Abstract
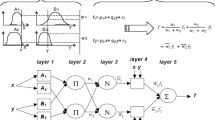
An adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference technique has been adopted to estimate light levels in a reservoir. The data were collected randomly from Doğanci Dam Reservoir over a number of years. The input data set is a matrix with vectors of time, depth, sampling location, and incident solar radiation. The output data set is a vector representing light measured at various depths. Randomization and logarithmic transformations have been applied as preprocessing. One-half of the data have been utilized for training; testing and validation steps utilized one-fourth each. An adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) has been built as a prediction model for light penetration. Very high correlation values between predictions and real values on light measurements with relatively low root mean square error values have been obtained for training, test, and validation data sets. Elimination of the overtraining problem was ensured by satisfying close root mean square error values for all sets.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang FJ, Chang YT (2006) Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system for prediction of water level in reservoirs. Adv Water Res 29:1–10
Chapra SC (1997) Surface water quality modeling. McGraw-Hill International Editions, Civil Engineering Series, Singapore
Efe MÖ, Kaynak O (1998) A comparative study of soft computing methodologies in identification of robotic manipulators. In: Proceedings, 3rd international conference on advanced mechatronics, August 1998, Okayama, Japan 1:21–26
Effler SW, Perkins M, Ohrazda N, Matthews DA, Gelda R, Peng F, Johnson DL, Stephczuk CL (2002) Tripton, transparency and light penetration in seven New York reservoirs. Hydrobiologia 468(1–3): 213–232
Halsted CP (1993) Brightness, limunance and confusion. Information display, March
Havens KE (2003) Phosphorus-algal bloom relationships in large lakes of South Florida: implications for establishing nutrient criteria. Lake Reservoir Manag 19(3):222–228
Hocking GC, Straskraba M (1999) The effect of light extinction on thermal stratification in reservoirs and lakes. Int Rev Hydrobiol 84(6):535–556
Jang JSR (1993) ANFIS: adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference systems. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybernet 23(3):665–685
Mamdani EH (1977) Applications of fuzzy logic to approximate reasoning using linguistic synthesis. IEEE Trans Comput 26(12):1182–1191
MathWorks Inc. (2001) Fuzzy Logic Toolbox, Natick, MA
Mills WB, Porcella DB, Ungs MJ, Gherini SA, Summers KV, Lingfung Mok GL, Rupp GL, Bowie GL (1985) Water quality assessment: a screening procedure for toxic and conventional pollutants, part I. EPA-600/6-82-004a. Tetra Tech. Inc., Environmental Research Laboratory. Office of Research and Development, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Athens, GA
Peng F, Effler SW (2005) Inorganic tripton in the Finger Lakes of New York: importance to optical characteristics. Hydrobiologia 543:259–277
Soyupak S, Karaer F, Gürbüz, H, Şentürk, E, Yazici A (2003) A neural network-based approach for calculating dissolved oxygen profiles in reservoirs. Neural Comput Appl 12:166–172
Takagi T, Sugeno M (1985) Fuzzy identification of systems and its applications to modeling and control. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybernet 16:116–132
Voros L, Callieri C, Balogh KV, Bertoni R (1998) Freshwater Picocyanobacteria along a trophic gradient and light quality range. Hydrobiologia 370:117–125
Zadeh L, Kacprzyk J (1992) Fuzzy logic for the management of uncertainty. Wiley, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soyupak, S., Karaer, F., Şentürk, E. et al. Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference technique for estimation of light penetration in reservoirs. Limnology 8, 103–112 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10201-007-0204-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10201-007-0204-6