Abstract
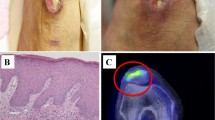
Polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) frequently occurs with giant cell arteritis (GCA). We report here two cases of PMR with aortitis in the absence of diminished pulse and manifestations related to GCA. Contrasted CT, MR angiography, and F-18-deoxyglucose positron emission tomography showed aortitis without stenosis that is not classified into any of large vasculitides. It should be acknowledged that aortitis might present as PMR and imaging studies are recommended.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Salvarani C, Cantini F, Boiardi L, Hunder GG. Polymyalgia rheumatica. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2004;18:705–22.
Arend WP, Michel BA, Bloch DA, Hunder GG, Calabrese LH, Edworthy SM, et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of Takayasu arteritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1990;33:1129–34.
Brack A, Martinez-Taboada V, Stanson A, Goronzy JJ, Weyand CM. Disease pattern in cranial and large-vessel giant cell arteritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1999;42:311–7.
Bird HA, Esselinckx W, Dixon AS, Mowat AG, Wood PH. An evaluation of criteria for polymyalgia rheumatica. Ann Rheum Dis. 1979;38:434–9.
Narvaez J, Narvaez JA, Nolla JM, Sirvent E, Reina D, Valverde J. Giant cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica: usefulness of vascular magnetic resonance imaging studies in the diagnosis of aortitis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005;44:479–83.
Blockmans D, Stroobants S, Maes A, Mortelmans L. Positron emission tomography in giant cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica: evidence for inflammation of the aortic arch. Am J Med. 2000;108:246–9.
Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Andrassy K, Bacon PA, Churg J, Gross WL, et al. Nomenclature of systemic vasculitides. Proposal of an international consensus conference. Arthritis Rheum. 1994;37:187–92.
Kobayashi S, Yano T, Matsumoto Y, Numano F, Nakajima N, Yasuda K, et al. Clinical and epidemiologic analysis of giant cell (temporal) arteritis from a nationwide survey in 1998 in Japan: the first government-supported nationwide survey. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;49:594–8.
Kobayashi Y, Numano F. 3. Takayasu arteritis. Intern Med. 2002;41:44–6.
Weyand CM, Goronzy JJ. Giant-cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica. Ann Intern Med. 2003;139:505–15.
Gravanis MB. Giant cell arteritis and Takayasu aortitis: morphologic, pathogenetic and etiologic factors. Int J Cardiol. 2000;75 Suppl 1:S21–3.
Iwamoto M, Ogawa-Shirota Y, Sato H, Yoshio T, Okazaki H, Fujita A, et al. Clinical images: early diagnosis of Takayasu arteritis using gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Arthritis Rheum. 1999;42:1549.
Acknowledgments
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Kataoka, H., Atsumi, T., Hashimoto, T. et al. Polymyalgia rheumatica as the manifestation of unclassified aortitis. Mod Rheumatol 18, 105–108 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-007-0019-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-007-0019-7