Abstract
Objective
The present health economic analysis investigated the cost-effectiveness-ratios of either (1) rituximab or (2) an alternative TNF-alpha-inhibiting agent as second line biological treatment in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and an inadequate response to etanercept therapy.
Methods
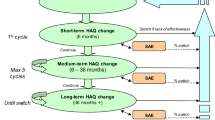
Incremental cost per quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) gained by rituximab treatment of RA is compared to TNF-inhibitor change (standard sequence) in a Markov-model (perspective: health care payer, full life-time approach). Direct cost components taken into account were treatment costs (medication-, administration- and monitoring costs) and resource utilisation (outpatient costs, inpatient costs). Indirect costs were estimated separately by the assessment of impaired work capacity due to RA (2008 Euro currency, discount rate 3.5%). Utility measures for the different treatment options were obtained from the ACR-response rates of published pivotal clinical trials.
Results
Direct costs amount to € 178,373 (standard sequence) and € 192,295 (rituximab sequence), respectively, rendering incremental direct costs of € 13,922. Incremental utilities yield 0.57 QALYs and the incremental cost-effectiveness-ratio (ICER) of rituximab compared to the standard sequence amounts to € 24,517. Inclusion of indirect costs leads to less incremental costs and a lower ICER of € 15,565/QALY. Thus, ICERs stay beneath the accepted threshold of € 50,000/QALY.
Conclusion
Rituximab appears to be a cost-effective treatment alternative compared to the switch between TNF-inhibitors as second line biological treatment in patients with active RA having failed etanercept.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smolen, J., Aletaha, D.: The burden of rheumatoid arthritis and access to treatment: a medical overview. Eur. J. Health Econ. 8(Suppl 2), S39–S47 (2008)
Kobelt, G., Jönsson, B.: The burden of rheumatoid arthritis and access to treatment: outcome and cost-utility of treatments. Eur. J. Health Econ. 8(Suppl 2), 95–106 (2008)
Kobelt, G., Woronoff, A.S., Richard, B., Peeters, P., Sany, J.: Disease status, costs and quality of life of patients with rheumatoid arthritis in France: the ECO-PR study. Joint Bone Spine 75(4), 408–415 (2008)
Pincus, T., Kavanaugh, A., Sokka, T.: Benefit/risk of therapies for rheumatoid arthritis: underestimation of the “side effects” or risks of RA leads to underestimation of the benefit/risk of therapies. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 22(suppl 35), S2–S11 (2004)
Kavanaugh, A., Cohen, S., Cush, J.: The evolving use of tumour necrosis factor inhibitors in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 31, 1881–1884 (2004)
Kavanaugh, A.: Economic consequences of established rheumatoid arthritis and its treatment. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 21, 929–942 (2007)
Wong, J.: Cost-effectiveness of anti-tumor necrosis factor agents. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 22(suppl 35), S65–S70 (2004)
Solomon, D., Maetzel, A.: Pharmacoeconomics of prescribing for rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Adv. Rheumatol. 2, 91–96 (2004)
Edwards, J.C., Szczepanski, L., Szechinski, J., Filipowicz-Sosnowska, A., Emery, P., Close, D.R., et al.: Efficacy of B-cell-targeted therapy with rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. New Engl. J. Med. 350, 2572–2581 (2004)
Emery, P., Fleischmann, R., Filipowicz-Sosnowska, A., Schechtman, J., Szczepanski, L., Kavanaugh, A., et al.: The efficacy and safety of rituximab in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite methotrexate treatment: results of a phase IIB randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging trial. Arthritis Rheum. 54, 1390–1400 (2006)
Cohen, S.B., Emery, P., Greenwald, M.W., Dougados, M., Furie, R.A., Genovese, M.C., et al.: Rituximab for rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy: results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III trial evaluating primary efficacy and safety at twenty-four weeks. Arthritis Rheum. 54, 2793–2806 (2006)
Manger, B., Michels, H., Nüsslein, H.G., Schneider, M., Sieper, J.: Komission Pharmakotherapie der deutschen Gesellschaft für Rheumatologie. Neufassung der Empfehlungen der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Rheumatologie zur Therapie mit Tumornekrosefaktor-hemmenden Wirkstoffen bei entzündlich-rheumatischen Erkrankungen (03/2006)
Kielhorn, A., Porter, D., Diamantopulos, A., Lewis, G.: Cost-utility analysis for the UK of rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis that failed to respond adequately to a biologic DMARD. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 24, 2639–2650 (2008)
Sculpher, M., Claxton, K., Brazier, J., Jönsson, B.: Nice guidelines for economic evaluation: methodological developments and remaining uncertainties. European conference on health economics 2004, London
Data on file reported to Roche by Zink A et al. 2004
Keystone, E., Fleischmann, R., Emery, P., Chubick, A., Duogados, M., Baldassare, A.R., et al.: Repeated treatment courses of rituximab in rheumatoid arthritis: sustained efficacy in patients with an inadequate response to one or more TNF inhibitors. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 66(Suppl II), 432 (2007)
Emery, P., Furst, D.E., Ferraccioli, G., Udell, J., van Vollenhoven, R.F., Rowe, K., et al.: Sustained efficacy of repeat treatment courses of rituximab in rheumatoid arthritis patients with an inadequate response to disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 66(Suppl II), 430 (2007)
