Abstract
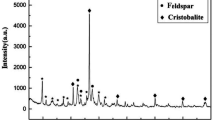
The large pores and the rather hydrophobic nature of silica-rich BEA-type zeolites make them promising dye adsorbents. Composites of such zeolites and magnetic particles (magnetic zeolites), commonly prepared using hydrothermal techniques, can be rapidly and reliably removed from treated wastewater through magnetic separation and are therefore more practical than conventional zeolites. However, the incorporation of magnetic particles is difficult to control since it depends greatly on whether the zeolite nucleation occurs in the vicinity of magnetic particles or not. To overcome this problem, we herein synthesize silica-rich magnetic BEA-type zeolites via a different route called dry-gel conversion, namely by exposing a precursor gel containing well-dispersed magnetite to water vapor at 180 °C for 12 h. The obtained samples were characterized by XRD and SEM–EDS and their dye adsorption performance were evaluated using methylene blue as a model. The results indicate that the precursor gel was successfully converted into BEA-type zeolites that contain homogeneously distributed magnetite, exhibit a high methylene blue adsorption capacity (133 mg/g), and can be easily separated by application of a magnetic field. Consequently, this study paves the way to the development of an efficient wastewater treatment technology and thus contributes to the establishment of a green society.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yagub MT, Sen T, Afroze S, Ang HM (2014) Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: a review. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 209:172–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2014.04.002
Katheresan V, Kansedo J, Lau SY (2018) Efficiency of various recent wastewater dye removal methods: a review. J Environ Chem Eng 6:4676–4697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.06.060
Huang T, Yan M, He K, Huang Z, Zeng G, Chen A, Peng M, Li H, Yuan L, Chen G (2019) Efficient removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions using magnetic graphene oxide modified zeolite. J Colloid Interface Sci 543:43–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.02.030
Modak JB, Bhowal A, Datta S (2016) Extraction of dye from aqueous solution in rotating packed bed. J Hazard Mater 304:337–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.10.062
Gupta VK, Carrot PJM, Ribeiro Carrot MML, Suhas (2009) Low-cost adsorbents: growing approach to wastewater treatment—a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 39:783–842. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643380801977610
Tsai WT, Hsien KJ, Hsu HC (2009) Adsorption of organic compounds from aqueous solution onto the synthesized zeolite. J Hazard Mater 166:635–641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.11.071
Crini G (2006) Non-conventional low-cost adsorbents for dye removal: a review. Bioresour Technol 97:1061–1085. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2005.05.001
Rafatullah M, Sulaiman O, Hashim R, Ahmad A (2010) Adsorption of methylene blue on low-cost adsorbents: a review. J Hazard Mater 177:70–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.12.047
Megias-Sayago C, Bingre R, Huang L, Lutzweiler G, Wang Q, Louis B (2019) CO2 adsorption capacities in zeolites and layered double hydroxide materials. Front Chem 7:551–560. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2019.00551
Sun K, Lu J, Ma L, Han Y, Fu Z, Ding J (2015) A comparative study on the catalytic performance of different types of zeolites for biodiesel production. Fuel 158:848–854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2015.06.048
Baerlocher C, McCusker LB (2019) Database of zeolite structures. https://www.iza-structure.org/databases/. Accessed 20 Mar 2019
Liu H, Peng S, Shu L, Chen T, Bao T, Frost RL (2013) Magnetic zeolite NaA: synthesis, characterization based on metakaolin and its application for the removal of Cu2+, Pb2+. Chemosphere 91:1539–1546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.12.038
Liu H, Peng S, Shu L, Chen T, Bao T, Frost RL (2013) Effect of Fe3O4 addition on removal of ammonium by zeolite NaA. J Colloid Interface Sci 390:204–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2012.09.010
Cao J, Chang G, Guo H, Chen J (2013) Synthesis and characterization of magnetic ZSM-5 zeolite. Trans Tianjin Univ 19:326–331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12209-013-1912-0
Cao JL, Liu XW, Fu R, Tan ZY (2008) Magnetic P zeolites: Synthesis, characterization and the behavior in potassium extraction from seawater. Sep Purif Technol 63:92–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2008.04.015
Aono H, Kaji N, Itagaki Y, Johan E, Matsue N (2016) Synthesis of mordenite and its composite material using chemical reagents for Cs decontamination. J Ceram Soc Jpn 124:617–623. https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.15317
Hagio T, Kunishi H, Yamaoka K, Kamimoto Y, Ichino R (2018) Seed-assisted synthesis of magnetic faujasite-type zeolite and its adsorption performance. Nanosci Nanotechnol Lett 10:862–867. https://doi.org/10.1166/nnl.2018.2640
Inoue T, Itakura M, Jon H, Oumi Y, Takahashi A, Fujitani T, Sano T (2009) Synthesis of LEV zeolite by interzeolite conversion method and its catalytic performance in ethanol to olefins reaction. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 122:149–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2009.02.027
