Abstract
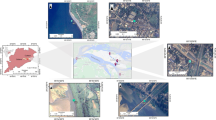
The present study examined the distribution and severity of heavy metal contamination in the sediments of the Ciujung Watershed and its tributaries in Banten Province, Indonesia. Surface sediments were collected from 11 sites and analyzed for As, Cd, Cr, Hg, and Pb via atomic absorption spectrometry. Environmental risk was assessed based on Igeo, EF, PERI, and biological effect. The mean As, Cd, Cr, Hg, and Pb concentrations by dry weight were 1.68 ± 0.63 mg kg−1, 0.80 ± 0.88 mg kg−1, 4.12 ± 0.88 mg kg−1, 0.61 ± 0.25, and 19.80 ± 7.51 mg kg−1, respectively. The Ciujung Watershed presented with no serious As, Cr, or Pb contamination but did display severe Hg and Cd pollution. At all sampling sites except S1, the concentrations of Hg (but not Cd) were higher than the permissible limits established according to Sediment Quality Guidelines. Hg originating from ASGM posed high ecological risk to the aquatic ecosystem. The present study accurately and comprehensively delineated the current heavy metal contamination status in the surface sediments of the Ciujung Watershed particularly Hg. The findings could help regulatory agencies formulate and enact effective control measures and raise awareness about Hg pollution among the Ciujung Watershed residents.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Islam MS, Proshad R, Ahmed S (2018) Ecological risk of heavy metals in sediment of an urban river in Bangladesh. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 24(3):699–720. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2017.1397499
Malsiu A, Shehu I, Stafilov T, Faiku F (2020) Assessment of heavy metal concentrations with fractionation method in sediments and waters of the badovci lake (Kosovo). J Environ Public Health 2020:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/3098594
Kumar V, Sharma A, Kumar R, Bhardwaj R, Kumar Thukral A, Rodrigo-Comino J (2020) Assessment of heavy-metal pollution in three different Indian water bodies by combination of multivariate analysis and water pollution indices. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 26(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1497946
Zhang Y, Zhang H, Zhang Z, Liu C, Sun C, Zhang W, Marhaba T (2018) Ph effect on heavy metal release from a polluted sediment. J Chem 2018(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7597640
Raknuzzaman M, Ahmed MK, Islam MS, Habibullah-Al-Mamun M, Tokumura M, Sekine M, Masunaga S (2016) Assessment of trace metals in surface water and sediment collected from polluted coastal areas of Bangladesh. J Water Environ Technol 14(4):247–259. https://doi.org/10.2965/jwet.15-038
Rahman Z, Singh VP (2019) The relative impact of toxic heavy metals (THMs) (arsenic (As), cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr)(VI), mercury (Hg), and lead (Pb)) on the total environment: an overview. Environ Monit Assess 191(7):1–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7528-7
Bin HS, Hossain MB, Hossain MS, Jolly YN, Sarker S (2021) Ecological risk evaluation in bottom-surface sediments and sub-surface water in the subtropical Meghna estuarine system. Heliyon 7(11):e08324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08324
Ali AE, Strezov V, Davies PJ, Wright I (2018) River sediment quality assessment using sediment quality indices for the Sydney basin, Australia affected by coal and coal seam gas mining. Sci Total Environ 616–617:695–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.259
Ong MC, Pan HJ, Shazili NAM, Menier D, Dupont V, Révillon S, Connell A (2021) Heavy metals concentration in sediments of South Brittany Waters, France: an ecological risk assessment approach. Open J Mar Sci 11(01):55–68. https://doi.org/10.4236/ojms.2021.111004
Bazrafshan E, Kord F, Esmaelnejad M, Reza G (2015) Concentration of heavy metals in surface water and sediments of Chah Nimeh water reservoir in Sistan and Baluchestan province, Iran Concentration of heavy metals in surface water and sediments of Chah Nimeh water reservoir in Sistan and Baluchestan province Iran. Desalin Water Treat 57(20):9332–9342. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1027958
