Abstract
Background
Anemia is common in chronic kidney disease (CKD) and may be associated with mortality in CKD patients. However, few studies have examined this relationship in Asian populations.
Methods
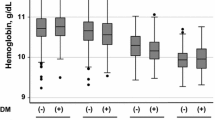
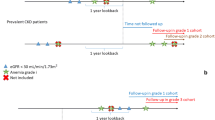
A total of 62,931 Japanese people (age 64.0 ± 8.0 years; men 38.5%) were followed up from 2008 to 2012. Participants were divided into six groups in accordance with their estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) (<45, 45–59, ≥60 mL/min/1.73 m2) and by hemoglobin levels (13.0 g/dL for men; 12.0 g/dL for women). Hazard ratio and confidence interval (CI) for mortality with a combination of eGFR and anemia were calculated. After matching using propensity score (PS) for anemia, survival analysis between anemic and non-anemic people, independent from some variables, including eGFR, was performed.
Results
A total of 828 (1.3%) participants died (non-anemic vs. anemic, 1.2 vs. 2.3%, p < 0.01). Multivariable Cox analysis showed that, independent of eGFR levels, anemic people had significantly higher mortality. Anemic people were found to have significantly poorer survival than non-anemic people as per a log-rank test (p < 0.01) for the PS-matching cohort. Further stratified logistic analysis using PS in the overall cohort odds ratio (95% CI) showed 2.25 (1.89–2.67) with p < 0.01.
Conclusion
The results of the present study showed that anemia was an independent risk factor of all-cause mortality.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramson JL, Jurkovitz CT, Vaccarino V, Weintraub WS, McClellan W. Chronic kidney disease, anemia, and incident stroke in a middle-aged, community-based population: the ARIC Study. Kidney Int. 2003;64(2):610–5.
Jurkovitz CT, Abramson JL, Vaccarino LV, Weintraub WS, McClellan WM. Association of high serum creatinine and anemia increases the risk of coronary events: results from the prospective community-based atherosclerosis risk in communities (ARIC) study. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003;14(11):2919–25.
Vlagopoulos PT, Tighiouart H, Weiner DE, Griffith J, Pettitt D, Salem DN, et al. Anemia as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality in diabetes: the impact of chronic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16(11):3403–10.
Singh AK, Szczech L, Tang KL, Barnhart H, Sapp S, Wolfson M, CHOIR Investigators, et al. Correction of anemia with epoetin alfa in chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(20):2085–98.
Drüeke TB, Locatelli F, Clyne N, Eckardt KU, Macdougall IC, Tsakiris D, CREATE Investigators, et al. Normalization of hemoglobin level in patients with chronic kidney disease and anemia. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(20):2071–84.
Sato Y, Yano Y, Fujimoto S, Konta T, Iseki K, Moriyama T, et al. Glycohemoglobin not as predictive as fasting glucose as a measure of prediabetes in predicting proteinuria. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012;27(10):3862–8.
Sato Y, Fujimoto S, Konta T, Iseki K, Moriyama T, Yamagata K, et al. U-shaped association between body mass index and proteinuria in a large Japanese general population sample. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2014;18(1):75–86.
Sato Y, Fujimoto S, Konta T, Iseki K, Moriyama T, Yamagata K, et al. Significance of estimated glomerular filtration rate in predicting brain or heart attacks in obese and non-obese populations. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2015;19(5):790–6.
Iseki K, Asahi K, Yamagata K, Fujimoto S, Tsuruya K, Narita I, et al. Mortality risk among screened subjects of the specific health check and guidance program in Japan 2008–2012. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2017. doi:10.1007/s10157-017-1392-y (Epub ahead of print).
Matsuo S, Imai E, Horio M, Yasuda Y, Tomita K, Nitta K, et al. Collaborators developing the Japanese equation for estimated GFR: revised equations for estimated GFR from serum creatinine in Japan. Am J Kidney Dis. 2009;53(6):982–92.
World Health Organization. Nutritional anaemias: report of a WHO scientific group. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. 1968;405:3–37.
American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2011;34(Suppl 1):S62–9. doi:10.2337/dc11-S062.
Silberberg J, Racine N, Barre P, Sniderman AD. Regression of left ventricular hypertrophy in dialysis patients following correction of anemia with recombinant human erythropoietin. Can J Cardiol. 1991;6(1):1–4.
