Abstract
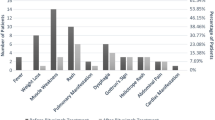
Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) therapy was administered to 15 patients who were refractory to traditional steroid therapy [eight with polymyosis (PM), seven with dermamyosis (DM)] to evaluate its efficacy. Serum creatine kinase (CK) significantly decreased from week 1, and manual muscle test scores (MMT) and activities of daily living (ADL) significantly increased from week 2. Efficacy rates were 93.3% (14/15 patients) as assessed using the MMT score, 80.0% (12/15 patients) using the ADL score, and 100% (15/15 patients) using the serum CK level. When changes in the serum CK level over two four-week periods, one before IVIG therapy (from week −4 to week 0) and one after IVIG therapy (from week 0 to week 4), were transformed to natural logarithms, the four-week change after IVIG therapy was significantly greater than that before IVIG therapy. The estimated duration of the serum CK level remaining normal in 50% of the patients after IVIG therapy was 334.5 days. Adverse reactions were observed in seven of 16 patients (43.8%) during the study period, but none of the adverse reactions were considered to be serious or required emergency treatment. In conclusion, the present study indicates that IVIG therapy is effective for steroid-resistant PM/DM.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bradley WG. Polymyositis. Br J Hosp Med 1977;17:351–5.
Cherin P. Recognition and management of myositis. Drugs 1997;54:39–49.
Blasczyk R, Westhoff U, Grosse-Wilde H. Soluble CD4, CD8, and HLA molecules in commercial immunoglobulin preparations. Lancet 1993;341:789–90.
Marchalonis JJ, Kaymaz H, Dedeoglu F, Schluter SF, Yocum DE, Edmundson AB. Human antoantibodies reactive with synthetic autoantigens from T-cell receptor β chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1992;89:3325–9.
Basta M, Dalakas MC. High-dose intravenous immunoglobulin exerts its beneficial effect in patients with dermatomyositis by blocking endomysial deposition of activated complement fragments. J Clin Invest 1994;94:1729–35.
Rigal D, Vermot-Desroches C, Heitz S, Bernaud J, Alfonsi F, Monier JC. Effects of Intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIG) on peripheral blood B, NK and T cell subpopulations in women with recurrent spontaneous abortions: specific effects on LFA-1 and CD56 molecules. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 1994;71:309–14.
Prasad NKA, Papoff G, Zeuner A, Bonnin E, Kazatchkine MD, Ruberti G, et al. Therapeutic preparations of normal polyspecific IgG (IVIg) induce apoptosis in human lymphocytes and monocytes: a novel mechanism of action of IVIg involving the Fas apoptotic pathway. J Immunol 1998;161:3781–90.
Roifman CM, Schaffer FM, Wachsmuth SE, Murphy G, Gelfand EW. Reversal of chronic polymyositis following intravenous immune serum globulin therapy. JAMA 1987;258:513–5.
Cherin P, Herson S, Wechsler B, Piette JC, Bletry O, Ziza JM, et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin for polymyositis and dermatomyositis [letter]. Lancet 1990;336:116.
Cherin P, Herson S, Wechsler B, Piette JC, Bletry O, Coutellier A, et al. Efficacy of intravenous gammaglobulin therapy in chronic refractory polymyositis and dermatomyositis: an open study with 20 adult patients. Am J Med 1991;91:162–8.
Lang BA, Laxer RM, Murphy G, Silverman ED, Roifman CM. Treatment of dermatomyositis with intravenous gammaglobulin. Am J Med 1991;91:169–72.
Breems DA, de Haas PW, Visscher F, Sabbe LJ, Busch HF, van Doorn PA. Intravenously-administered immunoglobulins as first-choice agent in juvenile dermatomyositis. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd 1993;137:1979–82.
Finielz P, Gendoo Z, Chuet C, Guiserix J. Dermatomyositis in a patient under chronic hemodialysis: treatment with intravenous immunoglobulins. Ann Med Interne (Paris) 1994;145:148–9.
Brownell AK. Intravenous immune globulin for dermatomyositis. N Engl J Med 1994;330:1392–3.
Cherin P, Herson S. Indications for intravenous gammaglobulin therapy in inflammatory myopathies. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1994;57(Suppl):50–4.