Tchounwou PB, Yedjou CG, Patlolla AK, Sutton DJ (2012) Molecular, clinical and environmental toxicicology Volume 3: Environmental Toxicology 101:133–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7643-8340-4
Aoshima K (2016) Itai-itai disease: renal tubular osteomalacia induced by environmental exposure to cadmium—historical review and perspectives. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 62(4):319–326. https://doi.org/10.1080/00380768.2016.1159116
Haghighi-Morad M, Zamani N, Hassanian-Moghaddam H, Shojaei M (2020) Encephalopathy following ingestion of Lead-contaminated opium; Magnetic resonance imaging findings. BMC Neurol 20(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-020-01750-z
Environmental and Forestry Agency of Banten Province in Indonesia (2019) Final Report of Environmental Protection and Management Plan
Difa (2019) Soal Pencemaran Sungai Ciujung, Pemprov Banten Ngaku tak Punya Solusi. 27 Agustus 2019. https://www.redaksi24.com/soal-pencemaran-sungai-ciujung-pemprov-banten-ngaku-tak-punya-solusi/. Accessed 27 Aug 2019
Belmer N, Wright IA, Tippler C (2015) Urban geochemical contamination of high conservation value upland urban geochemical contamination of high conservation value upland swamps, Blue Mountains Australia. Water Air Soil Pollut 226(10):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2607-z
Wright IA, Ryan MM (2016) Impact of mining and industrial pollution on stream macroinvertebrates: importance of taxonomic resolution, water geochemistry and EPT indices for impact detection. Hydrobiologia 772(1):103–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-016-2644-7
Th RM (2012) Distribution of heavy metals in sediments of the Ciujung watersheds Banten. Jurnal Teknologi Reaktor Nuklir 14(3):157–169
Haq A, Achmadi UF, Mallongi A (2018) Environmental health risk assessment due to exposure to mercury in artisanal and small-scale gold mining area of Lebak District. Global J Health Sci 10(3):125. https://doi.org/10.5539/gjhs.v10n3p125
Prilia D, Oginawati K, Ariesyady HD (2013) Analysis of mercury in water and sediment distribution and its bioaccumulation potential in fish in the small scale gold mining area (case study : Ciberang River, Lebak, Banten). J Water Sustain 3(2):107–116. https://doi.org/10.11912/jws.3.2.107-116
Ali MM, Ali ML, Islam MS, Rahman MZ (2016) Preliminary assessment of heavy metals in water and sediment of Karnaphuli River, Bangladesh. Environ Nanotechnol Monitor Manag 5:27–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2016.01.002
Knap A, Michaels A, Close HD, Dickson A (1996) Protocols for the joint global ocean flux study (JGOFS) core measurements. JGOFS, Reprint of the IOC Manuals and Guides No. 29, UNESCO 1994, 19
Andersen JM (1976) An ignition method for determination of total phosphorus in lake sediments. Water Res 10(4):329–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(76)90175-5
Long ER, Macdonald DD, Smith SL, Calder FD (1995) Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Environ Manag 19(1):81–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02472006
Macdonald DD, Ingersoll CG, Berger TA (2000) Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment effect concentrations for polychlorinated biphenyls. Environ Toxicol Chem Int J 19(5):1403–1413
Muller G (1969) Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal 2(3):108–118
Suwandana E (2012) Comparative study on water quality assessment between urban and rural watersheds: a case study of Ciliwung and Ciujung watershed, Indonesia. Dissertation, Hiroshima University, Japan
Stoffers P, Glasby GP, Wilson CJ, Davis KR, Walter P (1986) Heavy metal pollution in wellington harbour. NZ J Mar Freshwat Res 20(3):495–512. https://doi.org/10.1080/00288330.1986.9516169
Abrahim GMS, Parker RJ (2008) Assessment of heavy metal enrichment factors and the degree of contamination in marine sediments from Tamaki Estuary, Auckland, New Zealand. Environ Monit Assess 136(1–3):227–238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-9678-2
Salomon W, Forstner U (1984) Metals in the hydrocycle. In: Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling. Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-69325-0
