Abstract
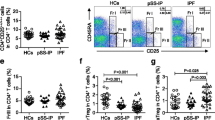
The expression of CD25 or CD28 on T cells was examined in patients with rheumatic diseases associated with interstitial pneumonitis (IP), in order to investigate the conditions of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells and CD8+CD28− suppressor T cells. Fifty-five patients with various rheumatic diseases and 23 normal controls were enrolled. CD4+CD25+ T cells of patients with IP were significantly decreased in comparison with non-IP patients, and the ratio of CD8+CD28− T cells in patients with IP was significantly higher than that in non-IP patients or normal controls. These results for CD8+CD28− T cells were in accord with the decrease in CD8+CD28+ T cells, and may be related to activation-induced CD8+CD28+ T-cell death. Thus, the abnormality of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells may be related to the pathogenesis of IP, and the survival and activation of CD8+ T cells.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kanai Y, Tokano Y, Tsuda H, Hashimoto H, Okumura K, Hirose S. HLA-DR positive T cells patients with polymyositis/dermatomyositis. J Rheumatol. 1993;20:77–9.
Piguet PF, Collart MA, Grau GE, Kapanci Y, Vassalli P. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin plays a key role in bleomycin-induced pneumopathy and fibrosis. J Exp Med. 1989;170:655–63.
Piguet PF, Collart MA, Grau GE, Sappino AP, Vassalli P. Requirement of tumour necrosis factor for development of silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Nature. 1990;344:245–7.
Zhang Y, TC Lee, Guillemin B, Yu MC, Rom WN. Enhanced IL-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha release and messenger RNA expression in macrophages from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis or after asbestos exposure. J Immunol. 1993;150:4188–96.
Chen ES, Greenlee BM, Willis-Karp M, Moller DR. Attenuation of inflammation and fibrosis in interferon-gamma-deficient mice after intratracheal bleomycin. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2001;24:545–55.
Piguet PF, Vesin C, Grau GE, Thompson RC. Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist (IL-1 ra) prevents or cures pulmonary fibrosis elicited in mice by bleomycin or silica. Cytokine. 1993;5:57–61.
Crystal RG, Bitterman PB, Mossman B, Schwarz MI, Sheppard O, Almasy L, et al. Future research directions in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: summary of a National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute working group. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;166:236–46.
Zhu Z, Homer RJ, Wang Z, Chen O, Geba GP, Wang J, et al. Pulmonary expression of interleukin-13 causes inflammation, mucus hypersecretion, subpithelial fibrosis, physiolosic abnormalities, and eotaxin production. J Clin Invest. 1999;103:779–88.
Lee CG, Homer RJ, Zhu Z, Lanone S, Wang X, Koteliansky V, et al. Interleukin-13 induces tissue fibrosis by selectively stimulating and activating transforming growth factor beta(1). J Exp Med. 2001;194:809–21.
Smith RE, Strieter RM, Phan SH, Lukacs NW, Huffnagle GB, Wilke CA, et al. Production and function of murine macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha in bleomycin-induced lung injury. J Immunol. 1994;153:4704–12.
Kaneko Y, Kuwano K, Kunitake R, Kawasaki M, Hagimoto N. B7-1, B7-2 and class II MHC molecules in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and bronchiolitis obliterans-organizing pneumonia. Eur Respir J. 2000;15:49–55.
Lee S, Kaneko K, Sekigawa I, Tokano Y, Takasaki Y, Hashimoto H. Circulating interleukin-16 in systemic lupus erythematosus. Br J Rheumatol. 1998;37:1334–7.
Hirashima M, Fukazawa T, Abe K, Morita Y, Kusaoi M, Hashimoto H. Expression and activity analyses of CTLA-4 in peripheral blood lymphocytes in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Lupus. 2004;13:24–31.
