Abstract
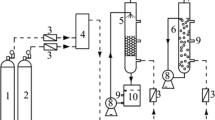
Biological process is getting more popular to remove hydrogen sulfide (H2S) from biogas. However, many challenges are yet to be addressed to make it more economically viable and environmentally friendlier. In this study, a 5-m3 bio-filter was packed with a propylene carrier with a packed-bed volume of 2.3 m3, and fed with biogas at a flow rate of 42.2 ± 2.2 m3 h−1 with an average inlet H2S of 3412 ppmv. Oxygen from air was fed and used as the final electron acceptor. Digestate was recirculated into the bio-filter as nutrient for the microbial population, while hot water was mixed with the trickled water to maintain the inside temperature around 32°C. The average H2S removal efficiency (RE) was 97%. RE was increased with temperature and sulfide concentration, while the opposite was observed at a pH between 3.23 and 1.77. A maximum H2S elimination capacity (EC) of 95.60 g m−3 h−1 was observed. The kinetic modeling study showed that EC was fitted better with Haldane model than Michaelis–Menten model, indicating the presence of inhibition during the biological treatment of high H2S. The microbial community analysis showed the predominance of Acidithiobacillus caldus, which is an extremely acidophilic bacterium and grows at a moderate thermophilic temperature.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andriamanohiarisoamanana FJ, Saikawa A, Kan T et al (2018) Semi-continuous anaerobic co-digestion of dairy manure, meat and bone meal and crude glycerol: process performance and digestate valorization. Renew Energy 128:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.05.056
Mwirigi JW, Makenzi PM, Ochola WO (2009) Socio-economic constraints to adoption and sustainability of biogas technology by farmers in Nakuru Districts, Kenya. Energy Sustain Dev 13:106–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esd.2009.05.002
Wilkinson KG (2011) A comparison of the drivers influencing adoption of on-farm anaerobic digestion in Germany and Australia. Biomass Bioenerg 35:1613–1622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2011.01.013
Andriamanohiarisoamanana F, Yamashiro T, Ihara I et al (2016) Farm-scale thermophilic co-digestion of dairy manure with a biodiesel byproduct in cold regions. Energy Convers Manag 128:273–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2016.09.084
Zhao J, Ge X, Vasco-Correa J, Li Y (2014) Fungal pretreatment of unsterilized yard trimmings for enhanced methane production by solid-state anaerobic digestion. Bioresour Technol 158:248–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.02.029
Zuo Z, Wu S, Qi X, Dong R (2015) Performance enhancement of leaf vegetable waste in two-stage anaerobic systems under high organic loading rate: Role of recirculation and hydraulic retention time. Appl Energy 147:279–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.03.001
Bond T, Templeton MR (2011) History and future of domestic biogas plants in the developing world. Energy Sustain Dev 15:347–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esd.2011.09.003
Aoki K, Umetsu K, Nishizaki K et al (2006) Thermophilic biogas plant for dairy manure treatment as combined power and heat system in cold regions. Int Congr Ser 1293:238–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ics.2006.03.014
Oliver B, Pain BF, Phillips VR (1986) Mesophilic anaerobic digestion of dairy cow slurry on a farm scale: economic considerations. J Agric Eng Res 34:229–243
Saikawa A, Takeuchi Y, Pan Z et al (2017) Digested slurry recirculation in thermophilic wet anaerobic digestion of dairy manure without water dilution. J Jpn Soc Agric Mach 79:242–247
Cherosky P, Li Y (2013) Hydrogen sulfide removal from biogas by bio-based iron sponge. Biosyst Eng 114:55–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2012.10.010
Rasi S, Läntelä J, Rintala J (2011) Trace compounds affecting biogas energy utilisation—a review. Energy Convers Manag 52:3369–3375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2011.07.005
Andriamanohiarisoamanana FJ, Sakamoto Y, Yamashiro T et al (2017) The seasonal effects of manure management and feeding strategies on hydrogen sulphide emissions from stored dairy manure. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-016-0519-7(in press)
Dai XR, Blanes-Vidal V (2013) Emissions of ammonia, carbon dioxide, and hydrogen sulfide from swine wastewater during and after acidification treatment: effect of pH, mixing and aeration. J Environ Manage 115:147–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.11.019
Andriamanohiarisoamanana FJ, Sakamoto Y, Yamashiro T et al (2015) Effects of handling parameters on hydrogen sulfide emission from stored dairy manure. J Environ Manage 154:110–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.02.003
Vollertsen J, Nielsen AH, Jensen HS et al (2008) Corrosion of concrete sewers—the kinetics of hydrogen sulfide oxidation. Sci Total Environ 4:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.01.028
Zhang L, De Schryver P, De Gusseme B et al (2008) Chemical and biological technologies for hydrogen sulfide emission control in sewer systems: a review. Water Res 42:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.07.013
Rattanapan C, Ounsaneha W (2012) Removal of hydrogen sulfide gas using bio-filtration—a review. Walailak J Sci Technol 9:9–18
Fortuny M, Gabriel D, Lafuente J, Gamisans X (2009) Technical and economical study of a full-scale bio-trickling filter for H2S removal from biogas. Water Pract Technol. https://doi.org/10.2166/wpt.2009.026
Fernández M, Ramírez M, Gómez JM, Cantero D (2014) Biogas biodesulfurization in an anoxic bio-trickling filter packed with open-pore polyurethane foam. J Hazard Mater 264:529–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.10.046
Kobayashi T, Li YY, Kubota K et al (2012) Characterization of sulfide-oxidizing microbial mats developed inside a full-scale anaerobic digester employing biological desulfurization. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93:847–857. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3445-6
