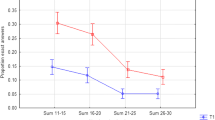
Abstract
Although an increasing number of studies have suggested that students with low mathematics achievement (LMA) tend to perform worse in arithmetic strategy use than children with typical development, the potential reasons remain unclear. Accordingly, the current study investigated the potential impact of task switching on strategy use for children with LMA in computational estimation. In order to determine whether the differences in strategy use by children with LMA were due to a developmental delay or a developmental defect, 21 sixth-graders with LMA, 20 sixth-grader age-matched normal students (AM), and 21 fifth-grade math achievement–matched normal students (MM) were selected. The combination of choice/no-choice method and switching paradigm was employed. Results showed that task switching had significant effects on rounding-down strategy in the strategy execution condition for all groups. However, its effect on rounding-up strategy was significant only for the LMA group. In addition, the AM group outperformed significantly the LMA and MM groups on strategy choice, but the latter two groups did not significantly differ. These results suggest that strategy switch costs were influenced by participants and strategy characteristics. Moreover, poor performance of strategy choice in LMA children was likely due to a developmental delay rather than a defect.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ardiale, E., & Lemaire, P. (2012). Within-item strategy switching: An age comparative study in adults. Psychology and Aging, 27(4), 1138–1151.
Campbell, J. I. D. (2005a). Asymmetrical language switching costs in Chinese-English bilinguals number naming and simple arithmetic. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition, 8(1), 85–91.
Campbell, J. I. D. (2005b). Hand book of mathematical cognition. New York: Psychology Press.
Chen, Y. H., & Wang, M. Y. (2009). The relationship between executive function and arithmetic cognition strategy. Psychological Science, 32(1), 34–37.
Faul, F., Erdfelder, E., Buchner, A., & Lang, A. G. (2009). Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behavior Research Methods, 41(4), 1149–1160.
French, J. W., Ekstrom, R. B., & Price, I. A. (1963). Kit of reference tests for cognitive factors. Princeton, NJ: Educational Testing Service.
Geary, D. C. (2015). The classification and cognitive characteristics of mathematical disabilities in children. In: R. C. Kadosh, R., & A. Dower (Eds.), The Oxford handbook of numerical cognition (pp.767–786). Oxford: Oxford press.
Hodzik, S., & Lemaire, P. (2011). Inhibition and shifting capacities mediate adults’ age-related differences in strategy selection and repertoire. Acta Psychologica, 137(3), 335–344.
Huang, B., Feng, H., Si, J., Zhang, J., & Wang, X. (2016). Dual-task coordination and task presentation mode influence arithmetic strategy execution in adults: Evidence from computational extimation. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 48(6), 671–683.
Imbo, I., Duverne, S., & Lemaire, P. (2007). Working memory, strategy execution, and strategy selection in mental arithmetic. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 60(9), 1246–1264.
Lemaire, P., & Lecacheur, M. (2010). Strategy switch costs in arithmetic problem solving. Memory and Cognition, 38(3), 322–332.
Lemaire, P., & Reder, L. (1999). What affects strategy selection in arithmetic? The example of parity and five effects on product verification. Memory and Cognition, 27(2), 364–382.
Lemaire, P., & Siegler, R. S. (1995). Four aspect of strategy change: Contributions to children’s learning of multiplication. Journal of Experiment Psychology: General, 124(1), 83–97.
Lemaire, P., Arnaud, L., & Lecacheur, M. (2004). Adults’ age-related differences in adaptivity of strategy choices: Evidence from computational estimation. Psychology and Aging, 19(3), 467–481.
Li, H., Zhang, M., Wang, X., Ding, X., & Si, J. (2018). The central executive mediates the relationship between children’s approximate number system acuity and arithmetic strategy utilization in computational estimation. Frontiers in Psychology, 9, 943. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.201800943.
Lin, C. E. (2013). Cognitive flexibility. New York: Springer.
Lovett, M. C., & Anderson, J. R. (1996). History of success and current context in problem solving: Combined influences on operator selection. Cognitive Psychology, 31(2), 168–217.
Luwel, K., Schillemans, V., Onghena, P., & Verschaffel, L. (2009). Does switching between strategies within the same task involve a cost? British Journal of Psychology, 100(4), 753–771.
Miyake, A., Friedman, N. P., Emerson, M. J., Witzki, A. H., Howerter, A., & Wager, T. D. (2000). The unity and diversity of executive function and their contribution to complex “Frontal Lobe” tasks: A latent variable analysis. Cognitive Psychology, 41(1), 49–100.
Monsell, S., & Mizon, G. A. (2006). Can the task-cuing paradigm measure an endogenous task-set reconfiguration process. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 32(3), 493–516.
