Abstract
This study developed a brief training, the Integrative Writing Training (IWT), to introduce students to two types of rhetorical devices (i.e., direct and indirect integration) that can be used to communicate cross-textual connections through writing. The training did not significantly increase the volume of integration included in students’ written responses, composed based on multiple texts, relative to a control group; although improvements were found when students were compared to others receiving a writing-organization focused training. Directions for future research and, particularly, the need to attend to students’ use of rhetorical devices to communicate integration when writing based on multiple texts are discussed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barzilai, S., Tal-Savir, D., Abed, F., Mor-Hagani, S., & Zohar, A. R. (2021). Mapping multiple documents: From constructing multiple document models to argumentative writing. Reading and Writing, 36, 809–847. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-021-10208-8
Barzilai, S., Thomm, E., & Shlomi-Elooz, T. (2020). Dealing with disagreement: The roles of topic familiarity and disagreement explanation in evaluation of conflicting expert claims and sources. Learning and Instruction, 69, 101367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2020.101367
Barzilai, S., Zohar, A. R., & Mor-Hagani, S. (2018). Promoting integration of multiple texts: A review of instructional approaches and practices. Educational Psychology Review, 30(3), 973–999. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-018-9436-8
Braasch, J. L., & Scharrer, L. (2020). The role of cognitive conflict in understanding and learning from multiple perspectives. In P. Van Meter, A. List, D. Lombardi, & P. Kendeou (Eds.), Handbook of learning from multiple representations and perspectives (pp. 205–222). Routledge.
Braasch, J. L., McCabe, R. M., & Daniel, F. (2016). Content integration across multiple documents reduces memory for sources. Reading and Writing, 29, 1571–1598. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-015-9609-5
Bråten, I., Braasch, J. L., & Salmerón, L. (2020). Reading multiple and non-traditional texts: New opportunities and new challenges. In E. B. Moje, P. Afflerbach, P. Enciso, & N. K. Lesaux (Eds.), Handbook of Reading Research (Vol. V, pp. 79–98). Routledge.
Britt, M. A., & Sommer, J. (2004). Facilitating textual integration with macro-structure focusing tasks. Reading Psychology, 25(4), 313–339. https://doi.org/10.1080/02702710490522658
Britt, M. A., Perfetti, C. A., Sandak, R. L., & Rouet, J.-F. (1999). Content integration and source separation in learning from multiple texts. In S. R. Goldman (Ed.), Essays in honor of Tom Trabasso (pp. 209–233). Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Inc.
Casado-Ledesma, L., Cuevas, I., & Martin, E. (2023). Learning science through argumentative synthesis writing and deliberative dialogues: A comprehensive and effective methodology in secondary education. Reading and Writing, 36(4), 965–996. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-021-10191-0
Cerdán, R., & Vidal-Abarca, E. (2008). The effects of tasks on integrating information from multiple documents. Journal of Educational Psychology, 100(1), 209–222. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.100.1.209
Daher, T. A., & Kiewra, K. A. (2016). An investigation of SOAR study strategies for learning from multiple online resources. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 46, 10–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2015.12.004
De La Paz, S., Monte-Sano, C., Felton, M., Croninger, R., Jackson, C., & Piantedosi, K. W. (2017). A historical writing apprenticeship for adolescents: Integrating disciplinary learning with cognitive strategies. Reading Research Quarterly, 52(1), 31–52. https://doi.org/10.1002/rrq.147
Du, H., & List, A. (2021). Evidence use in argument writing based on multiple texts. Reading Research Quarterly, 56(4), 715–735. https://doi.org/10.1002/rrq.366
Du, H., & List, A. (2022). Reasoning about text-based evidence. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 68, 102038. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2021.102038
Foley, M. (1989). Unteaching the five-paragraph essay. Teaching English in the Two-Year College, 16(4), 231–235. Retrieved from https://eric.ed.gov/?id=EJ405028
Gil, L., Bråten, I., Vidal-Abarca, E., & Strømsø, H. I. (2010a). Summary versus argument tasks when working with multiple documents: Which is better for whom? Contemporary Educational Psychology, 35(3), 157–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2009.11.002
Gil, L., Bråten, I., Vidal-Abarca, E., & Strømsø, H. I. (2010b). Understanding and integrating multiple science texts: Summary tasks are sometimes better than argument tasks. Reading Psychology, 31(1), 30–68. https://doi.org/10.1080/02702710902733600