Shirani M, Afzali KN, Jahan S, Strezov V, Soleimani-Sardo M (2020) Pollution and contamination assessment of heavy metals in the sediments of Jazmurian playa in southeast Iran. Sci Rep 10(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-61838-x
Watts MJ, Mitra S, Marriott AL, Sarkar SK (2017) Source, distribution and ecotoxicological assessment of multielements in superficial sediments of a tropical turbid estuarine environment: a multivariate approach. Mar Pollut Bull 115(1–2):130–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.11.057
Ge M, Liu G, Liu H, Liu Y (2020) Distribution, bioavailability and contamination assessment of mercury and arsenic in the surface sediments from the Yellow River Estuary, China. Hum Ecol Risk Assess Int J 27(1):274–288. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2019.1710460
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res 14(8):975–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
Gao X, Chen CTA (2012) Heavy metal pollution status in surface sediments of the coastal Bohai Bay. Water Res 46(6):1901–1911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.01.007
ANZECC, ARMCANZ (2000) Australian and New Zealand guidelines for fresh and marine water quality The Guidelines Australian and New Zealand Environment and Conservation Council Agriculture and Resource Management Council of Australia and New Zealand. National Water Quality Management Strategy 1(4):314. http://www.dofa.gov.au/infoaccess/
Long ER, MacDonald DD (2016) Recommended uses of empirically derived, sediment quality guidelines for marine and estuarine ecosystems. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 4(5):1019–1039. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039891284956
Mccready S, Birch GF, Long ER (2006) Metallic and organic contaminants in sediments of Sydney Harbour, Australia and vicinity—a chemical dataset for evaluating sediment quality guidelines. Environ Int 32(4):455–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2005.10.006
Astatkie H, Ambelu A, Mengistie E (2021) Contamination of stream sediment with heavy metals in the Awetu watershed of Southwestern Ethiopia. Front Earth Sci 9(July):1–13. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2021.658737
Tomno RM, Nzeve JK, Mailu SN, Shitanda D, Waswa F (2020) Heavy metal contamination of water, soil and vegetables in urban streams in Machakos municipality, Kenya. Sci Afr 9:e00539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sciaf.2020.e00539
Gan Y, Huang X, Li S, Liu N, Li YC, Freidenreich A, Wang W, Wang R, Dai J (2019) Source quantification and potential risk of mercury, cadmium, arsenic, lead, and chromium in farmland soils of Yellow River Delta. J Clean Prod 221:98–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.02.157
ATSDR (2007a) Toxicological Profile for Arsenic. http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp2.pdf
Tang H, Ke Z, Yan M, Wang W, Nie H, Li B, Zhang J, Xu X, Wang J (2018) Concentrations, distribution, and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in Daya Bay, China. Water (Switzerland) 10(6):780. https://doi.org/10.3390/W10060780
Xu JY, Zheng LL, Xu LG, Wang XL (2019) Ecological risk assessment and source analysis of heavy metals in surface sediments of rivers located in the hilly area of southern China. Zhongguo Huanjing Kexue/China Environmental Science 39(8):3420–3429
Huang L, Fang H, Ni K, Yang W, Zhao W, He G, Han Y, Li X (2018) Distribution and potential risk of heavy metals in sediments of the Three Gorges Reservoir: the relationship to environmental variables. Water (Switzerland) 10(12):1840. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10121840
Algül F, Beyhan M (2020) Concentrations and sources of heavy metals in shallow sediments in Lake Bafa, Turkey. Sci Rep 10(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-68833-2
Ohba T, Kimura Y, Fujimaki H (2007) High-magnesian andesite produced by two-stage magma mixing: a case study from Hachimantai, Northern Honshu, Japan. J Petrol 48(3):627–645. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/egl075
Platias S, Vatalis KI, Charalampides G (2014) Suitability of quartz sands for different industrial applications. Proc Econ Finance 14(14):491–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2212-5671(14)00738-2
