Abstract
Objectives
Although high-throughput sequencing is revolutionising medicine, data on the actual cost of whole exome sequencing (WES) applications are needed. We aimed at assessing the cost of WES at a French cancer institute in 2015 and 2018.
Methods
Actual costs of WES application in oncology research were determined using both micro-costing and gross-costing for the years 2015 and 2018, before and after the acquisition of a new sequencer. The entire workflow process of a WES test was tracked, and the number and unit price of each resource were identified at the most detailed level, from library preparation to bioinformatics analyses. In addition, we conducted an ad hoc analysis of the bioinformatics storage costs of data issued from WES analyses.
Results
The cost of WES has decreased substantially, from €1921 per sample (i.e. cost of €3842 per patient) in 2015 to €804 per sample (i.e. cost of €1,608 per patient) in 2018, representing a decrease of 58%. In the meantime, the cost of bioinformatics storage has increased from €19,836 to €200,711.
Conclusion
This study suggests that WES cost has decreased significantly in recent years. WES has become affordable, even though clinical utility and efficiency still need to be confirmed.

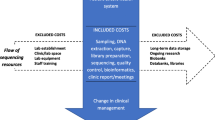
Source: Gustave Roussy genomic platform and bioinformatics platform

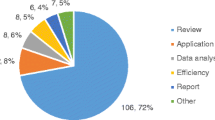
Source: Gustave Roussy genomic platform and bioinformatics platform

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buxbaum, J.D., Daly, M.J., Devlin, B., Lehner, T., Roeder, K., State, M.W.: The Autism Sequencing Consortium: Large scale, high throughput sequencing in autism spectrum disorders. Neuron (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2012.12.008
Xue, Y., Ankala, A., Wilcox, W.R., Hegde, M.R.: Solving the molecular diagnostic testing conundrum for Mendelian disorders in the era of next-generation sequencing: single-gene, gene panel, or exome/genome sequencing. Genet. Med. Off. J. Am. Coll. Med. Genet. 17, 444–451 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/gim.2014.122
Mosele, F., Remon, J., Mateo, J., Westphalen, C.B., Barlesi, F., Lolkema, M.P., Normanno, N., Scarpa, A., Robson, M., Meric-Bernstam, F., Wagle, N., Stenzinger, A., Bonastre, J., Bayle, A., Michiels, S., Bièche, I., Rouleau, E., Jezdic, S., Douillard, J.-Y., Reis-Filho, J.S., Dienstmann, R., André, F.: Recommendations for the use of next-generation sequencing (NGS) for patients with metastatic cancers: a report from the ESMO Precision Medicine Working Group. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annonc.2020.07.014
Mueller, S., Jain, P., Liang, W.S., Kilburn, L., Kline, C., Gupta, N., Panditharatna, E., Magge, S.N., Zhang, B., Zhu, Y., Crawford, J.R., Banerjee, A., Nazemi, K., Packer, R.J., Petritsch, C.K., Truffaux, N., Roos, A., Nasser, S., Phillips, J.J., Solomon, D., Molinaro, A., Waanders, A.J., Byron, S.A., Berens, M.E., Kuhn, J., Nazarian, J., Prados, M., Resnick, A.C.: A pilot precision medicine trial for children with diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma-PNOC003: a report from the Pacific Pediatric Neuro-Oncology Consortium. Int. J. Cancer. 145, 1889–1901 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.32258