Cherin P, Piette JC, Wechsler B, Bletry O, Ziza JM, Laraki R, et al. Intravenous gamma globulin as first line therapy in polymyositis and dermatomyositis: an open study in 11 adult patients. J Rheumatol 1994;21:1092–7.
Vedanarayanan V, Subramony SH, Ray LI, Evans OB. Treatment of childhood dermatomyositis with high dose intravenous immunoglobulin. Pediatr Neurol 1995;13:336–9.
Galeazzi M, Bellucci AM, Girardelli CR, Bono R, De Pita O, Puddu P. Efficacy of intravenous immunoglobulin therapy in a case of juvenile dermatomyositis. Clin Rheumatol 1996;15:215–6.
Moriguchi M, Suzuki T, Tateishi M, Hara M, Kashiwazaki S. Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy for refractory myositis. Intern Med 1996;35:663–7.
Tsai MJ, Lai CC, Lin SC, Chiang BL, Chou CC, Hsieh KH. Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy in juvenile dermatomyositis. Acta Paediatr Sin 1997;38:111–5.
Furuya Y, Takahashi T, Hamamoto H, Nishimura M, Kawakami Y. High-dose immunoglobulin therapy for a patient with dermatomyositis. Intern Med 1998;37:642–5.
Peake MF, Perkins P, Elston DM, Older SA, Vinson RP. Cutaneous ulcers of refractory adult dermatomyositis responsive to intravenous immunoglobulin. Cutis 1998;62:89–93.
Kokori H, Fotoulaki M, Giannakopoulou C, Hatzidaki E, Tantros S, Sbyrakis S. Intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in a girl with juvenile dermatomyositis. Pediatr Int 1999;41:696–7.
Sadayama T, Miyagawa S, Shirai T. Low-dose intravenous immunoglobulin therapy for intractable dermatomyositis skin lesions. J Dermatol 1999;26:457–9.
Gottfried I, Seeber A, Anegg B, Rieger A, Stingl G, Volc-Platzer B. High dose intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) in dermatomyositis: clinical responses and effect on sIL-2R levels. Eur J Dermatol 2000;10:29–35.
Amemiya K, Semino-Mora C, Granger RP, Dalakas MC. Downregulation of TGF-β1 mRNA and protein in the muscles of patients with inflammatory myopathies after treatment with high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin. Clin Immunol 2000;94:99–104.
Al-Mayouf SM, Laxer RM, Schneider R, Silverman ED, Feldman BM. Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy for juvenile dermatomyositis: efficacy and safety. J Rheumatol 2000;27:2498–503.
Hara M, Kinoshita M, Saito E, Hashimoto H, Miyasaka N, Yoshida T, et al. Prospective study of high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin for the treatment of steroid-resistant polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Mod Rheumatol 2003;13:319–25.
Dalakas MC, Illa I, Dambrosia JM, Soueidan SA, Stein DP, Otero C, et al. A controlled trial of high-dose intravenous immune globulin infusions as treatment for dermatomyositis. N Engl J Med 1993;329:1993–2000.
Bohan A, Peter JB. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis. N Engl J Med 1975;292:344–7.
Saito E. Relationship between serum CK levels and effectiveness on polymyositis or dermatomyositis after corticosteroid therapy. Clin Rheumatol 2004;16:188–96.
Reinhart WH, Berchtold PE. Effect of high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin therapy on blood rheology. Lancet 1992;339:662–4.
Dalakas MC. High-dose intravenous immunoglobulin and serum viscosity: Risk of precipitating thromboembolic events. Neurology 1994;44:223–6.
Woodruff RK, Grigg AP, Firkin FC, Smith IL. Fatal thrombotic events during treatment of autoimmune thrombocytopenia with intravenous immunoglobulin in elderly patients. Lancet 1986;26:217–8.
Silbert PL, Knezevic WV, Bridge DT. Cerebral infarction complicating intravenous immunoglobulin therapy for polyneuritis cranialis. Neurology 1992;42:257–8.
Kurlander RJ. Reversible and irreversible loss of Fc receptor function of human monocytes as a consequence of interaction with immunoglobulin G. J Clin Invest 1980;66:773–81.