Hopkins, C. (2002). Improving tenth-grade students’ five paragraph essay writing skills using various writing strategies, guided assignments, and portfolios for growth. Nova Southeastern University. Retrieved from: https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED471633.pdf, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-021-10248-0, >https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2021.102018
Kullberg, N., Kiili, C., Bråten, I., González-Ibáñez, R., & Leppänen, P. H. (2023). Sixth graders’ selection and integration when writing from multiple online texts. Instructional Science, 51, 39–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11251-022-09613-5
Latini, N., Bråten, I., Anmarkrud, Ø., & Salmerón, L. (2019). Investigating effects of reading medium and reading purpose on behavioral engagement and textual integration in a multiple text context. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 59, 101797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2019.101797
List, A. (2022). Demonstrating the effectiveness of two scaffolds for fostering students’ domain perspective reasoning. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 38, 1343–1376. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10212-022-00643-8
List, A. (2023). The Limits of Reasoning: Students’ Evaluations of Anecdotal, Descriptive, Correlational, and Causal Evidence. The Journal of Experimental Education, 1–31. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220973.2023.2174487
List, A., Du, H., & Lee, H. Y. (2021). How do students integrate multiple texts? An investigation of top-down processing. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 36, 599–626. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10212-020-00497-y
List, A., Du, H., & Lyu, B. (2022). Examining undergraduates’ text-based evidence identification, evaluation, and use. Reading and Writing, 35(5), 1059–1089. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-021-10219-5
List, A., Du, H., & Wang, Y. (2019a). Understanding students’ conceptions of task assignments. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 59, 101801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2019.101801
List, A., Du, H., Wang, Y., & Lee, H. Y. (2019b). Toward a typology of integration: Examining the documents model framework. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 58, 228–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2019.03.003
Luna, M., Villalón, R., Martínez-Álvarez, I., & Mateos, M. (2023). Online interventions to help college students to improve the degree of integration of their argumentative synthesis. Reading and Writing, 36(4), 937–963.
Martinez, C. T., Kock, N., & Cass, J. (2011). Pain and pleasure in short essay writing: Factors predicting university students’ writing anxiety and writing self-efficacy. Journal of Adolescent & Adult Literacy, 54(5), 351–360. https://doi.org/10.1598/JAAL.54.5.5
Martínez, I., Mateos Sanz, M. D. M., Martín, E., & Rijlaarsdam, G. (2015). Learning history by composing synthesis texts: Effects of an instructional programme on learning, reading and writing processes, and text quality. Journal of Writing Research, 7(2), 275–302. https://doi.org/10.17239/jowr-2015.07.02.03
Mason, A. E., Braasch, J. L., Greenberg, D., Kessler, E. D., Allen, L. K., & McNamara, D. S. (2023). Comprehending multiple controversial texts about childhood vaccinations: Topic beliefs and integration instructions. Reading Psychology, 44(4), 436–462. https://doi.org/10.1080/02702711.2022.2156952
McCarthy, K. S., Yan, E. F., Allen, L. K., Sonia, A. N., Magliano, J. P., & McNamara, D. S. (2022). On the basis of source: Impacts of individual differences on multiple-document integrated reading and writing tasks. Learning and Instruction, 79, 101599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2022.101599
McCutchen, D. (2000). Knowledge, processing, and working memory: Implications for a theory of writing. Educational Psychologist, 35(1), 13–23. https://doi.org/10.1207/S15326985EP3501_3
Nash, J. G., Schumacher, G. M., & Carlson, B. W. (1993). Writing from sources: A structure-mapping model. Journal of Educational Psychology, 85(1), 159–170. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.85.1.159
Nelson, N., & King, J. R. (2023). Discourse synthesis: Textual transformations in writing from sources. Reading and Writing, 36(4), 769–808. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-021-10243-5
Nunnally, T. E. (1991). Breaking the five-paragraph-theme barrier. The English Journal, 80(1), 67–71. https://doi.org/10.2307/818100
Olive, T., & Kellogg, R. T. (2002). Concurrent activation of high-and low-level production processes in written composition. Memory & Cognition, 30(4), 594–600. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03194960
Perfetti, C. A., Rouet, J.-F., & Britt, M. A. (1999). Towards a theory of documents representation. In H. van Oostendorp & S. R. Goldman (Eds.), The construction of mental representations during reading (pp. 99–122). Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Inc.
Primor, L., & Katzir, T. (2018). Measuring multiple text integration: a review. Frontiers in Psychology, 9, Article 2294. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02294
Primor, L., Yeari, M., & Katzir, T. (2021). Choosing the right question: The effect of different question types on multiple text integration. Reading and Writing, 34, 1539–1567. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-021-10127-8
Rouet, J.-F., & Britt, M. A. (2011). Relevance processes in multiple document comprehension. In G. Schraw, M. McCrudden, & J. P. Magliano (Eds.), Text relevance and learning from text (pp. 19–52). Information Age Publishing.
Schoor, C., Rouet, J. F., Artelt, C., Mahlow, N., Hahnel, C., Kroehne, U., & Goldhammer, F. (2021). Readers’ perceived task demands and their relation to multiple document comprehension strategies and outcome. Learning and Individual Differences, 88, 102018.
Schwartz, L. H. (2014). Challenging the tyranny of the five-paragraph essay: Teachers and students as semiotic boundary workers in classroom and digital space. Literacy, 48(3), 124–135. https://doi.org/10.1111/lit.12021
Seo, B. I. (2007). Defending the five-paragraph essay. English Journal, 97(2), 15–16.
Smith, K. (2006). In defense of the five-paragraph essay. English Journal, 95(4), 16–17.
Sonia, A. N., Magliano, J. P., McCarthy, K. S., Creer, S. D., McNamara, D. S., & Allen, L. K. (2022). Integration in multiple-document comprehension: A natural language processing approach. Discourse Processes, 59(5–6), 417–438. https://doi.org/10.1080/0163853X.2022.2079320
Spivey, N. N. (1990). Transforming texts: Constructive processes in reading and writing. Written Communication, 7(2), 256–287. https://doi.org/10.1177/0741088390007002004
Tarchi, C., & Villalón, R. (2021). The influence of thinking dispositions on integration and recall of multiple texts. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 91(4), 1498–1516. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjep.12432
Thomm, E., & Bromme, R. (2016). How source information shapes lay interpretations of science conflicts: Interplay between sourcing, conflict explanation, source evaluation, and claim evaluation. Reading and Writing, 29, 1629–1652. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-016-9638-8
Van Ockenburg, L., van Weijen, D., & Rijlaarsdam, G. (2019). Learning to write synthesis texts: A review of intervention studies. Journal of Writing Research, 10(3), 401–428. https://doi.org/10.17239/jowr-2019.10.03.01
Wagner, R. K., Puranik, C. S., Foorman, B., Foster, E., Wilson, L. G., Tschinkel, E., & Kantor, P. T. (2011). Modeling the development of written language. Reading and Writing, 24(2), 203–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-010-9266-7
Wesley, K. (2000). The ill effects of the five paragraph theme. The English Journal, 90(1), 57–60.
Wiley, J., & Voss, J. F. (1999). Constructing arguments from multiple sources: Tasks that promote understanding and not just memory for text. Journal of Educational Psychology, 91(2), 301–311. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.91.2.301
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Eunseo Lee. Dept. of Educational Psychology, Counseling, and Special Education, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, United States. Email: eunseolee@psu.edu.
Current themes of research:
Designing scaffolds for learning from reading and writing.
Automated feedback on students’ science writing and its effects on science learning.
Higher-order reasoning (e.g., problem-solving, analogical reasoning) in STEM + CS education.
Most relevant publications in the field of Psychology of Education:
Hattan, C., Lee, E., & List, A. (2023). Comprehension, Diagram Analysis, Integration, and Interest: A Cross-Sectional Analysis. Reading Psychology, 1–30. https://doi.org/10.1080/02702711.2023.2187907
Kim, C., Puntambekar, S., Lee, E., Gnesdilow, D., Dey, I., Cang, X., … & Passonneau, R. (2023, July). Understanding of a law of science and its relation to science writing with automated feedback. In Proceedings of the International Conference of Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning.