Massard, C., Michiels, S., Ferté, C., Deley, M.-C.L., Lacroix, L., Hollebecque, A., Verlingue, L., Ileana, E., Rosellini, S., Ammari, S., Ngo-Camus, M., Bahleda, R., Gazzah, A., Varga, A., Postel-Vinay, S., Loriot, Y., Even, C., Breuskin, I., Auger, N., Job, B., Baere, T.D., Deschamps, F., Vielh, P., Scoazec, J.-Y., Lazar, V., Richon, C., Ribrag, V., Deutsch, E., Angevin, E., Vassal, G., Eggermont, A., André, F., Soria, J.-C.: High-throughput genomics and clinical outcome in hard-to-treat advanced cancers: results of the MOSCATO 01 trial. Cancer Discov. 7, 586–595 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-1396
European Proof-of-Concept Therapeutic Stratification Trial of Molecular Anomalies in Relapsed or Refractory Tumors - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02813135
Harttrampf, A.C., Lacroix, L., Deloger, M., Deschamps, F., Puget, S., Auger, N., Vielh, P., Varlet, P., Balogh, Z., Abbou, S., Allorant, A., Valteau-Couanet, D., Sarnacki, S., Gamiche-Rolland, L., Meurice, G., Minard-Colin, V., Grill, J., Brugieres, L., Dufour, C., Gaspar, N., Michiels, S., Vassal, G., Soria, J.-C., Geoerger, B.: Molecular screening for cancer treatment optimization (MOSCATO-01) in pediatric patients: a single-institutional prospective molecular stratification trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 23, 6101–6112 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-0381
Clinical application of comprehensive next generation sequencing in the management of metastatic cancer in adults. J. Clin. Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2017.35.15_suppl.101
Park, J.J.H., Siden, E., Zoratti, M.J., Dron, L., Harari, O., Singer, J., Lester, R.T., Thorlund, K., Mills, E.J.: Systematic review of basket trials, umbrella trials, and platform trials: a landscape analysis of master protocols. Trials 20, 572 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-019-3664-1
Malone, E.R., Oliva, M., Sabatini, P.J.B., Stockley, T.L., Siu, L.L.: Molecular profiling for precision cancer therapies. Genome Med. 12, 8 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13073-019-0703-1
Lian, T., Li, C., Wang, H.: Trametinib in the treatment of multiple malignancies harboring MEK1 mutations. Cancer Treat. Rev. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2019.101907
The Cost of Sequencing a Human Genome, https://www.genome.gov/about-genomics/fact-sheets/Sequencing-Human-Genome-cost. Accessed 23 Dec 2019
Wright, C.: PHG Foundation: Next steps in the sequence: the implications of whole genome sequencing for health in the UK. https://www.phgfoundation.org/documents/report_next_steps_Sequence.pdf. Accessed 23 Dec 2019
Schwarze, K., Buchanan, J., Taylor, J.C., Wordsworth, S.: Are whole-exome and whole-genome sequencing approaches cost-effective? A systematic review of the literature. Genet. Med. Off. J. Am. Coll. Med. Genet. 20, 1122–1130 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/gim.2017.247
Plöthner, M., Frank, M., von der Schulenburg, J.-M.G.: Cost analysis of whole genome sequencing in German clinical practice. Eur. J. Health Econ. 18, 623–633 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10198-016-0815-0
Beale, S., Sanderson, D., Sanniti, A., Dundar, Y., Boland, A.: A scoping study to explore the cost-effectiveness of next-generation sequencing compared with traditional genetic testing for the diagnosis of learning disabilities in children. Health Technol. Assess. Winch. Engl. 19, 1–90 (2015)