Murphy, M. M., Mazzocco, M. M. M., Hanich, L. B., & Early, M. C. (2007). Cognitive characteristics of children with mathematics learning disability (MLD) vary as a function of the cutoff criterion used to define MLD. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 40(5), 458–478.
National Research Council & Mathematics Learning Study Committee. (2001). Adding it up: Helping children learn mathematics. Washington, DC: National Academies Press.
Rousselle, L., & Noël, M. P. (2008). Mental arithmetic in children with mathematics learning disabilities: The adaptive use of approximate calculation in an addition verification task. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 41(6), 498–513.
Shen, L. (2004). A primary research on the relative meaning of learning. Journal of Psychological Science, 27(1), 88–91.
Si, J. W., Yang, J., Jia, G. J., & Zhou, C. (2012). The effect of central executive load on adult’s strategy using in computational estimation. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 44(11), 1490–1500.
Si, J., Li, H., Sun, Y., Xu, Y., & Sun, Y. (2016). Age-related differences of individuals’ arithmetic strategy utilization with different level of math anxiety. Frontiers in Psychology, 7, 1612. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2016.01612.
Siegler, R. S., & Arraya, R. (2005). A computational model of conscious and unconscious strategy discovery. In R. V. Kail (Ed.), Advances in child development and behaviour (pp. 1–42). Oxford: Elsevier.
Siegler, R. S., & Lemaire, P. (1997). Older and younger adults’ strategy choices in multiplication: Testing predictions of ASCM using the choice/no-choice method. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 126(1), 71–92.
Swanson, H. L., Jerman, O., & Zheng, X. (2009). Math disabilities and reading disabilities: Can they be separated? Journal of Psychoeducational Assessment, 27(3), 175–196.
Taillan, J., Ardiale, E., & Lemaire, P. (2015). Relationships between strategy switching and strategy switch costs in young and older adults: A study in arithmetic problem solving. Experimental Aging Research, 41(2), 136–156.
Torbeyns, J., Verschaffel, L., & Ghesquière, P. (2004). Strategic aspects of simple addition and subtraction: The influence of mathematical ability. Learning and Instruction, 14(2), 177–195.
Vasilyeva, M., Laski, E. V., & Shen, C. (2015). Computational fluency and strategy choice predict individual and cross-national differences in complex arithmetic. Developmental Psychology, 51(10), 1489–1500.
Verdine, B. N., Irwin, C. M., Golinkoff, R. M., & Hirsh-Pasek, K. (2014). Contributions of executive function and spatial skills to preschool mathematics achievement. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 126(1), 37–51.
Yang, W., Zhang, T., Li, H., Zhang, J., & Si, J. (2018). The effect of central executive load on strategy utilization of computational estimation in children with mathematics learning difficulties. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 50(5), 501–516.
Yeung, N., & Monsell, S. (2003). Switching between tasks of unequal familiarity: The role of stimulus-attribute and response-set selection. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 29(2), 455–469.
Zhang, H., & Wang, X. (1989). Standardization research on Raven’s Standard Progressive Matrices in China. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 21(2), 3–11.
Acknowledgment
We thank the children who participated in this research, and Xiaoyu Liu, Changzhi Wu, and Xichao Zhu for helping with the language.
Funding
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31371048) and Humanities and Social Sciences Foundation of the Ministry of Education of China (18YJA190014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Hongxia Li. School of Psychology, Shandong Normal University, No. 88 East Wen Hua Road, Li Xia District , Jinan, 250014 Shandong, China.
Current themes of research:
Cognitive and neural basic of arithmetic computational estimation strategy utilization.
Reciprocal relationship between mathematics anxiety and mathematics ability.
Most relevant publications in the field of Psychology of Education:
Zhang, M., Si, J., Yang, W., Xing, S., Li, H., & Zhang, J. (2018). Interaction effects between BDNF gene rs6265 polymorphism and parent-involved education on basic mathematical ability in primary school children. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 50(9),1007–1017.
Li, H., Zhang, M., Wang, X., Ding, X., & Si, J. (2018). Central executive mediates the relationship between children’s approximate number system acuity and arithmetic strategy utilization in computational estimation. Frontiers in Psychology, 9, 1–12.
Yang, W., Zhang, T., Li, H., Zhang, J., & Si, J. (2018). The effect of central executive load on strategy utilization of computational estimation in children with mathematics learning difficulties. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 50(5), 501–516.
