Abstract
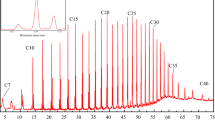
This paper gives the results of partial oxidation experiments of polyethylene (PE) in supercritical water (SCW). The experiments were carried out at a reaction temperature of 693K and a reaction time of 30 min using 6 cm3 of a batch-type reactor. The loaded sample weight was 0.3 g and there was 2.52 g water (0.42 g/cm3). The ratio of oxygen atoms to carbon atoms was 0.3. The results show a significant CO formation in O2–SCW, and the 1-alkene/n-alkane ratio in partial oxidation was higher than that in SCW pyrolysis. These results suggest the possibility of the hydrogenation of hydrocarbon through partial oxidation followed by a water–gas shift reaction.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: July 19, 2000 / Accepted: September 28, 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Watanabe, M., Sawamoto, S., Adschiri, T. et al. Polyethylene conversion by partial oxidation in supercritical water. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 3, 99–102 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-000-0045-4
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-000-0045-4