Abstract
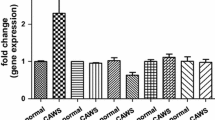
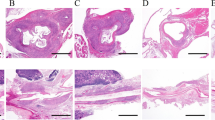
We investigated the inhibitory effect of human immunoglobulin (h-Ig) on the development of coronary arteritis in a murine model of vasculitis induced with a Candida albicans water-soluble fraction (CAWS). CAWS was intraperitoneally injected to C57BL/6 mice for 5 days. Then h-Ig was administered according to various schedules. The animals were sacrificed in week 5, and the status of vasculitis in the coronary arteries and the aortic root was investigated histologically. The groups in which h-Ig was administered for 5 days from day 3 and from day 5 of the experiment showed a significant reduction in the incidence of panvasculitis. In addition, the scope and severity of the inflammation of the aortic root and the coronary arteries were reduced in both groups. In the group administered h-Ig for 5 days from day 1 and the group administered a high dose of h-Ig once on day 1 or day 3, no suppression of development of vasculitis was observed. The h-Ig acted by suppressing the generation and progression of vasculitis in this CAWS-induced murine vasculitis model.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kawasaki T. Acute febrile muco-cutaneous lymph node syndrome in young children with unique digital desquamation. Jpn J Allergol. 1967;16:178–222.
Kawasaki T, Kosaki F, Okawa S, Shigematsu I, Yanagawa H. New infantile acute febrile mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome (MLNS) prevailing in Japan. Pediatrics. 1974;54:271–6.
Nakamura Y, Yashiro M, Uehara R, Oki I, Kayaba K, Yanagawa H. Increasing incidence of Kawasaki disease in Japan: nationwide survey. Pediatr Int. 2008;50:287–90.
Naoe S, Takahashi K, Masuda H, et al. Kawasaki disease with particular emphasis on arterial lesions. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1991;41:785–97.
Murata H. Experimental Candida-induced arteritis in mice. Relation to arteritis in the mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome. Microbiol Immunol. 1979;23:825–31.
Murata H, Iijima H, Naoe S, Atobe T, Uchiyama S, Arakawa S. The pathogenesis of experimental arteritis induced by Candida alkali extract in mice. Jpn J Exp Med. 1987;57:305–13.
Takahashi K, Oharaseki T, Wakayama M, Yokouchi Y, Naoe S, Murata H. Histopathological features of murine systemic vasculitis caused by Candida albicans extract—an animal model of Kawasaki disease. Inflamm Res. 2004;53:72–7.
Kurihara K, Miura NN, Uchiyama M, Ohno N, Adachi Y, Aizawa M, et al. Measurement of blood clearance time by Limulus G test of Candida water-soluble polysaccharide fraction, CAWS, in mice. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2000;29:69–76.
Kurihara K, Shingo Y, Miura NN, Horie S, Usui Y, Adachi Y, et al. Effect of CAWS, a mannoprotein–beta-glucan complex of Candida albicans, on leukocyte, endothelial cell, and platelet functions in vitro. Biol Pharm Bull. 2003;26:233–40.
Uchiyama M, Ohno N, Miura NN, Adachi Y, Aizawa MW, Tamura H. Chemical and immunochemical characterization of limulus factor G-activating substance of Candida spp. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 1999;24:411–20.
Miura NN, Shingo Y, Adachi Y, Okawara IA, Oharaseki T, Takahashi K, et al. Induction of coronary arteritis with administration of CAWS (Candida albicans water soluble fraction) depending on mouse strains. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2004;26:527–43.
Miura NN, Harada T, Shinohara H, Kurihara K, Adachi Y, Okawara IA, et al. Lethal and severe coronary arteritis in DBA/2 mice induced by fungal pathogen, CAWS, Candida albicans water-soluble fraction. Atherosclerosis. 2006;186:310–20.
