Abstract
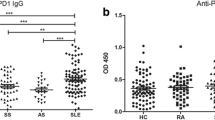
Autoantibodies to ribosomal P proteins (anti-P) are detected in 12–16% of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and have been found to be associated with some manifestations, including lupus psychosis, nephritis and hepatitis. We have recently disclosed that anti-P react with activated human peripheral blood monocytes, and enhance their production of tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin (IL)-6. It is also possible that anti-P might regulate other monocyte functions, including the regulation of T helper (Th) responses. The current study was therefore undertaken to explore the effects of anti-P on the induction of Th1 responses. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from healthy donors were cultured with affinity-purified anti-P or control IgG. Highly purified monocytes were cultured with interferon (IFN)-γ in the presence of anti-P or normal IgG. Anti-P significantly enhanced the production of IFN-γ by PBMC. Of note, anti-IL-12 monoclonal antibodies almost completely abrogated the anti-P-mediated upregulation of the IFN-γ production of PBMC. Accordingly, anti-P significantly enhanced the production of IL-12 by activated monocytes. These results indicate that anti-P induce Th1 responses by upregulating the production of IL-12 by activated monocytes. The data therefore suggest that anti-P play an important role in the pathogenesis of SLE through the promotion of Th1 responses.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Elkon K, Skelly S, Parnassa A, Moller W, Danho W, Weissbach H, et al. Identification and chemical synthesis of a ribosomal protein antigenic determinant in systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1986;83:7419–23.
Bonfa E, Golombek SJ, Kaufman LD, Skelly S, Weissbach H, Brot N, et al. Association between lupus psychosis and anti-ribosomal P protein antibodies. N Engl J Med. 1987;317:265–71.
Schneebaum AB, Singleton JD, West SG, Blodgett JK, Allen LG, Cheronis JC, et al. Association of psychiatric manifestations with antibodies to ribosomal P proteins in systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med. 1991;90:54–62.
Hulsey M, Goldstein R, Scully L, Surbeck W, Reichlin M. Antiribosomal P antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus: a case control study correlating hepatic and renal disease. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1995;74:252–6.
Koren E, Reichlin MW, Koscec M, Fugate RD, Reichlin M. Autoantibodies to the ribosomal P proteins react with a plasma membrane-related target on human cells. J Clin Invest. 1992;89:1236–41.
Hirohata S, Nakanishi K. Antiribosomal P protein antibody in human systemic lupus erythematosus reacts specifically with activated T cells. Lupus. 2001;10:612–21.
Nagai T, Arinuma Y, Yanagida T, Yamamoto K, Hirohata S. Anti-ribosomal P protein antibody in human systemic lupus erythematosus up-regulates the expression of proinflammatory cytokines by human peripheral blood monocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52:847–55.
Abbas AK, Murphy KM, Sher A. Functional diversity of helper T lymphocytes. Nature. 1996;383:787–93.
Constant SL, Bottomly K. Induction of Th1 and Th2 CD4+ T cell responses: the alternative approaches. Annu Rev Immunol. 1997;15:297–322.
Lichtman AH, Abbas AK. T-cell subsets: recruiting the right kind of help. Curr Biol. 1997;7:R242–4.
Romagnani S. The Th1/Th2 paradigm. Immunol Today. 1997;18:263–6.
Mosmann TR, Coffman RL. TH1 and TH2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:145–73.
Kamogawa Y, Minasi LA, Carding SR, Bottomly K, Flavell RA. The relationship of IL-4- and IFN gamma-producing T cells studied by lineage ablation of IL-4-producing cells. Cell. 1993;75:985–95.
Wolf SF, Temple PA, Kobayashi M, Young D, Dicig M, Lowe L, et al. Cloning of cDNA for natural killer cell stimulatory factor, a heterodimeric cytokine with multiple biologic effects on T and natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1991;146:3074–81.
Trinchieri G. Interleukin-12 and its role in the generation of Th1 cells. Immunol Today. 1993;14:335–8.
Manetti R, Parronchi P, Giudizi MG, Piccinni MP, Maggi E, Trinchieri G, et al. Natural killer cell stimulatory factor (interleukin 12 [IL12]) induces T helper type 1 (Th1)-specific immune responses and inhibits the development of IL-4-producing Th cells. J Exp Med. 1993;177:1199–204.
Schmitt E, Hoehn P, Germann T, Rüde E. Differential effects of interleukin-12 on the development of naive mouse CD4+ T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1994;24:343–7.
Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF, Masi AT, McShane DJ, Rothfield NF, et al. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982;25:1271–7.
Shibuya H, Nagai T, Ishii A, Yamamoto K, Hirohata S. Differential regulation of Th1 responses and CD154 expression in human CD4+ T cells by IFN-alpha. Clin Exp Immunol. 2003;132:216–24.