Frank, M., Prenzler, A., Eils, R., von der Schulenburg, G.J.-M., Lander, E., Linton, L., Birren, B., Venter, J., Adams, M., Myers, E., Collins, F., Green, E., Guttmacher, A., Guyer, M., Majewski, J., Schwartzentruber, J., Lalonde, E., Montpetit, A., Jabado, N., Ng, S., Turner, E., Robertson, P., Turner, E., Lee, C., Ng, S., Nickerson, D., Shendure, J., Sanger, F., Nicklen, S., Coulson, A., Bubnoff, A.V., Drummond, M., Sculpher, M., Torrance, G., O’Brien, B., Stoddart, G., Tucker, T., Marra, M., Friedman, J., Glenn, T., Pareek, C., Smoczynski, R., Tretyn, A., Moore, G., Shendure, J., Ji, H., Kircher, M., Kelso, J., Mardis, E., Stone, K., Levenson, D., Bick, D., Dimmock, D., Carr, P., Church, G., Valle, D., Hansson, M., Wolf, S., Lawrenz, F., Nelson, C., Wolf, S., Crock, B., Ness, B.V.: Genome sequencing: a systematic review of health economic evidence. Health Econ. Rev. 3, 29 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/2191-1991-3-29
McInerney-Leo, A.M., Marshall, M.S., Gardiner, B., Benn, D.E., McFarlane, J., Robinson, B.G., Brown, M.A., Leo, P.J., Clifton-Bligh, R.J., Duncan, E.L.: Whole exome sequencing is an efficient and sensitive method for detection of germline mutations in patients with phaeochromcytomas and paragangliomas. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 80, 25–33 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1111/cen.12331
Neveling, K., Feenstra, I., Gilissen, C., Hoefsloot, L.H., Kamsteeg, E.-J., Mensenkamp, A.R., Rodenburg, R.J.T., Yntema, H.G., Spruijt, L., Vermeer, S., Rinne, T., van Gassen, K.L., Bodmer, D., Lugtenberg, D., de Reuver, R., Buijsman, W., Derks, R.C., Wieskamp, N., van den Heuvel, B., Ligtenberg, M.J.L., Kremer, H., Koolen, D.A., van de Warrenburg, B.P.C., Cremers, F.P.M., Marcelis, C.L.M., Smeitink, J.A.M., Wortmann, S.B., van Zelst-Stams, W.A.G., Veltman, J.A., Brunner, H.G., Scheffer, H., Nelen, M.R.: A post-hoc comparison of the utility of sanger sequencing and exome sequencing for the diagnosis of heterogeneous diseases. Hum. Mutat. 34, 1721–1726 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.22450
Schieving, J.H.: PP05.5 – 3064: the role of exome sequencing in daily pediatric neurology practice. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 19, S47 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1090-3798(15)30154-9
Schofield, D., Alam, K., Douglas, L., Shrestha, R., MacArthur, D.G., Davis, M., Laing, N.G., Clarke, N.F., Burns, J., Cooper, S.T., North, K.N., Sandaradura, S.A., O’Grady, G.L.: Cost-effectiveness of massively parallel sequencing for diagnosis of paediatric muscle diseases. NPJ Genom. Med. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41525-017-0006-7
Soden, S.E., Saunders, C.J., Willig, L.K., Farrow, E.G., Smith, L.D., Petrikin, J.E., LePichon, J.-B., Miller, N.A., Thiffault, I., Dinwiddie, D.L., Twist, G., Noll, A., Heese, B.A., Zellmer, L., Atherton, A.M., Abdelmoity, A.T., Safina, N., Nyp, S.S., Zuccarelli, B., Larson, I.A., Modrcin, A., Herd, S., Creed, M., Ye, Z., Yuan, X., Brodsky, R.A., Kingsmore, S.F.: Effectiveness of exome and genome sequencing guided by acuity of illness for diagnosis of neurodevelopmental disorders. Sci. Transl. Med. 6, 265 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3010076
Stark, Z., Schofield, D., Alam, K., Wilson, W., Mupfeki, N., Macciocca, I., Shrestha, R., White, S.M., Gaff, C.: Prospective comparison of the cost-effectiveness of clinical whole-exome sequencing with that of usual care overwhelmingly supports early use and reimbursement. Genet. Med. 19, 867–874 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/gim.2016.221
Yohe, S., Thyagarajan, B.: Review of clinical next-generation sequencing. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 141, 1544–1557 (2017). https://doi.org/10.5858/arpa.2016-0501-RA