van Tendeloo L, Haouas M, Matens JA, Kirschhock CEA, Breynaert E, Taulelle F (2015) Zeolite synthesis in hydrated silicate ionic liquids. Faraday Discuss 179:437–449. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4fd00234b
Park M, Choi CL, Lim WT, Kim MC, Choi J, Heo NH (2000) Molten-salt method for the synthesis of zeolitic materials I. Zeolite formation in alkaline molten-salt system. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 37:81–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1387-1811(99)00196-1
Ren L, Wu Q, Yang C, Zhu L, Li C, Zhang P, Zhang H, Meng X, Xiao FS (2012) Solvent-free synthesis of zeolites from solid raw materials. J Am Chem Soc 134:15173–15176. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja3044954
Petkowicz DI, Canal S, Finger PH, Mignoni ML, dos Santos JHZ (2017) Synthesis of hybrid zeolites using a solvent-free method in the presence of different organosilanes. Microporous Mesoporous Mat 241:98–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2016.11.030
Wenyang Xu, Dong J, Li J, Li J, Wu F (1990) A novel method for the preparation of zeolite ZSM-5. J Chem Soc Chem Commun 10:755–756. https://doi.org/10.1039/C39900000755
Hari Prasad Rao PR, Matsukata M (1996) Dry-gel conversion technique for synthesis of zeolite BEA. Chem Commun 12:1441–1442. https://doi.org/10.1039/CC9960001441
Mohammadparast F, Halladj R, Askari S (2018) The synthesis of nano-sized ZSM-5 zeolite by dry gel conversion method and investigating the effects of experimental parameters by Taguchi experimental design. J Exp Nanosci 13:160–173. https://doi.org/10.1080/17458080.2018.1453172
Li YS, Church JS, Woodhead AL (2012) Infrared and Raman spectroscopic studies on iron oxide magnetic nano-particles and their surface modifications. J Magn Magn Mater 324:1543–1550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2011.11.065
Matsui M, Kiyozumi Y, Mizushina Y, Sakaguchi K, Mizukami F (2015) Adsorption and desorption behavior of basic proteins on zeolites. Sep Purif Technol 149:103–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2015.05.023
Damjanovic L, Rakic V, Rac V, Stosic D, Auroux A (2010) The investigation of phenol removal from aqueous solutions by zeolites as solid adsorbents. J Hazard Mater 184:477–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.08.059
Grieco SA, Ramarao BV (2013) Removal of TCEP from aqueous solutions by adsorption with zeolites. Colloids Surf A 434:329–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2013.04.042
Belaabed R, Elabed S, Addaou A, Laajab A, Rodríguez MA, Lahsini A (2016) Synthesis of LTA zeolite for bacterial adhesion. Bol Soc Esp Cerám Vidri 55:152–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bsecv.2016.05.001
Wang S, Zhu ZH (2006) Characterisation and environmental application of an Australian natural zeolite for basic dye removal from aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 136:946–952. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.01.038
Wang S, Li H, Xu L (2006) Application of zeolite MCM-22 for basic dye removal from wastewater. J Colloid Interface Sci 295:71–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2005.08.006
Jin X, Jiang MQ, Shan XQ, Pei ZG, Chen Z (2008) Adsorption of methylene blue and orange II onto unmodified and surfactant-modified zeolite. J Colloid Interface Sci 328:243–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2008.08.066
Han R, Zhang J, Han P, Wang Y, Zhao Z, Tang M (2009) Study of equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic parameters about methylene blue adsorption onto natural zeolite. Chem Eng J 145:496–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2008.05.003
Sohrabnezhad S, Pourahmad A (2010) Comparison absorption of new methylene blue dye in zeolite and nanocrystal zeolite. Desalination 256:84–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.02.009
Sun Z, Li C, Wu D (2010) Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by adsorption onto zeolite synthesized from coal fly ash and its thermal regeneration. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 85:845–850. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.2377
Sapawe N, Jalil AA, Triwahyono S, Shah MIA, Jusoh R, Salleh NFM, Hameed BH, Karim AH (2013) Cost-effective microwave rapid synthesis of zeolite NaA for removal of methylene blue. Chem Eng J 229:388–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.06.005
Kariminezhad H, Habibi M, Mirzababayi N (2015) Nanosized ZSM-5 will improve photodynamic therapy using methylene blue. J Photochem Photobiol B 148:107–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2015.03.013
Acknowledgements
This research was partially supported by (i) the Project of Creation of Life Innovation Materials for Interdisciplinary and International Researcher Development of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan (ii) the JSPS Core-to-Core Program, B. Asia-Africa Science Platforms, and (iii) the International Science Program, Uppsala University, Sweden. We would also like to thank Editage for editing and reviewing this manuscript for English language.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Phouthavong, V., Hiraiwa, M., Hagio, T. et al. Magnetic BEA-type zeolites: preparation by dry-gel conversion method and assessment of dye removal performance. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 22, 375–382 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-020-00994-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-020-00994-8