Abstract
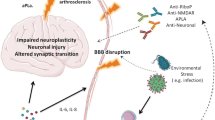
Systemic lupus erythematosus is a chronic, multisystemic, autoimmune disease that may involve the central, peripheral, and autonomic nervous systems and can present with a wide variety of neurological and psychiatric manifestations. In this article, we review the recent literature pertaining to the pathogenesis of neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus (NPSLE). We searched the PUBMED database with no chronological constraints using the following terms: “neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus” cross-referenced with the terms “pathogenesis” and “biomarkers” for full-text articles in English. The etiology of NPSLE is as yet unknown, though numerous autoantibodies and cytokines have been suggested as possible mediators. Of the numerous autoantibodies and biomarkers examined, anti-phospholipid, anti-ribosomal P, anti-neuronal, anti-glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), anti-endothelial cell, anti-N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA), microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP-2), and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) appear to be elevated in patients with NPSLE. Cytokines that may be involved in the pathology of NPSLE include interleukin (IL)-2, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, and interferons (IFN)-α and -γ. With continued advances in immunological research, new insights into the pathophysiologic mechanisms of NPSLE may lead to the development of biomarkers and new treatment strategies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Valesini G, Alessandri C, Celestino D, Conti F. Anti-endothelial antibodies and neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2006;1069:118–28.
The American College of Rheumatology nomenclature and case definitions for neuropsychiatric lupus syndromes. Arthritis Rheum 1999;42(4):599–608.
Hanly JG, McCurdy G, Fougere L, Douglas JA, Thompson K. Neuropsychiatric events in systemic lupus erythematosus: attribution and clinical significance. J Rheumatol. 2004;31(11):2156–62.
Bresnihan B, Hohmeister R, Cutting J, Travers RL, Waldburger M, Black C, et al. The neuropsychiatric disorder in systemic lupus erythematosus: evidence for both vascular and immune mechanisms. Ann Rheum Dis. 1979;38(4):301–6.
Tatsukawa H, Ishii K, Haranaka M, Kumagi M, Hino I, Yoshimatsu H. Evaluation of average amount of cerebral blood flow measured by brain perfusion index in patients with neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2005;14(6):445–9.
Hanly JG, Walsh NM, Sangalang V. Brain pathology in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 1992;19(5):732–41.
Devinsky O, Petito CK, Alonso DR. Clinical and neuropathological findings in systemic lupus erythematosus: the role of vasculitis, heart emboli, and thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Ann Neurol. 1988;23(4):380–4.
Greenwood DL, Gitlits VM, Alderuccio F, Sentry JW, Toh BH. Autoantibodies in neuropsychiatric lupus. Autoimmunity. 2002;35(2):79–86.
Zaccagni H, Fried J, Cornell J, Padilla P, Brey RL. Soluble adhesion molecule levels, neuropsychiatric lupus and lupus-related damage. Front Biosci. 2004;9:1654–9.
Asherson RA, Khamashta MA, Gil A, Vazquez JJ, Chan O, Baguley E, et al. Cerebrovascular disease and antiphospholipid antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus, lupus-like disease, and the primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Am J Med. 1989;86(4):391–9.
Trysberg E, Tarkowski A. Cerebral inflammation and degeneration in systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2004;16(5):527–33.
Gomez-Pacheco L, Villa AR, Drenkard C, Cabiedes J, Cabral AR, Alarcon-Segovia D. Serum anti-beta2-glycoprotein-I and anticardiolipin antibodies during thrombosis in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Am J Med. 1999;106(4):417–23.
Meroni PL, Tincani A, Sepp N, Raschi E, Testoni C, Corsini E, et al. Endothelium and the brain in CNS lupus. Lupus. 2003;12(12):919–28.
Steens SC, Bosma GP, Steup-Beekman GM, le Cessie S, Huizinga TW, van Buchem MA. Association between microscopic brain damage as indicated by magnetization transfer imaging and anticardiolipin antibodies in neuropsychiatric lupus. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006;8(2):R38.
Sanna G, Bertolaccini ML, Cuadrado MJ, Laing H, Khamashta MA, Mathieu A, et al. Neuropsychiatric manifestations in systemic lupus erythematosus: prevalence and association with antiphospholipid antibodies. J Rheumatol. 2003;30(5):985–92.
Hanly JG, Hong C, Smith S, Fisk JD. A prospective analysis of cognitive function and anticardiolipin antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1999;42(4):728–34.
Menon S, Jameson-Shortall E, Newman SP, Hall-Craggs MR, Chinn R, Isenberg DA. A longitudinal study of anticardiolipin antibody levels and cognitive functioning in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1999;42(4):735–41.