Fokstuen, S., Makrythanasis, P., Hammar, E., Guipponi, M., Ranza, E., Varvagiannis, K., Santoni, F.A., Albarca-Aguilera, M., Poleggi, M.E., Couchepin, F., Brockmann, C., Mauron, A., Hurst, S.A., Moret, C., Gehrig, C., Vannier, A., Bevillard, J., Araud, T., Gimelli, S., Stathaki, E., Paoloni-Giacobino, A., Bottani, A., Sloan-Béna, F., Sizonenko, L.D., Mostafavi, M., Hamamy, H., Nouspikel, T., Blouin, J.L., Antonarakis, S.E.: Experience of a multidisciplinary task force with exome sequencing for Mendelian disorders. Hum. Genom. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40246-016-0080-4
Monroe, G.R., Frederix, G.W., Savelberg, S.M.C., de Vries, T.I., Duran, K.J., van der Smagt, J.J., Terhal, P.A., van Hasselt, P.M., Kroes, H.Y., Verhoeven-Duif, N.M., Nijman, I.J., Carbo, E.C., van Gassen, K.L., Knoers, N.V., Hövels, A.M., van Haelst, M.M., Visser, G., van Haaften, G.: Effectiveness of whole-exome sequencing and costs of the traditional diagnostic trajectory in children with intellectual disability. Genet. Med. 18, 949–956 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/gim.2015.200
Bonnefond, A., Philippe, J., Durand, E., Muller, J., Saeed, S., Arslan, M., Martínez, R., Graeve, F.D., Dhennin, V., Rabearivelo, I., Polak, M., Cavé, H., Castaño, L., Vaxillaire, M., Mandel, J.-L., Sand, O., Froguel, P.: Highly sensitive diagnosis of 43 monogenic forms of diabetes or obesity through one-step PCR-based enrichment in combination with next-generation sequencing. Diabetes Care 37, 460–467 (2014). https://doi.org/10.2337/dc13-0698
Gordon, L.G., White, N.M., Elliott, T.M., Nones, K., Beckhouse, A.G., Rodriguez-Acevedo, A.J., Webb, P.M., Lee, X.J., Graves, N., Schofield, D.J.: Estimating the costs of genomic sequencing in cancer control. BMC Health Serv. Res. 20, 492 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-020-05318-y
Sabatini, L.M., Mathews, C., Ptak, D., Doshi, S., Tynan, K., Hegde, M.R., Burke, T.L., Bossler, A.D.: Genomic sequencing procedure microcosting analysis and health economic cost-impact analysis: a report of the Association for Molecular Pathology. J. Mol. Diagn. 18, 319–328 (2016)
Sabatini, L.M., Mathews, C., Ptak, D., Doshi, S., Tynan, K., Hegde, M.R., Burke, T.L., Bossler, A.D.: Genomic sequencing procedure microcosting analysis and health economic cost-impact analysis: a report of the association for molecular pathology. J. Mol. Diagn. JMD 18, 319–328 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmoldx.2015.11.010
Schwarze, K., Buchanan, J., Fermont, J.M., Dreau, H., Tilley, M.W., Taylor, J.M., Antoniou, P., Knight, S.J.L., Camps, C., Pentony, M.M., Kvikstad, E.M., Harris, S., Popitsch, N., Pagnamenta, A.T., Schuh, A., Taylor, J.C., Wordsworth, S.: The complete costs of genome sequencing: a microcosting study in cancer and rare diseases from a single center in the United Kingdom. Genet. Med. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41436-019-0618-7
Postel-Vinay, S., Boursin, Y., Massard, C., Hollebecque, A., Ileana, E., Chiron, M., Jung, J., Lee, J.S., Balogh, Z., Adam, J., Vielh, P., Angevin, E., Lacroix, L., Soria, J.-C.: Seeking the driver in tumours with apparent normal molecular profile on comparative genomic hybridization and targeted gene panel sequencing: what is the added value of whole exome sequencing? Ann. Oncol. 27, 344–352 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdv570
Drummond, M.F., Sculpher, M.J., Claxton, K., Stoddart, G.L., Torrance, G.W.: Methods for the Economic Evaluation of Health Care Programmes. Oxford University Press (2015)
Guerre, P., Hayes, N., Bertaux, A.-C.: French Costing Group: [Hospital costs estimation by micro and gross-costing approaches]. Rev. Epidemiol. Sante Publ. 66(Suppl 2), S65–S72 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respe.2018.02.001