Rosales RM, Faz A, Gómez-Garrido M, Muñoz MA, Murcia FJ, González V, Acosta JA (2017) Geochemical speciation of chromium related to sediments properties in the riverbed contaminated by tannery effluents. J Soils Sediments 17(5):1437–1448. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-016-1412-7
Goix S, Maurice L, Laffont L, Rinaldo R, Lagane C, Chmeleff J, Menges J, Heimbürger LE, Maury-Brachet R, Sonke JE (2019) Quantifying the impacts of artisanal gold mining on a tropical river system using mercury isotopes. Chemosphere 219:684–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.12.036
Agarwalla H, Senapati RN, Das TB (2021) Mercury emissions and partitioning from Indian coal-fired power plants. J Environ Sci (China) 100:28–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2020.06.035
Raj D, Maiti SK (2020) Sources, bioaccumulation, health risks and remediation of potentially toxic metal(loid)s (As, Cd, Cr, Pb and Hg): an epitomised review. Environ Monit Assess 192(2):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-8060-5
ATSDR (2007b) Toxicological Profile for Lead. http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/ToxProfiles/tp13.pdf
Bird BW, Wilson JJ, Escobar J, Kamenov GD, Pollard HJ, Monaghn GW (2019) Pre-Columbian lead pollution from Native American galena processing and land use in the midcontinental United States. Geology 47(12):1193–1197. https://doi.org/10.1130/G46673.1
Liu Q, Wang F, Meng F, Jiang L, Li G, Zhou R (2018) Assessment of metal contamination in estuarine surface sediments from Dongying City, China: Use of a modified ecological risk index. Mar Pollut Bull 126(November 2017):293–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.11.017
Iordache AM, Nechita C, Zgavarogea R, Voica C, Varlam M, Ionete RE (2022) Accumulation and ecotoxicological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Olt River, Romania. Scientific Reports 12(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-04865-0
Iordache AM, Nechita C, Zgavarogea R, Voica C, Varlam M, Ionete RE (2022) Accumulation and ecotoxicological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Olt River, Romania. Sci Rep 12(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-04865-0
Elvira MV, Faustino-Eslava DV, Fukuyama M, de Chavez ERC, Padrones JT (2020) Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the bottom sediments of Laguna de Bay, Philippines. Mindanao J Sci Technol 18(2):311–335
Mandeng EPB, Bidjeck LMB, Bessa AZE, Ntomb YD, Wadjou JW, Doumo EPE, Dieudonné LB (2019) Contamination and risk assessment of heavy metals, and uranium of sediments in two watersheds in Abiete-Toko gold district Southern Cameroon. Heliyon 5(10):e02591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02591
Agah H (2021) Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediment, fish, and human hair from Chabahar Bay, Makoran, Iran. Marine Pollution Bulletin 169:112345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112345
Da Silva YJAB, Cantalice JRB, Singh, VP, Do Nascimento CWA, Wilcox BP, Bezerra Da Silva YJA (2019) Heavy metal concentrations and ecological risk assessment of the suspended sediments of a multi-contaminated Brazilian watershed. Acta Scientiarum - Agronomy, 41(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.4025/actasciagron.v41i1.42620
Nugraha WC, Jeong H, Phan Dinh Q, Ishibashi Y, Arizono K (2022) Combination of vortex agitation and ultrasonic irradiation for mercury removal from sediment by acid extraction. Bull Eviron Contam Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-022-03471-0
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by an international postgraduate scholarship for research on mercury from the Kumamoto Prefectural Government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nugraha, W.C., Ishibashi, Y. & Arizono, K. Assessment of heavy metal distribution and contamination in the sediment of the Ciujung Watershed, Banten Province, Indonesia. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 25, 2619–2631 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-023-01661-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-023-01661-4