Lebrero R, Toledo-Cervantes A, Muñoz R et al (2016) Biogas upgrading from vinasse digesters: a comparison between an anoxic bio-trickling filter and an algal-bacterial photobioreactor. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 91:2488–2495. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.4843
Muñoz R, Meier L, Diaz I, Jeison D (2015) A review on the state-of-the-art of physical/chemical and biological technologies for biogas upgrading. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 14:727–759. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-015-9379-1
Ramos I, Peña M, Fdz-Polanco M (2014) Where does the removal of H2S from biogas occur in microaerobic reactors? Bioresour Technol 166:151–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.05.058
Ben JM, Couvert A, Amrane A et al (2016) Bio-filtration of high concentration of H2S in waste air under extreme acidic conditions. N Biotechnol 33:136–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2015.09.008
Gallastegui G, Ávalos Ramirez A, Elías A et al (2011) Performance and macro-kinetic analysis of bio-filtration of toluene and p-xylene mixtures in a conventional bio-filter packed with inert material. Bioresour Technol 102:7657–7665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.05.054
Rattanapan C, Boonsawang P, Kantachote D (2009) Removal of H2S in down-flow GAC bio-filtration using sulfide oxidizing bacteria from concentrated latex wastewater. Bioresour Technol 100:125–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.05.049
Dumont É (2017) Validation of a rapid procedure to determine biofilter performances. J Environ Chem Eng 5:2668–2680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.05.022
Zhu R, Li S, Bao X, Dumont É (2017) Comparison of biological H2S removal characteristics between a composite packing material with and without functional microorganisms. Sci Rep 7:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep42241
Sologar VS, Lu Z, Allen DG (2003) Biofiltration of concentrated mixtures of hydrogen sulfide and methanol. Environ Prog 22:129–136. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.670220215
Zhou Q, Liang H, Yang S, Jiang X (2015) The removal of hydrogen sulfide from biogas in a microaerobic bio-trickling filter using polypropylene carrier as packing material. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 175:3763–3777. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1545-y
Díaz I, Pérez SI, Ferrero EM, Fdz-Polanco M (2011) Effect of oxygen-dosing point and mixing on the microaerobic removal of hydrogen sulphide in sludge digesters. Bioresour Technol 102:3768–3775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.12.016
Chaiprapat S, Mardthing R, Kantachote D, Karnchanawong S (2011) Removal of hydrogen sulfide by complete aerobic oxidation in acidic bio-filtration. Process Biochem 46:344–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2010.09.007
Dumont E (2015) H2S removal from biogas using bioreactors: a review. Int J Energy Environ 6:479–498
Oyarzún P, Arancibia F, Canales C, Aroca GE (2003) Bio-filtration of high concentration of hydrogen sulphide using Thiobacillus thioparus. Process Biochem 39:165–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(03)00050-5
Romero Hernandez AC, Rodríguez Susa MS, Andrès Y, Dumont E (2013) Steady-and transient-state H2S bio-filtration using expanded schist as packing material. N Biotechnol 30:210–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2012.07.003
Yang Y, Allen ER (2012) Bio-filtration control of hydrogen sulfide 1 design and operational parameters. Air Waste 44:863–868. https://doi.org/10.1080/1073161x.1994.10467287
Chung Y-C, Huang C, Tseng C-P (1996) Operation optimization of Thiobacillus thioparus CH11 bio-filter for hydrogen sulfide removal. J Biotechnol 52:31–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-1656(96)01622-7
Charnnok B, Suksaroj T, Boonswang P, Chaiprapat S (2013) Oxidation of hydrogen sulfide in biogas using dissolved oxygen in the extreme acidic bio-filtration operation. Bioresour Technol 131:492–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.12.114
de Arespacochaga N, Valderrama C, Mesa C et al (2014) Biogas biological desulphurisation under extremely acidic conditions for energetic valorisation in solid oxide fuel cells. Chem Eng J 255:677–685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.06.073
Ho KL, Chung YC, Lin YH, Tseng CP (2008) Microbial populations analysis and field application of bio-filter for the removal of volatile-sulfur compounds from swine wastewater treatment system. J Hazard Mater 152:580–588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.07.021
Rodriguez G, Dorado AD, Fortuny M et al (2014) Bio-trickling filters for biogas sweetening: Oxygen transfer improvement for a reliable operation. Process Saf Environ Prot 92:261–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2013.02.002
Chung Y-C, Huang C, Tseng C-P (1996) Biodegradation of hydrogen sulfide by a laboratory-scale immobilized Pseudomonas putida CH11 bio-filter. Biotechnol Prog 12:773–778. https://doi.org/10.1021/bp960058a
Wang R, Lin JQ, Liu XM et al (2019) Sulfur oxidation in the acidophilic autotrophic Acidithiobacillus spp. Front Microbiol 10:1–20. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.03290
Zhou QG, Bo F, Hong Bo Z et al (2007) Isolation of a strain of Acidithiobacillus caldus and its role in bioleaching of chalcopyrite. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 23:1217–1225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-007-9350-6
Acuña LG, Cárdenas JP, Covarrubias PC et al (2013) Architecture and gene repertoire of the flexible genome of the extreme acidophile Acidithiobacillus caldus. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0078237
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andriamanohiarisoamanana, F.J., Yasui, S., Iwasaki, M. et al. Performance study of a bio-trickling filter to remove high hydrogen sulfide concentration from biogas: a pilot-scale experiment. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 22, 1390–1398 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-020-01031-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-020-01031-4