Wetterstrand, K.A.: DNA sequencing costs: data from the NHGRI Large-Scale Genome Sequencing Program. 2016. www.genome.gov/sequencingcostsdata. Accessed 23 Dec 2019
Perrier, L., Heinz, D., Baffert, S., Zou, Z., Zaleski, I.D., Rouleau, E., Wang, Q., Haddad, V., Bringuier, P., Merlio, J., Caumont, C., Lacroix, L., Marino, P., Borget, I.: Cost of genome analysis: the sanger sequencing method. Value Health. 18, A353 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jval.2015.09.654
Van Nimwegen, K.J.M., Van Soest, R.A., Veltman, J.A., Nelen, M.R., Van Der Wilt, G.J., Vissers, L.E.L.M., Grutters, J.P.C.: Is the 1000 genome as near as we think? A cost analysis of next-generation sequencing. Clin. Chem. 62, 1458–1464 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2016.258632
Tsiplova, K., Zur, R.M., Marshall, C.R., Stavropoulos, D.J., Pereira, S.L., Merico, D., Young, E.J., Sung, W.W.L., Scherer, S.W., Ungar, W.J.: A microcosting and cost–consequence analysis of clinical genomic testing strategies in autism spectrum disorder. Genet. Med. 19, 1268–1275 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/gim.2017.47
Taber, K.A.J., Dickinson, B.D., Wilson, M.: The promise and challenges of next-generation genome sequencing for clinical care. JAMA Intern. Med. 174, 275–280 (2014)
Muir, P., Li, S., Lou, S., Wang, D., Spakowicz, D.J., Salichos, L., Zhang, J., Weinstock, G.M., Isaacs, F., Rozowsky, J., Gerstein, M.: The real cost of sequencing: scaling computation to keep pace with data generation. Genome Biol. 17, 53 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-016-0917-0
Mardis, E.R.: The $1,000 genome, the $100,000 analysis? Genome Med. 2, 84 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1186/gm205
Glenn, T.C.: Field guide to next-generation DNA sequencers. Mol Ecol. Resour. 11, 759–769 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-0998.2011.03024.x
Souilmi, Y., Lancaster, A.K., Jung, J.-Y., Rizzo, E., Hawkins, J.B., Powles, R., Amzazi, S., Ghazal, H., Tonellato, P.J., Wall, D.P.: Scalable and cost-effective NGS genotyping in the cloud. BMC Med. Genom. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12920-015-0134-9
Sboner, A., Mu, X.J., Greenbaum, D., Auerbach, R.K., Gerstein, M.B.: The real cost of sequencing: higher than you think! Genome Biol. 12, 125 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2011-12-8-125
Sun, Y., Ruivenkamp, C.A.L., Hoffer, M.J.V., Vrijenhoek, T., Kriek, M., van Asperen, C.J., den Dunnen, J.T., Santen, G.W.E.: Next-generation diagnostics: gene panel, exome, or whole genome? Hum. Mutat. 36, 648–655 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.22783
Flinter, F.: Should we sequence everyone’s genome? No. BMJ. 346, f3132 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.f3132
Douglas, M.P., Ladabaum, U., Pletcher, M.J., Marshall, D.A., Phillips, K.A.: Economic evidence on identifying clinically actionable findings with whole genome sequencing: a scoping review. Genet Med Off J Am Coll Med Genet 18, 111–116 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/gim.2015.69
Caulfield, T., Evans, J., McGuire, A., McCabe, C., Bubela, T., Cook-Deegan, R., Fishman, J., Hogarth, S., Miller, F.A., Ravitsky, V., Biesecker, B., Borry, P., Cho, M.K., Carroll, J.C., Etchegary, H., Joly, Y., Kato, K., Lee, S.S.-J., Rothenberg, K., Sankar, P., Szego, M.J., Ossorio, P., Pullman, D., Rousseau, F., Ungar, W.J., Wilson, B.: Reflections on the cost of “Low-Cost” whole genome sequencing: framing the health policy debate. PLoS Biol. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1001699