Si, J., Li, H., Sun, Y., Xu, Y., & Sun, Y. (2016). Age-related differences of individuals’ arithmetic strategy utilization with different level of math anxiety. Frontiers in Psychology, 7, 1612. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2016.01612
Xiaoteng Hua. School of Psychology, Shandong Normal University, No. 88 East Wen Hua Road, Li Xia District , Jinan, 250014 Shandong, China.
Current themes of research:
Cognitive and neural basic of arithmetic computational estimation strategy utilization.
Most relevant publications in the field of Psychology of Education:
Liu, W., Hua, X., Feng, H., Hu, D., & Si, J. (2014). The Age-Related Differences of Arithmetic Strategy Use in Calculation: The Role of Metacognitive Monitoring and Arithmetic Knowledge. Psychological Development and Education, 30(3), 234–243.
Yalin Yang. School of Psychology, Shandong Normal University, No. 88 East Wen Hua Road, Li Xia District , Jinan, 250014 Shandong, China.
Jinglun Primary School, Jinan, China.
Current themes of research:
Cognitive and neural basic of arithmetic computational estimation strategy utilization.
Most relevant publications in the field of Psychology of Education:
Yang, Y., Yang, W., Zhang, M., & Si, J. (2017). From numerosity representation to number representation: The acquisition of human numerical competence under embodied cognition perspective. Journal of Psychological Science, 41(1), 91–97.
Bijuan Huang. School of Psychology, Shandong Normal University, No. 88 East Wen Hua Road, Li Xia District , Jinan, 250014 Shandong, China. E-mail: sijiwei1974@126.com
Current themes of research:
Cognitive and neural basic of arithmetic computational estimation strategy utilization.
Most relevant publications in the field of Psychology of Education:
Huang, B., Feng, H., Si, J., Zhang, J., & Wang, X. (2016). Dual-task coordination and task presentation mode influence arithmetic strategy execution in adults: Evidence from computational extimation. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 48(6), 671–683.
Jiwei Si. School of Psychology, Shandong Normal University, No. 88 East Wen Hua Road, Li Xia District , Jinan, 250014 Shandong, China. E-mail: sijiwei1974@126.com
Current themes of research:
Cognitive and neural basic of arithmetic computational estimation strategy utilization.
Most relevant publications in the field of Psychology of Education:
Zhang, M., Si, J., Yang, W., Xing, S., Li, H., & Zhang, J. (2018). Interaction effects between BDNF gene rs6265 polymorphism and parent-involved education on basic mathematical ability in primary school children. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 50(9), 1007–1017.
Li, H., Zhang, M., Wang, X., Ding, X., & Si, J. (2018). Central executive mediates the relationship between children’s approximate number system acuity and arithmetic strategy utilization in computational estimation. Frontiers in Psychology, 9, 1–12.
Yang, W., Zhang, T., Li, H., Zhang, J., & Si, J. (2018). The effect of central executive load on strategy utilization of computational estimation in children with mathematics learning difficulties. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 50(5), 501–516.
Ai, J. Yang, J., Zhang, T., Si, J. & Liu, Y. (2017). The effect of central executive load on fourth and sixth graders’ use of arithmetic strategies. Psychologica Belgica, 57(2), 154–172. doi:https://doi.org/10.5334/pb.360
Ding, X., Lv, N., Yang, Y., Si, J. (2017). Age-related differences of different components of working memory: The predictive effect on strategy utilization in arithmetic. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 49(6), 759–770.
Si, J., Li, H., Sun, Y., Xu, Y., & Sun, Y. (2016). Age-related differences of individuals’ arithmetic strategy utilization with different level of math anxiety. Frontiers in Psychology, 7, 1612. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2016.01612
Ai, J., Zhang, H., Si, J. (2016). The effects of presenting mode, reaction order of dual task on adults’ arithmetic strategy choice and execution, Acta Psychologica Sinica, 48(10), 1248–1257.
Huang, B., Feng, H., Si, J., Zhang, J., Wang, X. (2016). Dual-task coordination and task presentation mode influence arithmetic strategy execution in adults: Evidence from computational estimation. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 48(6), 671–683.
Lu, C., Guo, H., Si, J. (2014). Representation patterns of children’s and adults’ fraction estimation on different number lines. Psychological Development and Education, 30(5), 449–456.
Liu, W., Hua, X., Feng, H., Hu, D., Si, J. (2014). The age-related differences of arithmetic strategy use in calculation: The role of metacognitive monitoring and arithmetic knowledge. Psychological Development and Education, 30(3), 234–243.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 53 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Hua, X., Yang, Y. et al. How does task switching affect arithmetic strategy use in children with low mathematics achievement? Evidence from computational estimation. Eur J Psychol Educ 35, 225–240 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10212-019-00425-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10212-019-00425-9