Pascual J, Teruel JL, Moya JL, Liaño F, Jiménez-Mena M, Ortuño J. Regression of left ventricular hypertrophy after partial correction of anemia with erythropoietin in patients on hemodialysis: a prospective study. Clin Nephrol. 1991;35(6):280–7.
Cannella G, La Canna G, Sandrini M, Gaggiotti M, Nordio G, Movilli E, et al. Reversal of left ventricular hypertrophy following recombinant human erythropoietin treatment of anaemic dialysed uraemic patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1991;6(1):31–7.
Ayus JC, Go AS, Valderrabano F, Verde E, de Vinuesa SG, Achinger SG, et al. Spanish group for the study of the anemia and left ventricular hypertrophy in pre-dialysis patients. Effects of erythropoietin on left ventricular hypertrophy in adults with severe chronic renal failure and hemoglobin <10 g/dL. Kidney Int. 2005;68(2):788–95.
Carlini RG, Alonzo EJ, Dominguez J, Blanca I, Weisinger JR, Rothstein M, et al. Effect of recombinant human erythropoietin on endothelial cell apoptosis. Kidney Int. 1999;55(2):546–53.
Bahlmann FH, De Groot K, Spandau JM, Landry AL, Hertel B, Duckert T, et al. Erythropoietin regulates endothelial progenitor cells. Blood. 2004;103(3):921–6.
Westenbrink BD, Lipsic E, van der Meer P, van der Harst P, Oeseburg H, Du Marchie Sarvaas GJ, et al. Erythropoietin improves cardiac function through endothelial progenitor cell and vascular endothelial growth factor mediated neovascularization. Eur Heart J. 2007;28(16):2018–27.
Harris TB, Ferrucci L, Tracy RP, Corti MC, Wacholder S, Ettinger WH Jr, et al. Associations of elevated interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein levels with mortality in the elderly. Am J Med. 1999;106(5):506–12.
Correia MI, Waitzberg DL. The impact of malnutrition on morbidity, mortality, length of hospital stay and costs evaluated through a multivariate model analysis. Clin Nutr. 2003;22(3):235–9.
Liu Y, Coresh J, Eustace JA, Longenecker JC, Jaar B, Fink NE, et al. Association between cholesterol level and mortality in dialysis patients: role of inflammation and malnutrition. JAMA. 2004;291(4):451–9.
Honda H, Qureshi AR, Heimbürger O, Barany P, Wang K, Pecoits-Filho R, et al. Serum albumin, C-reactive protein, interleukin 6, and fetuin a as predictors of malnutrition, cardiovascular disease, and mortality in patients with ESRD. Am J Kidney Dis. 2006;47(1):139–48.
Liu L, Miura K, Fujiyoshi A, Kadota A, Miyagawa N, Nakamura Y, et al. Impact of metabolic syndrome on the risk of cardiovascular disease mortality in the United States and in Japan. Am J Cardiol. 2014;113(1):84–9.
Tanaka K, Watanabe T, Takeuchi A, Ohashi Y, Nitta K, Akizawa T, CKD-JAC Investigators, et al. Cardiovascular events and death in Japanese patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2017;91(1):227–34.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Health and Labor Sciences Research Grants for “Design of the Comprehensive Health Care System for Chronic Kidney Disease Based on the Individual Risk Assessment by Specific Health Check” from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan, and a Grant-in-Aid for “Research on Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease (REACH-J), Practical Research Project for Renal Disease” from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YS designed the study, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. SF participated in designing the study as well as in collecting and analyzing the data. TK, KI, TM, KY, KT, IN, MK, MK, YS, KA, and TW contributed to the study design, data collection, study supervision, and manuscript revision. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
Ethics Committees and Institutional Review Boards at the main institutes and each participating center approved the trial (approval numbers: 1485 and 2771 in Fukushima Medical University). This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was not obtained from each participant because all data were anonymized before analysis.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Sato, Y., Fujimoto, S., Konta, T. et al. Anemia as a risk factor for all-cause mortality: obscure synergic effect of chronic kidney disease. Clin Exp Nephrol 22, 388–394 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-017-1468-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-017-1468-8