Merlevede, J., Droin, N., Qin, T., Meldi, K., Yoshida, K., Morabito, M., Chautard, E., Auboeuf, D., Fenaux, P., Braun, T., Itzykson, R., de Botton, S., Quesnel, B., Commes, T., Jourdan, E., Vainchenker, W., Bernard, O., Pata-Merci, N., Solier, S., Gayevskiy, V., Dinger, M.E., Cowley, M.J., Selimoglu-Buet, D., Meyer, V., Artiguenave, F., Deleuze, J.-F., Preudhomme, C., Stratton, M.R., Alexandrov, L.B., Padron, E., Ogawa, S., Koscielny, S., Figueroa, M., Solary, E.: Mutation allele burden remains unchanged in chronic myelomonocytic leukaemia responding to hypomethylating agents. Nat. Commun. 7, 10767 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10767
Bertucci, F., Ng, C.K.Y., Patsouris, A., Droin, N., Piscuoglio, S., Carbuccia, N., Soria, J.C., Dien, A.T., Adnani, Y., Kamal, M., Garnier, S., Meurice, G., Jimenez, M., Dogan, S., Verret, B., Chaffanet, M., Bachelot, T., Campone, M., Lefeuvre, C., Bonnefoi, H., Dalenc, F., Jacquet, A., De Filippo, M.R., Babbar, N., Birnbaum, D., Filleron, T., Le Tourneau, C., André, F.: Genomic characterization of metastatic breast cancers. Nature 569, 560–564 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1056-z
Wright, C.: PHG Foundation: Next Steps in the Sequence: The Implications of Whole Genome Sequencing for Health in the UK. PHG Foundation, Cambridge (2011)
Plan France Médecine Génomique 2025 / aviesan, https://www.aviesan.fr/aviesan/accueil/toute-l-actualite/plan-france-medecine-genomique-2025. Accessed 23 Dec 2019
Nimwegen, K., van Vissers, L., Willemsen, M., Schieving, J., Veltman, J., Wil, G., van Grutters, D.J.P.: The cost-effectiveness of whole-exome sequencing in complex paediatric neurology. Value Health. 19, A695 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jval.2016.09.1998
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Marie Breckler, who was timed during the realisation of a WES experiment. The authors acknowledge laboratory and bioinformatics teams, including Guillaume Meurice. Our study received financial support from the French National Agency for Research (ANR-10-IBHU-0001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Arnaud Bayle: None. Nathalie Droin: None. Benjamin Besse: Sponsored Research at Gustave Roussy Cancer Center: Abbvie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Biogen, Blueprint Medicines, BMS, Celgene, Eli Lilly, GSK, Ignyta, IPSEN, Merck KGaA, MSD, Nektar, Onxeo, Pfizer, Pharma Mar, Sanofi, Spectrum Pharmaceuticals, Takeda, Tiziana Pharma. Zou Zhaomin: None. Yannick Boursin: None. Simon Rissel: None. Eric Solary: None. Ludovic Lacroix: Sponsored Research at Gustave Roussy Cancer Center: Abbott, Astrazeneca, Bayer, Beckman, Boeringer, BMS, Illumina, Genomic Health, Myriad, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Siemens, Thermofisher, VelaDx. Etienne Rouleau: AstraZeneca: Consulting fees—Travel, BMS: Consulting fees—Travel, Roche: consulting fees. Isabelle Borget: Roche, merck, Novartis, Janssen: consulting fees. Julia Bonastre: BMS: Travel for attending to Congress, consulting fees; MSD: consulting fees.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bayle, A., Droin, N., Besse, B. et al. Whole exome sequencing in molecular diagnostics of cancer decreases over time: evidence from a cost analysis in the French setting. Eur J Health Econ 22, 855–864 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10198-021-01293-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10198-021-01293-1