Shibuya H, Hirohata S. Differential effects of IFN-alpha on the expression of various TH2 cytokines in human CD4+ T cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005;116:205–12.
Hirohata S. Human Th1 responses driven by IL-12 are associated with enhanced expression of CD40 ligand. Clin Exp Immunol. 1999;115:78–85.
Collart MA, Baeuerle P, Vassalli P. Regulation of tumor necrosis factor α transcription in macrophages: involvement of four κB-like motifs and of constitutive and inducible forms of NF-κB. Mol Cell Biol. 1990;10:1498–506.
Liu H, Sidiropoulos P, Song G, Pagliari LJ, Birrer MJ, Stein B, et al. TNF-α gene expression in macrophages: regulation by NF-κB is independent of c-Jun or C/EBP β. J Immunol. 2000;164:4277–85.
Shimizu H, Mitomo K, Watanabe T, Okamoto S, Yamamoto K. Involvement of a NF-kappa B-like transcription factor in the activation of the interleukin-6 gene by inflammatory lymphokines. Mol Cell Biol. 1990;10:561–8.
Libermann TA, Baltimore D. Activation of interleukin-6 gene expression through the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1990;10:2327–34.
Zhang YH, Lin JX, Vilcek J. Interleukin-6 induction by tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 in human fibroblasts involves activation of a nuclear factor binding to a kappa B-like sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1990;10:3818–23.
Murphy TL, Cleveland MG, Kulesza P, Magram J, Murphy KM. Regulation of interleukin 12 p 40 expression through NF-kappa B half site. Mol Cell Biol. 1995;15:5258–67.
Ma X, Chow JM, Gri G, Carra G, Gerosa F, Wolf SF, et al. The interleukin 12 p40 gene promoter is primed by interferon gamma in monocytic cells. J Exp Med. 1996;183:147–57.
Gri G, Savio D, Trinchieri G, Ma X. Synergistic regulation of the human interleukin-12 p40 promoter by NFkB and Ets transcription factors in Epstein–Barr virus transformed B cells and macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:6431–8.
Li X, Qin J. Modulation of Toll-interleukin 1 receptor mediated signaling. J Mol Med. 2005;83:258–66.
Hagiwara E, Gourley MF, Lee S, Klinman DK. Disease severity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus correlates with an increased ratio of interleukin 10: interferon-gamma-secreting cells in the peripheral blood. Arthritis Rheum. 1996;39:379–85.
Okada H, Konishi K, Nakazato Y, Kanno Y, Suzuki H, Sakaguchi H, et al. Interleukin-4 expression in mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis. Am J Kidney Dis. 1994;23:242–6.
Funauchi M, Ikoma S, Enomoto H, Horiuchi A. Decreased Th1-like and increased Th2-like cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Scand J Rheumatol. 1998;27:219–24.
Al-Janadi M, Al-Balla S, Al-Dalaan A, Raziuddin S. Cytokine profile in systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and other rheumatic disease. J Clin Immunol. 1993;13:58–67.
Takahashi S, Fossati L, Iwamoto M, Merino R, Motta R, Kobayakawa T, et al. Imbalance towards Th1 predominance is associated with acceleration of lupus-like autoimmune syndrome in MRL mice. J Clin Invest. 1996;97:1597–604.
Akahoshi M, Nakashima H, Tanaka Y, Kohsaka T, Nagano S, Ohgami E, et al. Th1/Th2 balance of peripheral T helper cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1999;42:1644–8.
Tucci M, Lombardi L, Richards HB, DammaccoF Silvestris F. Overexpression of interleukin-12 and T helper 1 predominance in lupus nephritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2008;154:247–54.
Schmidt-Weber CB, Akdis M, Akdis CA. TH17 cells in the big picture of immunology. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;120:247–54.
Ouyang W, Kolls JK, Zheng Y. The biological functions of T helper 17 cell effector cytokines in inflammation. Immunity. 2008;28:454–67.
Takatori H, Kanno Y, Chen Z, O’Shea JJ. New complexities in helper T cell fate determination and the implications for autoimmune diseases. Mod Rheumatol. 2008;18:533–41.
Zhang Z, Kyttaris VC, Tsokos GC. The role of IL-23/IL-17 axis in lupus nephritis. J Immunol. 2009;183:3160–9.
Jacob N, Yang H, Pricop L, Liu Y, Gao X, Zheng SG, et al. Accelerated pathological and clinical nephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus-prone New Zealand Mixed 2328 mice doubly deficient in TNF receptor 1 and TNF receptor 2 via a Th17-associated pathway. J Immunol. 2009;182:2532–41.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Nagai, T., Yanagida, T. & Hirohata, S. Anti-ribosomal P protein antibody induces Th1 responses by enhancing the production of IL-12 in activated monocytes. Mod Rheumatol 21, 57–62 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-010-0354-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-010-0354-y