Conti F, Alessandri C, Bompane D, Bombardieri M, Spinelli FR, Rusconi AC, et al. Autoantibody profile in systemic lupus erythematosus with psychiatric manifestations: a role for anti-endothelial-cell antibodies. Arthritis Res Ther. 2004;6(4):R366–72.
Elkon KB, Parnassa AP, Foster CL. Lupus autoantibodies target ribosomal P proteins. J Exp Med. 1985;162(2):459–71.
Francoeur AM, Peebles CL, Heckman KJ, Lee JC, Tan EM. Identification of ribosomal protein autoantigens. J Immunol. 1985;135(4):2378–84.
Bonfa E, Golombek SJ, Kaufman LD, Skelly S, Weissbach H, Brot N, et al. Association between lupus psychosis and anti-ribosomal P protein antibodies. N Engl J Med. 1987;317(5):265–71.
West SG, Emlen W, Wener MH, Kotzin BL. Neuropsychiatric lupus erythematosus: a 10-year prospective study on the value of diagnostic tests. Am J Med. 1995;99(2):153–63.
Watanabe T, Sato T, Uchiumi T, Arakawa M. Neuropsychiatric manifestations in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: diagnostic and predictive value of longitudinal examination of anti-ribosomal P antibody. Lupus. 1996;5(3):178–83.
Arnett FC, Reveille JD, Moutsopoulos HM, Georgescu L, Elkon KB. Ribosomal P autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Frequencies in different ethnic groups and clinical and immunogenetic associations. Arthritis Rheum. 1996;39(11):1833–9.
Tzioufas AG, Tzortzakis NG, Panou-Pomonis E, Boki KA, Sakarellos-Daitsiotis M, Sakarellos C, et al. The clinical relevance of antibodies to ribosomal-P common epitope in two targeted systemic lupus erythematosus populations: a large cohort of consecutive patients and patients with active central nervous system disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000;59(2):99–104.
Nojima Y, Minota S, Yamada A, Takaku F, Aotsuka S, Yokohari R. Correlation of antibodies to ribosomal P protein with psychosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992;51(9):1053–5.
Isshi K, Hirohata S. Differential roles of the anti-ribosomal P antibody and antineuronal antibody in the pathogenesis of central nervous system involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1998;41(10):1819–27.
Isshi K, Hirohata S. Association of anti-ribosomal P protein antibodies with neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1996;39(9):1483–90.
Press J, Palayew K, Laxer RM, Elkon K, Eddy A, Rakoff D, et al. Antiribosomal P antibodies in pediatric patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and psychosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1996;39(4):671–6.
Massardo L, Burgos P, Martinez ME, Perez R, Calvo M, Barros J, et al. Antiribosomal P protein antibodies in Chilean SLE patients: no association with renal disease. Lupus. 2002;11(6):379–83.
Yoshio T, Hirata D, Onda K, Nara H, Minota S. Antiribosomal P protein antibodies in cerebrospinal fluid are associated with neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 2005;32(1):34–9.
Hirohata S, Arinuma Y, Takayama M, Yoshio T. Association of cerebrospinal fluid anti-ribosomal p protein antibodies with diffuse psychiatric/neuropsychological syndromes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9(3):R44.
Schneebaum AB, Singleton JD, West SG, Blodgett JK, Allen LG, Cheronis JC, et al. Association of psychiatric manifestations with antibodies to ribosomal P proteins in systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med. 1991;90(1):54–62.
Gerli R, Caponi L, Tincani A, Scorza R, Sabbadini MG, Danieli MG, et al. Clinical and serological associations of ribosomal P autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus: prospective evaluation in a large cohort of Italian patients. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2002;41(12):1357–66.
Jonsen A, Bengtsson AA, Nived O, Ryberg B, Truedsson L, Ronnblom L, et al. The heterogeneity of neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus is reflected in lack of association with cerebrospinal fluid cytokine profiles. Lupus. 2003;12(11):846–50.
Teh LS, Bedwell AE, Isenberg DA, Gordon C, Emery P, Charles PJ, et al. Antibodies to protein P in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992;51(4):489–94.
van Dam A, Nossent H, de Jong J, Meilof J, ter Borg EJ, Swaak T, et al. Diagnostic value of antibodies against ribosomal phosphoproteins. A cross sectional and longitudinal study. J Rheumatol. 1991;18(7):1026–34.
Sato T, Uchiumi T, Ozawa T, Kikuchi M, Nakano M, Kominami R, et al. Autoantibodies against ribosomal proteins found with high frequency in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus with active disease. J Rheumatol. 1991;18(11):1681–4.