Lajas, C., Abasolo, L., Bellajdel, B., Hernandez-Garcia, C., Carmona, L., Vargas, E., et al.: Costs and predictors of costs in rheumatoid arthritis: a prevalence-based study. Arthritis Rheum. 49, 64–70 (2003)
Michaud, K., Messer, J., Choi, H.K., Wolfe, F.: Direct medical costs and their predictors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a three-year study of 7, 527 patients. Arthritis Rheum. 48, 2750–2762 (2003)
Pugner, K.M., Scott, D.I., Holmes, J.W., Hieke, K.: The costs of rheumatoid arthritis: an international long-term view. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 29, 305–320 (2000)
Yelin, E., Wanke, L.A.: An assessment of the annual and long-term direct costs of rheumatoid arthritis: the impact of poor function and functional decline. Arthritis Rheum. 42, 1209–1218 (1999)
Weinblatt, M.E., Kremer, J.M., Bankhurst, A.D., Bulpitt, K.J., Fleischmann, R.M., Fox, R.I., Jackson, C.G. et al.: A trial of etanercept, a recombinant tumor necrosis factor receptor-FC fusion protein, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving methotrexate. New Engl. J. Med. 340; 253–259 (1999)
Keystone, E.C., Kavanaugh, A.F., Sharp, J.T., Tannenbaum, H., Hua, Y., Teoh, L.S., et al.: Radiographic, clinical and functional outcomes of treatment with adalimumab (a human anti-tumor necrosis factor monoclonal antibody) in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis receiving concomitant methotrexate therapy. Arthritis Rheum. 50, 1400–1411 (2004)
Genovese, M.C., Becker, J.C., Schiff, M., Luggen, M., Sherrer, Y., Kremer, J., Birbara, C., Box, J., Natarajan, K., Nuamah, I., Li, T., Aranda, T., Hagerty, D.T., Dougados, M.: Abatacept for rheumatoid arthritis refractory to tumour necrosis factor alpha inhibition. New Engl. J. Med. 353, 1114–1123 (2005)
Maini, R., St Clair, E.W., Breedveld, F., Furst, D., Kalden, J., Weisman, M., et al.: Infliximab (chimeric anti-tumour necrosis factor α monoclonal antibody) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving concomitant methotrexate: a randomised phase III trial. Lancet 354, 1932–1939 (1999)
Bansback, N., Brennan, A., Ghatnekar, O.: Cost-effectiveness of adalimumab in the treatment of patients with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis in Sweden. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 64, 995–1002 (2005)
Scott, D.L., Garood, T.: Quality of life measures: use and abuse. Baillieres Clin. Rheumatol. 14, 663–687 (2000)
Briggs, A.H., O′Brien, B.J., Blackhouse, G.: Thinking outside the box: recent advances in the analysis and presentation of uncertainty in cost-effectiveness studies. Annu. Rev. Public. Health 23, 377–401 (2002)
O′Brien, B.J., Briggs, A.H.: Analysis of uncertainty in health care cost-effectiveness studies: an introduction to statistical issues and methods. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 11, 455–468 (2002)
Finckh, A., Ciurea, A., Brulhart, L., Kyburz, D., Moller, B., Dehler, S., et al.: B cell depletion may be more effective than switching to an alternative anti-tumor necrosis factor agent in rheumatoid arthritis patients with inadequate response to anti-tumor necrosis factor agents. Arthritis Rheum. 56, 1417–1423 (2007)
Lindgren, P., Geborek, P., Kobelt, G.: Modeling the cost-effectiveness of treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with rituximab using registry data from southern Sweden. Int. J. Technol. Assess. Health Care 25, 181–189 (2009)
Russell, A., Beresniak, A., Bessette, L., Haraoui, B., Rahman, P., Thorne, C., Maclean, R., Dupont, D.: Cost-effectiveness modeling of abatacept versus other biologic agents in DMARDS and anti-TNF inadequate responders for the management of moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 28, 403–412 (2009)
Brennan, A., Bansback, N., Nixon, R., Madan, J., Harrison, M., Watson, K., Symmons, D.: Modelling the cost effectiveness of TNF-alpha antagonists in the management of rheumatoid arthritis: results from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Registry. Rheumatology 46, 1345–1354 (2007)
Vera-Llonch, M., Massarotti, E., Wolfe, F., Shadick, N., Westhovens, R., Sofrygin, O., Maclean, R., Li, T., Oster, G.: Cost-effectiveness of abatacept in patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis and inadequate response to tumour necrosis factor-alpha antagonists. J. Rheumatol. 35, 1745–1753 (2008)
Glenny, A., Altman, D., Song, F., Sakarovitch, C., Deeks, J., D’Amico, R. et al.: Indirect comparisons of competing interventions. Health Technol. Assess. 2005;9(26)
Wong, J.B., Singh, G., Kavanaugh, A.: Estimating the cost-effectiveness of 54 weeks of infliximab for rheumatoid arthritis. Am. J. Med. 113, 400–408 (2002)
Kobelt, G., Jönsson, L., Young, A., Eberhardt, K.: The cost-effectiveness of infliximab (Remicade) in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in Sweden and the United Kingdom based on the ATTRACT study. Rheumatology 42, 326–335 (2003)
Hurst, S., Platen, E., Rachev, S.: Subordinated market index models: a comparison. In: Miura R (ed) Asia-Pacific financial markets, vol 4(2). Springer, Berlin, pp. 97–124
Kobelt, G., Eberhardt, K., Jönsson, L., Jönsson, B.: Economic consequences of the progression of rheumatoid arthritis in Sweden. Arthritis Rheum. 42(2):347–356 (1999)
Acknowledgments
Conflict of interest statement
There are no competing interests to be declared by the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Merkesdal, S., Kirchhoff, T., Wolka, D. et al. Cost-effectiveness analysis of rituximab treatment in patients in Germany with rheumatoid arthritis after etanercept-failure. Eur J Health Econ 11, 95–104 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10198-009-0205-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10198-009-0205-y