Abstract
Background
Elevated urine Mg excretion and its correlation with histological damage in tubulo-interstitial nephropathy (TIN) were reported. Here we investigated the clinical significance of the fractional excretion of Mg (FEMg) for the prediction of TIN.
Methods
We enrolled and assessed 94 adult patients with various renal diseases diagnosed principally by renal biopsy.
Results
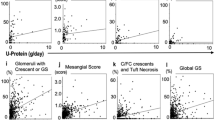
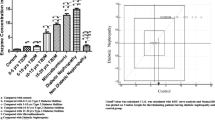
Our stratified analysis based on the value of the conventional TIN parameter N-acetylglucosaminidase (NAG) excretion showed that the high-NAG index group (more than median value of NAG-to-Cr ratio, n = 47) demonstrated significantly high FEMg values (p = 0.017). A univariate analysis revealed a significant correlation between the FEMg and the NAG index (R = 0.60) but not for other parameters. A multivariate regression analysis confirmed the significance of the FEMg as an effective predictor of the NAG index. The FEMg showed a significant correlation with the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) in the patients with eGFR ≤ 30 mL/min. The correlation of FEMg with the NAG index was not observed in the primary glomerulonephritis patients but was apparent in the patients with hypertensive nephrosclerosis or interstitial nephritis.
Conclusion
Our findings may indicate that the combination of the FEMg and the NAG index can provide a specific, sensitive assessment for TIN in patients without renal insufficiency.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mackensen-Haen S, Bader R, Grund KE, Bohle A. Correlations between renal cortical interstitial fibrosis, atrophy of the proximal tubules and impairment of the glomerular filtration rate. Clin Nephrol. 1981;15:167–71.
Nath KA. Tubulointerstitial changes as a major determinant in the progression of renal damage. Am J Kidney Dis. 1992;20:1–17.
Rodriguez-Iturbe B, Johnson RJ, Herrera-Acosta J. Tubulointerstitial damage and progression of renal failure. Kidney Int Suppl. 2005;99:S82–6.
Gilbert RE, Cooper ME. The tubulointerstitium in progressive diabetic kidney disease: more than an aftermath of glomerular injury? Kidney Int. 1999;56:1627–37.
Donadio C. Serum and urinary markers of early impairment of GFR in chronic kidney disease patients: diagnostic accuracy of urinary beta-trace protein. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010;299:F1407–23.
Morii T, Fujita H, Narita T, Koshimura J, Shimotomai T, Fujishima H, Yoshioka N, Imai H, Kakei M, Ito S. Increased urinary excretion of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in proteinuric renal diseases. Ren Fail. 2003;25:439–44.
Braden GL, Germain MJ, Fitzgibbons JP. Impaired potassium and magnesium homeostasis in acute tubulo-interstitial nephritis. Nephron. 1985;41:273–8.
Futrakul P, Yenrudi S, Futrakul N, Sensirivatana R, Kingwatanakul P, Jungthirapanich J, Cherdkiadtikul T, Laohapaibul A, Watana D, Singkhwa V, Futrakul S, Pongsin P. Tubular function and tubulointerstitial disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 1999;33:886–91.
Miura K, Nakatani T, Asai T, Yamanaka S, Tamada S, Tashiro K, Kim S, Okamura M, Iwao H. Role of hypomagnesemia in chronic cyclosporine nephropathy. Transplantation. 2002;73:340–7.
Deekajorndech T. A biomarker for detecting early tubulointerstitial disease and ischemia in glomerulonephropathy. Ren Fail. 2007;29:1013–7.
Khositseth S, Sudjaritjan N, Tananchai P, Ong-ajyuth S, Sitprija V, Thongboonkerd V. Renal magnesium wasting and tubular dysfunction in leptospirosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008;23:952–8.
Kim YK, Song HC, Kim WY, Yoon HE, Choi YJ, Ki CS, Park CW, Yang CW, Kim J, Kim YS, Choi EJ, Bang BK. Acquired Gitelman syndrome in a patient with primary Sjogren syndrome. Am J Kidney Dis. 2008;52:1163–7.
Ogihara T, Kikuchi K, Matsuoka H, Fujita T, Higaki J, Horiuchi M, Imai Y, Imaizumi T, Ito S, Iwao H, Kario K, Kawano Y, Kim-Mitsuyama S, Kimura G, Matsubara H, Matsuura H, Naruse M, Saito I, