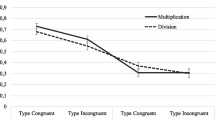
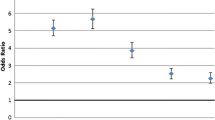
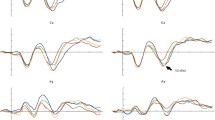
Abstract
Processing rational numbers is difficult for many children. The natural number bias is one possible explanation for why children struggle with rational numbers. It refers to the tendency to overgeneralize the properties of natural numbers. In this study, it is argued that in order to be successful in rational number tasks, individuals need to inhibit or suppress their unwanted impulses (in this case the tendency to apply natural number properties). It was investigated whether inhibition plays a role in the occurrence of the natural number bias among primary school children by administering two rational number tasks, two Stroop tasks and a questionnaire measuring inhibitory skills. The results indicated that primary school children were hampered by the natural number bias both in terms of accuracy rates and response times. Additionally, the results did not yield strong evidence for a relationship between inhibition and the occurrence of the natural number bias.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, upon reasonable request.
References
Avgerinou, V. A., & Tolmie, A. (2020). Inhibition and cognitive load in fractions and decimals. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 90(1), 240–256. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjep.12321
Bellon, E., Fias, W., & De Smedt, B. (2016). Are individual differences in arithmetic fact retrieval in children related to inhibition? Frontiers in Psychology, 7, 825. https://doi.org/10.3389/psyg.2016.00825
Christou, K. (2015). Natural number bias in operations with missing numbers. ZDM: The International Journal on Mathematics Education, 47(5), 747–758. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-015-0675-6
De Neys, W., Moyens, E., & Vansteenwegen, D. (2010). Feeling we’re biased: Autonomic arousal and reasoning conflict. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 10, 208–216. https://doi.org/10.3758/CABN.10.2.208
DeWolf, M., & Vosniadou, S. (2014). The representation of fraction magnitudes and the whole number bias reconsidered. Learning and Instruction, 37, 39–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lerninstruc.2014.07.002
Diamond, A. (2013). Executive functions. Annual Review of Psychology, 64(1), 135–168. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-psych-113011-143750
Durkin, K., & Rittle-Johnson, B. (2014). Diagnosing misconceptions: Revealing changing decimal fraction knowledge. Learning and Instruction, 37, 21–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2014.08.003
Evans, J. (2008). Dual-processing accounts of reasoning. Judgment, and Social Cognition., 59(1), 255–278. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.psych.59.103006.093629
Fu, X., Li, X., Xu, P., & Zeng, J. (2020). Inhibiting the whole number bias in a fraction comparison task: An event-related potential study. Psychology Research and Behavior Management, 13, 245–255. https://doi.org/10.2147/PRBM.S240263
Gelman, R. (2000). The epigenesis of mathematical thinking. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 21(1), 27–37.
Gillard, E., Van Dooren, W., Schaeken, W., & Verschaffel, L. (2009). Dual processes in the psychology of mathematics education and cognitive psychology. Human Development, 52(2), 95–108. https://doi.org/10.1159/000202728
Gómez, D. M., Jiménez, A., Bobadilla, R., Reyes, C., & Dartnell, P. (2015). The effect of inhibitory control on general mathematics achievement and fraction comparison in middle school children. ZDM, 47, 801–811. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-015-0685-4
González-Forte, J. M., Fernández, C., Van Hoof, J., & Van Dooren, W. (2020). Various ways to determine rational number size: An exploration across primary and secondary education. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 35(3), 549–565. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10212-019-00440-w
Greer, B. (2004). The growth of mathematics through conceptual restructuring. Learning and Instruction, 14(5), 541–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2004.06.018
Hedge, C., Powell, G., & Sumner, P. (2017). The reliability paradox: Why robust cognitive tasks do not produce reliable individual differences. Behavior Research Methods, 50(3), 1166–1186. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13428-017-0935-1
Houdeé, O., & Guichart, E. (2001). Negative priming effect after inhibition of number/length interference in a Piaget-like task. Developmental Science, 4(1), 119–123. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-7687.00156
Huizinga, M. &, Smidts, D. (2020) BRIEF-2: Vragenlijst executieve functies voor 5- tot en met 18-jarigen. Hogrefe Uitgevers.
Liang, K. Y., & Zeger, S. L. (1986). Longitudinal data analysis using generalized linear models. Biometrika, 73(1), 13–22. https://doi.org/10.1093/biomet/73.1.13
Luna, B. (2009). Developmental changes in cognitive control through adolescence. Advances in Child Development and Behavior, 37, 233–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2407(09)03706-9
Meert, G., Grégoire, J., & Noël, M. (2010). Comparing the magnitude of two fractions with common components: Which representations are used by 10- and 12-year-olds? Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 107(3), 244–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jecp.2010.04.008
Merenluoto, K., & Lehtinen, E. (2004). Number concept and conceptual change: Towards a systemic model of the processes of change. Learning and Instruction, 14(5), 519–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2004.06.016
Ni, Y., & Zhou, Y. (2005). Teaching and learning fraction and rational numbers: The origins and implications of whole number bias. Educational Psychologist, 40(1), 27–52. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15326985ep4001_3
Obersteiner, A., Alibali, M. W., & Marupudi, V. (2020). Complex fraction comparisons and the natural number bias: The role of benchmarks. Learning and Instruction, 67, 101307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2020.101307
Obersteiner, A., Van Dooren, W., Van Hoof, J., & Verschaffel, L. (2013). The natural number bias and magnitude representation in fraction comparison by expert mathematicians. Learning and Instruction, 28, 64–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2013.05.003
Reinhold, F., Obersteiner, A., Hoch, S., Hofer, S. I., & Reiss, K. (2020). The interplay between the natural number bias and fraction magnitude processing in low-achieving students. Frontiers in Education, 5, 29. https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2020.00029
Resnick, L., Nesher, P., Leonard, F., Magone, M., Omanson, S., & Peled, I. (1989). Conceptual bases of arithmetic errors: The case of decimal fractions. Journal for Research in Mathematics Education, 20(1), 8–27.
Roell, M., Viarouge, A., Hilscher, E., Houdé, O., & Borst, G. (2019a). Evidence for a visuospatial bias in decimal number comparison in adolescents and in adults. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-51392-6
Roell, M., Viarouge, A., Houdé, O., & Borst, G. (2019b). Inhibition of the whole number bias in decimal number comparison: A developmental negative priming study. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 177, 240–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jecp.2018.08.010
Rossi, S., Vidal, J., Letang, M., Houdé, O., & Borst, G. (2019). Adolescents and adults need inhibitory control to compare fractions. Journal of Numerical Cognition, 5(3), 314–336. https://doi.org/10.5964/jnc.v5i3.197
Sackur-Grisvard, C., & Léonard, F. (1985). Intermediate cognitive organizations in the process of learning a mathematical concept: The order of positive decimal numbers. Cognition and Instruction, 2(2), 157–174. https://doi.org/10.1207/s1532690xci0202_3
Siegler, R. S., Duncan, G. J., Davis-Kean, P. E., Duckworth, K., Claessens, A., Engel, M., Susperreguy, M. I., & Chen, M. (2012). Early predictors of high school mathematics achievement. Psychological Science, 23(7), 691–697. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797612440101
Smith, C., Solomon, G., & Carey, S. (2005). Never getting to zero: Elementary school students’ understanding of the infinite divisibility of number and matter. Cognitive Psychology, 51(2), 101–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogpsych.2005.03.001
Vamvakoussi, X., & Vosniadou, S. (2004). Understanding the structure of the set of rational numbers: A conceptual change approach. Learning and Instruction, 14(5), 453–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2004.06.013
Vamvakoussi, X., & Vosniadou, S. (2010). How many decimals are there between two fractions? Aspects of secondary school students’ understanding of rational numbers and their notation. Cognition and Instruction, 28(2), 181–209. https://doi.org/10.1080/07370001003676603
Vamvakoussi, X., Van Dooren, W., & Verschaffel, L. (2012). Naturally biased? In search for reaction time evidence for a natural number bias in adults. Journal of Mathematical Behavior, 31(3), 344–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmathb.2012.02.001
Van Dooren, W., Lehtinen, E., & Verschaffel, L. (2015). Unraveling the gap between natural and rational numbers. Learning And Instruction, 37, 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2015.01.001
Van Hoof, J., Lijnen, T., Verschaffel, L., & Van Dooren, W. (2013). Are secondary school students still hampered by the natural number bias? A reaction time study on fraction comparison tasks. Research in Mathematics Education, 15(2), 154–164. https://doi.org/10.1080/14794802.2013.797747
Van Hoof, J., Janssen, R., Verschaffel, L., & Van Dooren, W. (2015a). Inhibiting natural knowledge in fourth graders: Towards a comprehensive test instrument. ZDM: The International Journal on Mathematics Education, 47(5), 849–857. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-014-0650-7
Van Hoof, J., Verschaffel, L., & Van Dooren, W. (2015b). Inappropriately applying natural number properties in rational number tasks: Characterizing the development of the natural number bias through primary and secondary education. Educational Studies in Mathematics, 90(1), 39–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10649-015-9613-3
Van Hoof, J., Vamvakoussi, X., Van Dooren, W., & Verschaffel, L. (2017a). The transition from natural to rational number knowledge. In Acquisition of complex arithmetic skills and higher-order mathematics concepts (3rd ed.). Elsevier.
Van Hoof, J., Verschaffel, L., Ghesquière, P., & Van Dooren, W. (2017b). The natural number bias and its role in rational number understanding in children with dyscalculia. Delay or deficit? Research in Developmental Disabilities, 71, 181–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2017.10.006
Van Hoof, J., Verschaffel, L., & Van Dooren, W. (2017c). Number sense in the transition from natural to rational numbers. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 87(1), 43–56.
Van Hoof, J., Ceulemans, E., & Van Dooren, W. (2021). The role of the inhibition of natural number based reasoning and strategy switch cost in a fraction comparison task. Studia Psychologica, 61(1), 64–76. https://doi.org/10.31577/sp.2021.01.814
Vosniadou, S. (1994). Capturing and modeling the process of conceptual change. Learning and Instruction, 4(1), 45–69.
Vosniadou, S., Vamvakoussi, X., & Skopeliti, I. (2008). The framework theory approach to conceptual change. In S. Vosniadou (Ed.), Handbook of research on conceptual change. Routledge.
Funding
We would like to thank the Academy of Finland (grant 336068, growing mind GM2, PI Minna Hannula-Sormunen).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Karen De Keersmaeker. Centre for Instructional Psychology and Technology, KU Leuven, Dekenstraat 2 box 3773, 3000 Leuven, Belgium.
Current themes of research:.
Psychology of mathematics education. Conceptual change.
Most relevant publications in the field of Psychology of Education:.
No Previous publications.
Jo Van Hoof. Department of Teacher Education, University of Turku, Assistentinkatu 5, 20500 Turku, Finland.
Current themes of research:.
Conceptual change approach to mathematics learning. The role of inhibition in mathematics reasoning. Learners’ rational number understanding. Intuitions, heuristics, and biases in human reasoning. Early mathematics learning.
Most relevant publications in the field of Psychology of Education:.
González-Forte, J. M., Fernández, C., Van Hoof, J., & Van Dooren, W. (2020). Various ways to determine rational number size: an exploration across primary and secondary education. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 35(3), 549–565. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10212-019–00,440-w.
Van Hoof, J., Ceulemans, E., & Van Dooren, W. (2021). The role of the inhibition of natural number based reasoning and strategy switch cost in a fraction comparison task. In Studia Psychologica, 63(1), 64–76. https://doi.org/10.31577/sp.2021.01.814.
Van Hoof, J., Verschaffel, L., Van Dooren, W. (2015). Inappropriately applying natural number properties in rational number tasks: characterizing the development of the natural number bias through primary and secondary education. Educational Studies in Mathematics, 90(1), 39–56.
Van Hoof, J., Verschaffel, L., & Van Dooren, W. (2017). Number sense in the transition from natural to rational numbers. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 87(1), 43–56.
Wim Van Dooren. Centre for Instructional Psychology and Technology, KU Leuven, Dekenstraat 2 box 3773, 3000 Leuven, Belgium.
Current themes of research:.
Mathematical thinking and problem solving, Conceptual change, Intuitions and biases in reasoning.
Most relevant publications in the field of Psychology of Education:.
Obersteiner, A., Van Dooren, W., Van Hoof, J., Verschaffel, L. (2013). The natural number bias and magnitude representation in fraction comparison by expert mathematicians. Learning and Instruction, 28, 64–72.
González-Forte, J. M., Fernández, C., Van Hoof, J., & Van Dooren, W. (2020). Various ways to determine rational number size: an exploration across primary and secondary education. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 35(3), 549–565. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10212-019–00,440-w.
Van Dooren, W., Lehtinen, E., & Verschaffel, L. (2015). Unraveling the gap between natural and rational numbers. Learning and Instruction, 37, 1–4.
Van Hoof, J., Ceulemans, E., & Van Dooren, W. (2021). The role of the inhibition of natural number based reasoning and strategy switch cost in a fraction comparison task. In Studia Psychologica, 63(1), 64–76.https://doi.org/10.31577/sp.2021.01.814.
Van Hoof, J., Verschaffel, L., Van Dooren, W. (2015). Inappropriately applying natural number properties in rational number tasks: characterizing the development of the natural number bias through primary and secondary education. Educational Studies in Mathematics, 90(1), 39–56.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
De Keersmaeker, K., Van Hoof, J. & Van Dooren, W. The relationship between primary school children’s inhibition and the processing of rational numbers. Eur J Psychol Educ 38, 1527–1549 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10212-022-00669-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10212-022-00669-y