Derksen RH, van Dam AP, Gmelig Meyling FH, Bijlsma JW, Smeenk RJ. A prospective study on antiribosomal P proteins in two cases of familial lupus and recurrent psychosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1990;49(10):779–82.
Karassa FB, Afeltra A, Ambrozic A, Chang DM, De Keyser F, Doria A, et al. Accuracy of anti-ribosomal P protein antibody testing for the diagnosis of neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus: an international meta-analysis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54(1):312–24.
Bluestein HG, Williams GW, Steinberg AD. Cerebrospinal fluid antibodies to neuronal cells: association with neuropsychiatric manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med. 1981;70(2):240–6.
Sanna G, Piga M, Terryberry JW, Peltz MT, Giagheddu S, Satta L, et al. Central nervous system involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus: cerebral imaging and serological profile in patients with and without overt neuropsychiatric manifestations. Lupus. 2000;9(8):573–83.
Trysberg E, Nylen K, Rosengren LE, Tarkowski A. Neuronal and astrocytic damage in systemic lupus erythematosus patients with central nervous system involvement. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48(10):2881–7.
Alessandri C, Conti F, Valesini G. Role of anti-glial fibrillary acidic protein antibodies in the pathogenesis of neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus should be clarified: comment on the article by Trysberg et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50(5):1698–9. author reply 1699.
Yoshio T, Masuyama J, Kano S. Antiribosomal P0 protein antibodies react with the surface of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Rheumatol. 1996;23(7):1311–2.
Yoshio T, Masuyama J, Ikeda M, Tamai K, Hachiya T, Emori T, et al. Quantification of antiribosomal P0 protein antibodies by ELISA with recombinant P0 fusion protein and their association with central nervous system disease in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 1995;22(9):1681–7.
Song J, Park YB, Lee WK, Lee KH, Lee SK. Clinical associations of anti-endothelial cell antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol Int. 2000;20(1):1–7.
Morris RG, Anderson E, Lynch GS, Baudry M. Selective impairment of learning and blockade of long-term potentiation by an N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonist, AP5. Nature. 1986;319(6056):774–6.
Lipton SA, Rosenberg PA. Excitatory amino acids as a final common pathway for neurologic disorders. N Engl J Med. 1994;330(9):613–22.
Skerry TM, Genever PG. Glutamate signalling in non-neuronal tissues. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2001;22(4):174–81.
Zipfel GJ, Lee JM, Choi DW. Reducing calcium overload in the ischemic brain. N Engl J Med. 1999;341(20):1543–4.
Cavalheiro EA, Olney JW. Glutamate antagonists: deadly liaisons with cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98(11):5947–8.
Choi DW, Rothman SM. The role of glutamate neurotoxicity in hypoxic-ischemic neuronal death. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1990;13:171–82.
Dubinsky JM, Rothman SM. Intracellular calcium concentrations during “chemical hypoxia” and excitotoxic neuronal injury. J Neurosci. 1991;11(8):2545–51.
Kotzin BL, Kozora E. Anti-DNA meets NMDA in neuropsychiatric lupus. Nat Med. 2001;7(11):1175–6.
DeGiorgio LA, Konstantinov KN, Lee SC, Hardin JA, Volpe BT, Diamond B. A subset of lupus anti-DNA antibodies cross-reacts with the NR2 glutamate receptor in systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Med. 2001;7(11):1189–93.
Ozawa S, Kamiya H, Tsuzuki K. Glutamate receptors in the mammalian central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol. 1998;54(5):581–618.
Kowal C, Degiorgio LA, Lee JY, Edgar MA, Huerta PT, Volpe BT, et al. Human lupus autoantibodies against NMDA receptors mediate cognitive impairment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103(52):19854–9.
Arinuma Y, Yanagida T, Hirohata S. Association of cerebrospinal fluid anti-NR2 glutamate receptor antibodies with diffuse neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58(4):1130–5.
Omdal R, Brokstad K, Waterloo K, Koldingsnes W, Jonsson R, Mellgren SI. Neuropsychiatric disturbances in SLE are associated with antibodies against NMDA receptors. Eur J Neurol. 2005;12(5):392–8.
Kudoh A, Takahira Y, Katagai H, Takazawa T. Small-dose ketamine improves the postoperative state of depressed patients. Anesth Analg. 2002;95(1):114–8. table of contents.
Berman RM, Cappiello A, Anand A, Oren DA, Heninger GR, Charney DS, et al. Antidepressant effects of ketamine in depressed patients. Biol Psychiatry. 2000;47(4):351–4.