Oharaseki T, Kameoka Y, Kura F, Persad AS, Suzuki K, Naoe S. Susceptibility loci to coronary arteritis in animal model of Kawasaki disease induced with Candida albicans-derived substances. Microbiol Immunol. 2005;49:181–9.
Okawara AI, Miura NN, Oharaseki T, Takahashi K, Okumra A, Tachikawa H, et al. Neutrophil activation and arteritis induced by C. albicans water-soluble mannoprotein–β-glucan complex (CAWS). Exp Mol Pathol. 2007;82:220–6.
Furusho K, Kamiya T, Nakano H, Kiyosawa N, Shinomiya K, Hayashidera T, et al. High-dose intravenous gammaglobulin for Kawasaki disease. Lancet. 1984;10:1055–8.
Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Beiser AS, Burns JC, Bastian J, Chung KJ, et al. A single intravenous infusion of gamma globulin as compared with four infusions in the treatment of acute Kawasaki syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1991;324:1633–9.
Danieli MG, Cappelli M, Malcangi G, Logullo F, Salvi A, Danieli G. Long term effectiveness of intravenous immunoglobulin in Churg-Strauss syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004;63:1649–54.
Jayne DR, Lockwood CM. Intravenous immunoglobulin as sole therapy for systemic vasculitis. Br J Rheumatol. 1996;35:1150–3.
Levy Y, Uziel Y, Zandman GG, Amital H, Sherer Y, Langevitz P, et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin in peripheral neuropathy associated with vasculitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003;62:1221–3.
Ihara IT, Ono T, Nogaki F, Suyama K, Tanaka M, Yonemoto S, et al. Clinical efficacy of intravenous immunoglobulin for patients with MPO-ANCA-associated rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis. Nephron Clin Pract. 2006;102:c35–42.
Jayne DR, Chapel H, Adu D, Misbah S, O’Donoghue D, Scott D, et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin for ANCA-associated systemic vasculitis with persistent disease activity. Q J Med. 2000;93:433–9.
Suzuki K, Okazaki T. Contribution of myeloperoxidase in vasculitis development. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2004;57:S2–4.
Okawara IA, Oharaseki T, Takahashi K, Hashimoto Y, Aratani Y, Koyama H, et al. Contribution of myeloperoxidase to coronary artery vasculitis associated with MPO–ANCA production. Inflammation. 2001;25:381–7.
Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Burns JC, Beiser AS, Chung KJ, Duffy CE, et al. The treatment of Kawasaki syndrome with intravenous gamma globulin. New Engl J Med. 1986;315:341–6.
Fujii A, Tomizawa A, Arimura Y, Nagasawa T, Ohashi YY, Hiyama T, et al. Epitope analysis of myeloperoxidase (MPO) specific antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies (ANCA) in MPO–ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis. Clin Nephrol. 2000;53:242–52.
Tomizawa K, Mine E, Fujii A, Ohashi YY, Yamagoe S, Hashimoto Y, et al. A panel set for epitope analysis of myeloperoxidase (MPO)-specific antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody MPO–ANCA using recombinant hexamer histidine-tagged MPO deletion mutants. J Clin Immunol. 1998;18:142–52.
Suzuki K, Kobayashi S, Yamazaki K, Gondo M, Tomizawa K, Arimura Y, et al. Analysis of risk epitopes of anti-neutrophil antibody MPO–ANCA in vasculitis in Japanese population. Microbiol Immunol. 2007;51:1215–20.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Ms. Hitomi Yamada and Mr. Yoshiaki Kaneshiro for their excellent technical assistance and helpful suggestions. This study was supported in part by a grant from the Japanese Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Takahashi, K., Oharaseki, T., Yokouchi, Y. et al. Administration of human immunoglobulin suppresses development of murine systemic vasculitis induced with Candida albicans water-soluble fraction: an animal model of Kawasaki disease. Mod Rheumatol 20, 160–167 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-009-0250-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-009-0250-5