Lazarus AH, Freedman J, Semple JW. Intravenous immunoglobulin and anti-D in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP): mechanisms of action. Transfus Sci 1998;19:289–94.
Sussmann GL, Pruzanski W. The role of intravenous infusions of gamma globulin in the therapy of polymyositis and dermatomyositis. J Rheumatol 1994;21:990–2.
Basta M, Kirshbom P, Frank MM, Fries LF. Mechanism of therapeutic effect of high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin: attenuation of acute, complement-dependent immune damage in a guinea pig model. J Clin Invest 1989;84:1974–81.
Qi M, Schifferli JA. Inhibition of complement activation by intravenous immunoglobulins. Arthritis Rheum 1995;38:146.
Achiron A, Margalit R, Hershkoviz R, Markovits D, Reshef T, Melamed E, et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin treatment of experimental T cell mediated autoimmune disease: upregulation of T cell proliferation and downregulation of tumor necrosis factor secretion. J Clin Invest 1994;93:600–5.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to the members of the GB-0998 Study Group who are not listed as authors but have provided valuable advice and data for the present study. This work was supported by Mitsubishi Pharma Corporation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10165-008-0050-3
Appendix: The list of additional members of the GB-0998 Study Group is given below
Appendix: The list of additional members of the GB-0998 Study Group is given below
-
Tatsuya Atsumi, MD; Yoshiharu Amasaki, MD; Akira Furusaki, MD; Yoshie Sakai, MD, Department of Medicine II, Hokkaido University Graduate School of Medicine
-
Tsutomu Takeuchi, MD; Koichi Amano, MD, Department of Internal Medicine, Saitama Medical Center, Saitama Medical School
-
Shigeto Kobayashi, MD; Yoshiaki Tokano, MD; Takeshi Yamaji, MD; Kazuhiko Kaneda, MD; Manami Seki, MD, Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Juntendo University School of Medicine
-
Ryuji Koike, MD; Takahiko Sugihara, MD, Department of Medicine & Rheumatology, Tokyo Medical and Dental University
-
Michito Hirakata, MD; Akira Suwa, MD; Shinji Sato, MD; Misako Suzuki, MD, Section of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Keio University School of Medicine
-
Mutsuto Tateishi, MD; Satomi Higami, MD; Naomi Ichikawa, MD, Institute of Rheumatology, Tokyo Women’s Medical University
-
Hiroshi Oka, MD, Division of Rheumatology and Allergy, Department of Internal Medicine, St. Marianna University School of Medicine
-
Jun Okada, MD; Akira Ishikawa, MD; Toshiya Hamana, MD, Division of Rheumatology and Infectious Disease, Kitasato University School of Medicine
-
Masatoshi Takaya, MD, Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Rheumatology, School of Medicine, Tokai University
-
Shunji Yoshida, MD; Hideo Yoshida, MD; Kenichi Kato, MD, Section of Rheumatology and Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Fujita Health University School of Medicine
-
Tsuneyo Mimori, MD; Hisanori Umehara, MD; Takao Fujii, MD; Hajime Yoshifuji, MD; Yoshimasa Fujita, MD, Department of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology, Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto University
-
Yukihiko Saeki, MD, Department of Molecular Medicine, Osaka University Medical School
-
Kazuyoshi Saito, MD; Mikiko Tokunaga, MD, The First Department of Internal Medicine, University of Occupational and Environmental Health
-
Susumu Shirabe, MD, The First Department of Internal Medicine, Graduate School of Biochemical Sciences, Nagasaki University
-
Hitoaki Okazaki, MD, Division of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology, Department of Medicine, Jichi Medical School
-
Kimihiro Suzuki, MD; Makoto Okada, MD, Internal Medicine I, National Defence Medical College
-
Shinichi Inada, MD; Takashi Ogasawara, MD, Division of Rheumatic Diseases, Tokyo Metropolitan Ohtsuka Hospital
-
Yasuo Matsuoka, MD, Department of Internal Medicine, Kawasaki Municipal Hospital
About this article
Cite this article
Saito, E., Koike, T., Hashimoto, H. et al. Efficacy of high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin therapy in Japanese patients with steroid-resistant polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Mod Rheumatol 18, 34–44 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-007-0013-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-007-0013-0