Lapteva L, Nowak M, Yarboro CH, Takada K, Roebuck-Spencer T, Weickert T, et al. Anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antibodies, cognitive dysfunction, and depression in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54(8):2505–14.
Husebye ES, Sthoeger ZM, Dayan M, Zinger H, Elbirt D, Levite M, et al. Autoantibodies to a NR2A peptide of the glutamate/NMDA receptor in sera of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005;64(8):1210–3.
Goetzl EJ, Banda MJ, Leppert D. Matrix metalloproteinases in immunity. J Immunol. 1996;156(1):1–4.
Ram M, Sherer Y, Shoenfeld Y. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 and autoimmune diseases. J Clin Immunol. 2006;26(4):299–307.
Faber-Elmann A, Sthoeger Z, Tcherniack A, Dayan M, Mozes E. Activity of matrix metalloproteinase-9 is elevated in sera of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 2002;127(2):393–8.
Ainiala H, Hietaharju A, Dastidar P, Loukkola J, Lehtimaki T, Peltola J, et al. Increased serum matrix metalloproteinase 9 levels in systemic lupus erythematosus patients with neuropsychiatric manifestations and brain magnetic resonance imaging abnormalities. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50(3):858–65.
Trysberg E, Blennow K, Zachrisson O, Tarkowski A. Intrathecal levels of matrix metalloproteinases in systemic lupus erythematosus with central nervous system engagement. Arthritis Res Ther. 2004;6(6):R551–6.
Williams RC Jr., Sugiura K, Tan EM. Antibodies to microtubule-associated protein 2 in patients with neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50(4):1239–47.
Lefranc D, Launay D, Dubucquoi S, de Seze J, Dussart P, Vermersch M, et al. Characterization of discriminant human brain antigenic targets in neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus using an immunoproteomic approach. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56(10):3420–32.
Jara LJ, Irigoyen L, Ortiz MJ, Zazueta B, Bravo G, Espinoza LR. Prolactin and interleukin-6 in neuropsychiatric lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol. 1998;17(2):110–4.
Hirohata S, Miyamoto T. Elevated levels of interleukin-6 in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and central nervous system involvement. Arthritis Rheum. 1990;33(5):644–9.
Hirohata S, Hayakawa K. Enhanced interleukin-6 messenger RNA expression by neuronal cells in a patient with neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1999;42(12):2729–30.
Winfield JB, Shaw M, Silverman LM, Eisenberg RA, Wilson HA 3rd, Koffler D. Intrathecal IgG synthesis and blood–brain barrier impairment in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and central nervous system dysfunction. Am J Med. 1983;74(5):837–44.
Alcocer-Varela J, Aleman-Hoey D, Alarcon-Segovia D. Interleukin-1 and interleukin-6 activities are increased in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with CNS lupus erythematosus and correlate with local late T-cell activation markers. Lupus. 1992;1(2):111–7.
Tsai CY, Wu TH, Tsai ST, Chen KH, Thajeb P, Lin WM, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid interleukin-6, prostaglandin E2 and autoantibodies in patients with neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus and central nervous system infections. Scand J Rheumatol. 1994;23(2):57–63.
Trysberg E, Carlsten H, Tarkowski A. Intrathecal cytokines in systemic lupus erythematosus with central nervous system involvement. Lupus. 2000;9(7):498–503.
Dellalibera-Joviliano R, Dos Reis ML, Cunha Fde Q, Donadi EA. Kinins and cytokines in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with neuropsychiatric lupus. J Rheumatol. 2003;30(3):485–92.
Fragoso-Loyo H, Richaud-Patin Y, Orozco-Narvaez A, Davila-Maldonado L, Atisha-Fregoso Y, Llorente L, et al. Interleukin-6 and chemokines in the neuropsychiatric manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56(4):1242–50.
Shiozawa S, Kuroki Y, Kim M, Hirohata S, Ogino T. Interferon-alpha in lupus psychosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1992;35(4):417–22.
Svenungsson E, Andersson M, Brundin L, van Vollenhoven R, Khademi M, Tarkowski A, et al. Increased levels of proinflammatory cytokines and nitric oxide metabolites in neuropsychiatric lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001;60(4):372–9.
Gilad R, Lampl Y, Eshel Y, Barak V, Sarova-Pinhas I. Cerebrospinal fluid soluble interleukin-2 receptor in cerebral lupus. Br J Rheumatol. 1997;36(2):190–3.