Kim, C., Dinç, E., Lee, E., Baabdullah, A., Zhang, A. Y., & Belland, B. R. (2023). Revisiting Analogical Reasoning in Computing Education: Use of Similarities Between Robot Programming Tasks in Debugging. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 07356331221142912.
Kim, C., Belland, B. R., Baabdullah, A., Lee, E., Dinç, E., & Zhang, A. Y. (2021). An ethnomethodological study of abductive reasoning while tinkering. AERA Open, 7, 23,328,584,211,008,111.
Alexandra List. Dept. of Educational Psychology, Counseling, and Special Education, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, United States. Email: azl261@psu.edu.
Current themes of research:
Critical digital literacy and learning on the Internet.
Learning from multiple texts and multiple resources.
Higher-order reasoning processes (e.g., critique, evaluation) in learning from texts.
Most relevant publications in the field of Psychology of Education:
List, A., Du, H., Wang, Y., & Lee, H. Y. (2019). Toward a typology of integration: Examining the documents model framework. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 58, 228–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2019.03.003
List, A., Du, H., & Lee, H. Y. (2021). How do students integrate multiple texts? An investigation of top-down processing. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 36, 599–626. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10212-020-00497-y
List, A., & Du, H. (2021). Reasoning beyond history: Examining students’ strategy use when completing a multiple text task addressing a controversial topic in education. Reading and Writing, 34, 1003–1048. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-020-10095-5
Gala Sofia Campos Oaxaca. Dept. of Educational Psychology, Counseling, and Special Education, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, United States. Email: gsc5138@psu.edu.
Current themes of research:
Academic writing.
Writing from multiple texts.
Discourse synthesis.
ESL writing.
Most relevant publications in the field of Psychology of Education:
Meyer, B. J., Campos Oaxaca, G. S, & Yu, J. (2022). Text structure: Reading, writing, cross language perspectives. (R. Horowitz, Ed.). In R. Horowitz (Ed.), The handbook of international research on writing. Routledge.
List, A., & Campos Oaxaca, G. (2023). Comprehension and critique: an examination of students evaluations of information in texts. Reading and Writing.
List, A., Campos Oaxaca, G. S., Lee, E., Du, H., & Lee, H. Y. (2021). Examining perceptions, selections, and products in undergraduates’ learning from multiple resources. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 91(4), 1555–1584.
Hye Yeon Lee. Wallace H. Coulter Department of Biomedical Engineering, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, United States. Email: hyeyeon.lee@bme.gatech.edu.
Current themes of research:
Learning from multiple texts and multiple resources.
Self-Regulated learning in multiple text use.
Most relevant publications in the field of Psychology of Education:
List, A., Du, H., Wang, Y., & Lee, H. Y. (2019). Toward a typology of integration: Examining the documents model framework. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 58, 228–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2019.03.003
Lee, H. Y., & List, A. (2023). The role of relevance determinations in multiple text reading and writing: an investigation of the MD-TRACE. Discourse Processes, 60(1), 42–72.
Hongcui Du. Florida Center for Reading Research, Florida State University, Tallahassee, FL, United States. Email: hdu@fsu.edu.
Current themes of research:
Multiple text reading and writing.
Evidence-based reasoning.
Intervention.
Most relevant publications in the field of Psychology of Education:
Du, H., & List, A. (2022). Reasoning about text-based evidence. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 68, 102,038.
Du, H., & List, A. (2021). Evidence use in argument writing based on multiple texts. Reading Research Quarterly, 56(4), 715–735.
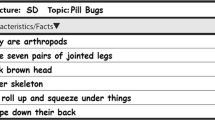
Appendix A. Sample training materials
Appendix A. Sample training materials
From the Integrative Writing Training:


From the Organization Condition:


Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, E., List, A., Campos Oaxaca, G.S. et al. Using rhetorical devices to improve integration in writing based on multiple texts. Eur J Psychol Educ (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10212-023-00778-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10212-023-00778-2