Lajaunias F, Ida A, Kikuchi S, Fossati-Jimack L, Martinez-Soria E, Moll T, et al. Differential control of CD22 ligand expression on B and T lymphocytes, and enhanced expression in murine systemic lupus. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48(6):1612–21.
Suzuki J, Nakano S, Nakiri Y Mitsuo A, Morimoto S, Tokano Y, et al. CD19/22 balance relates to improvement of disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Mod Rheumatol. 2006;16:235–8.
Nakiri Y, Suzuki J, Mitsuo A, Amano H, Morimoto S, Hashimoto H, et al. Expression of CD22 on peripheral B cells in Patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Relation to CD5 positive B cells. Clin Rheumatol. 2007;26:1721–3.
Filaci G, Bacilieri S, Fravega M, Monetti M, Contini P, Indiveri F. Impairment of CD8+ T suppressor cell function in patients with active systemic erythematosus. J Immunol. 2001;166:6452–7.
Sakaguchi S, Sakaguchi N, Asano M, Itoh M, Toda M. Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by activated T cells expressing IL-2 receptor alpha-chains(CD25). Breakdown of a single mechanism of self-tolerance causes various autoimmune diseases. J Immunol. 1995;155:1151–64.
Asano M, Toda M, Sakaguchi N, Sakaguchi S. Autoimmune disease as a consequence of developmental abnormality of a T cell subpopulation. J Exp Med. 1996;184:387–96.
Subcommittee for Scleroderma Criteria of the American Committee. Preliminary criteria for the classification of systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1980;23:581–90.
Arnett FC, Edwothy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries FJ, Cooper NS, et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988;31:315–24.
Kotajima L, Aotsuka S, Sumiya M, Yokohari R, Tojo T, Kasukawa R. Clinical features of patients with juvenile onset mixed connective tissue disease: analysis of date collected in a nationwide collaborative study in Japan. J Rheumatol. 1996;23:1088–94.
Bohan A, Peter JB. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis. N Engl J Med 1975;292:344–7, 403–7.
Iezzi G, Sheidegger D, Lanzavecchia A. Migration and function of anti-primed nonpolarized T lymphocytes in vivo. J Exp Med. 2001;193:987–93.
Masopust D, Vezys V, Usherwood EJ, Cauley LS, Olson S, Marzo AL, et al. Activated primary and memory CD8 T cells migrate to nonlymphoid tissues regardless of site of activation or tissue of origin. J Immunol. 2004;172:4875–82.
Suzuki J, Morimoto S, Amano H, Tokano Y, Takasaki Y, Hashimoto H. Serum levels of interleukin 15 in patients with rheumatic diseases. J Rheumatol. 2001;28:2389–91.
Fu S, Yopp AC, Mao X, Chen D, Zhanq N, Chen D, et al. CD4+CD25+CD62L+T-regulatory cell subset has optimal suppressive and proliferative potential. Am J Transplant. 2004;4:65–78.
Mottonen M, Heikkinen J, Mustonen L, Isomaki P, Luukkainen R, Lassila O. CD4+CD25+ T cells with the phenotypic and functional characteristics of regulatory T cells are enriched in the synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2005;140:360–7.
Cao D, van Vollenhoven R, Klareskog L, Trollmo C, Malmstrom V. CD25brightCD4+regulatory T cells are enriched in inflamed joints of patients with chronic rheumatic disease. Arthritis Res Ther. 2004;6:R335–46.
Kaneko H, Saito K, Hashimoto H, Yagita H, Okumura K, Azuma M. Preferential elimination of CD28+ T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and the relation with activation-induced apoptosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1996;106:218–29.
Conflict of interest
All of the authors confirm that there is no conflict of interest with regard to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Katagiri, A., Morimoto, S., Nakiri, Y. et al. Decrease in CD4+CD25+ and CD8+CD28+ T cells in interstitial pneumonitis associated with rheumatic disease. Mod Rheumatol 18, 562–569 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-008-0090-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-008-0090-8