Santer DM, Yoshio T, Minota S, Moller T, Elkon KB. Potent induction of IFN-alpha and chemokines by autoantibodies in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with neuropsychiatric lupus. J Immunol. 2009;182(2):1192–201.
Hanly JG, Harrison MJ. Management of neuropsychiatric lupus. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2005;19(5):799–821.
Khamashta MA, Cuadrado MJ, Mujic F, Taub NA, Hunt BJ, Hughes GR. The management of thrombosis in the antiphospholipid-antibody syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1995;332(15):993–7.
Bertsias G, Ioannidis JP, Boletis J, Bombardieri S, Cervera R, Dostal C, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus. Report of a Task Force of the EULAR Standing Committee for International Clinical Studies Including Therapeutics. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008;67(2):195–205.
Sanna G, Bertolaccini ML, Khamashta MA. Neuropsychiatric involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus: current therapeutic approach. Curr Pharm Des. 2008;14(13):1261–9.
Valesini G, Priori R, Francia A, Balestrieri G, Tincani A, Airo P, et al. Central nervous system involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus: a new therapeutic approach with intrathecal dexamethasone and methotrexate. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1994;16(2–3):313–21.
Milstone AM, Meyers K, Elia J. Treatment of acute neuropsychiatric lupus with intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG): a case report and review of the literature. Clin Rheumatol. 2005;24(4):394–7.
Tomer Y, Shoenfeld Y. Successful treatment of psychosis secondary to SLE with high dose intravenous immunoglobulin. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1992;10(4):391–3.
Sherer Y, Levy Y, Langevitz P, Lorber M, Fabrizzi F, Shoenfeld Y. Successful treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus cerebritis with intravenous immunoglobulin. Clin Rheumatol. 1999;18(2):170–3.
Traynor AE, Barr WG, Rosa RM, Rodriguez J, Oyama Y, Baker S, et al. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for severe and refractory lupus. Analysis after five years and fifteen patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46(11):2917–23.
Lehnhardt FG, Scheid C, Holtik U, Burghaus L, Neveling M, Impekoven P, et al. Autologous blood stem cell transplantation in refractory systemic lupus erythematodes with recurrent longitudinal myelitis and cerebral infarction. Lupus. 2006;15(4):240–3.
Gorman C, Leandro M, Isenberg D. Does B cell depletion have a role to play in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus? Lupus. 2004;13(5):312–6.
Looney RJ, Anolik JH, Campbell D, Felgar RE, Young F, Arend LJ, et al. B cell depletion as a novel treatment for systemic lupus erythematosus: a phase I/II dose-escalation trial of rituximab. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50(8):2580–9.
Anolik JH, Barnard J, Cappione A, Pugh-Bernard AE, Felgar RE, Looney RJ, et al. Rituximab improves peripheral B cell abnormalities in human systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50(11):3580–90.
Tokunaga M, Fujii K, Saito K, Nakayamada S, Tsujimura S, Nawata M, et al. Down-regulation of CD40 and CD80 on B cells in patients with life-threatening systemic lupus erythematosus after successful treatment with rituximab. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005;44(2):176–82.
Leandro MJ, Edwards JC, Cambridge G, Ehrenstein MR, Isenberg DA. An open study of B lymphocyte depletion in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46(10):2673–7.
Neuwelt CM, Young RG, McGhee RA, Freeman J. Role of rituximab in the treatment of severe central nervous system neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus as monotherapy or in combination therapy. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005;64(Suppl III):57.
Tokunaga M, Saito K, Kawabata D, Imura Y, Fujii T, Nakayamada S, et al. Efficacy of rituximab (anti-CD20) for refractory systemic lupus erythematosus involving the central nervous system. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007;66(4):470–5.
Hirohata S, Kanai Y, Mitsuo A, Tokano Y, Hara M, Kubota T, et al. Efficacy of cerebrospinal fluid IL-6 testing for diagnosis of lupus psychosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65(Suppl II):197.
Hillen N, Stevanovic S. Contribution of mass spectrometry-based proteomics to immunology. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2006;3(6):653–64.
Hofstadler SA, Severs JC, Smith RD, Swanek FD, Ewing AG. Analysis of single cells with capillary electrophoresis electrospray ionization Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 1996;10(8):919–22.
Rood MJ, Keijsers V, van der Linden MW, Tong TQ, Borggreve SE, Verweij CL, et al. Neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus is associated with imbalance in interleukin 10 promoter haplotypes. Ann Rheum Dis. 1999;58(2):85–9.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Efthimiou, P., Blanco, M. Pathogenesis of neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus and potential biomarkers. Mod Rheumatol 19, 457–468 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-009-0198-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-009-0198-5