Abstract
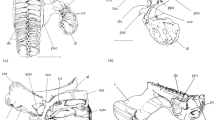
Barbels of the Mullidae and Polymixiidae were observed osteologically and myologically. They were considered to be derived from branchiostegal rays. Four muscles, the extensor tentaculi, retractor tentaculi, and two sections of rotator tentaculi, were related to the barbels in both families. These muscles originate from almost all the hyoid bones in mullids, whereas they originate only from the ventral hypohyal and fifth branchiostegal ray in polymixiids. In addition, each muscle related to the barbel of the former is independent from others, but that of the latter is interconnected. These muscular differences indicate that the barbels occurring in the two families are nonhomologous.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: August 27, 2000 / Revised: April 11, 2001/ Accepted: May 13, 2001
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, BJ., Yabe, M. & Nakaya, K. Barbels and related muscles in Mullidae (Perciformes) and Polymixiidae (Polymixiiformes). Ichthyol Res 48, 409–413 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10228-001-8165-y
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10228-001-8165-y