9, Mekong River Commission, Phnom Penh
Yamaguchi M, Miya M, Okiyama M, Nishida M (2000) Molecular phylogeny and larval morphological diversity of the Lanternfish genus Hygophum (Teleostei: Myctophidae). Mol Phylogenet Evol 15:103–114
Yi B, Liang Z, Yu Z, Lin R, He M (2006) A study of the early development of grass carp, black carp, silver carp and bighead carp in the Yangtze River, China. In: Chapman DC (ed) Early development of four cyprinids native to the Yangtze River. US Geological Survey, Reston, pp 15–51
Acknowledgments
We express our sincere gratitude to all of the staff of the project of the JICA (Japan International Cooperation Agency) at the National Aquaculture Development Center, Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry, Laos. Species identification by K. Shibukawa and K. Utsugi, Nagao Natural Environment Foundation, Japan, was deeply appreciated. Our thanks also to G. Hardy for his constructive English revision of our paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Ogata, Y., Morioka, S., Sano, K. et al. Growth and morphological development of laboratory-reared larvae and juveniles of the Laotioan indigenous cyprinid Hypsibarbus malcolmi . Ichthyol Res 57, 389–397 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10228-010-0173-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10228-010-0173-3