Abstract
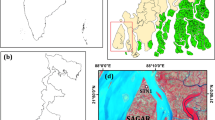
A 2-year study was designed to investigate the spatiotemporal distribution of sulphide in the water column of a saline lake, Lake Hiruga in Fukui, Japan. Water samples were collected in Lake Hiruga periodically between April 2014 and March 2016 at appropriate depths with simultaneous in situ measurements of physicochemical parameters such as temperature, salinity and dissolved oxygen (DO) concentration. Sulphide started accumulating in the hypolimnion in September 2014, whilst that did in June 2015. The sulphide concentrations increased toward the end of December in both 2014 and 2015. Then the sulphide disappeared from the hypolimnion in April 2015 and February 2016. The difference in starting season of the sulphide accumulation was closely connected with DO concentrations in the hypolimnion in circulation periods of winter season. The DO concentrations were regulated by water column stability before thermal stratification periods. Our analysis of the sulphide distribution for the 2 years of the study suggested that accumulation of sulphide in the hypolimnion during stratified periods appears to be associated with strength of water column stability in the winter-spring seasons before stagnant periods in Lake Hiruga.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdollahi H, Nedwell DB (1979) Seasonal temperature as a factor influencing bacterial sulfate reduction in a saltmarsh sediment. Microb Ecol 5:73–79
Agustí S, Duarte CM (1999) Phytoplankton chlorophyll a distribution and water column stability in the central Atlantic Ocean. Oceanol Acta 22:193–203
Effler SW, Hassett JP, Auer MT, Johnson N (1988) Depletion of epilimnetic oxygen and accumulation of hydrogen sulfide in the hypolimnion of Onondag Lake, NY, U.S.A. Water Air Soil Pollut 39:59–74
Houry S, Dombrowsky E, Mey PD, Minster J-F (1987) Brunt-Väisälä frequency and Rossby Radii in the South Atlantic. J Phys Oceanogr 17:1619–1626
Kondo R, Butani J (2007) Comparison of the diversity of sulfate-reducing bacterial communities in the water column and the surface sediments of a Japanese meromictic lake. Limnology 8:131–141
Kondo R, Kasashima N, Matsuda H, Hata Y (2000) Determination of thiosulfate in a meromictic lake. Fish Sci 66:1076–1081
Kondo R, Nedwell DB, Purdy KJ, Silva SQ (2004) Detection and enumeration of sulphate-reducing bacteria in estuarine sediments by competitive PCR. Geomicrobiol J 21:145–157
Kondo R, Mori Y, Sakami T (2012) Comparison of sulphate-reducing bacterial communities in Japanese fish farm sediments with different levels of organic enrichment. Microbes Environ 27:193–199
Nedwell DB, Abram JW (1979) Relative influence of temperature and electron donor and electron acceptor concentrations on bacterial sulfate reduction in saltmarsh sediment. Microb Ecol 5:67–72
Postgate JR (1984) The sulphate-reducing bacteria, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Simpson JH, Bowers D (1981) Models of stratification and frontal movement in shelf seas. Deep-Sea Res 28A:727–738
Simpson JH, Sharples J (2012) Introduction to the physical and biological oceanography of shelf seas. Cambridge University Press, New York, pp 176–181
Takahashi M, Ichimura S (1968) Vertical distribution and organic matter production of photosynthetic sulfur bacteria in Japanese lakes. Limnol Oceanogr 13:644–655
Takahashi T, Nakata H, Hirano K, Matsuoka K, Iwataki M, Yamaguchi H, Kasuya T (2009) Upwelling of oxygen-depleted water (Sumishio) in Omura Bay, Japan. J Oceanogr 65:113–120
Yoshimura S (1934) Chemical compositions of the lake waters of Japan. IV Hydrogen sulphide. Jpn J Limnol 4:11–27 (in Japanese)
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to H. Nagai, a fish farm manager, and Y. Takao from our laboratory for their assistance during field investigations. We also gratefully acknowledge valuable comments by anonymous reviewers and the associate editor.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Akio Imai.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kondo, R., Momoki, M., Yamamoto, M. et al. Spatiotemporal shift in sulphide concentration in hypolimnic water column in Lake Hiruga, a saline lake in Japan. Limnology 19, 277–283 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10201-018-0541-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10201-018-0541-7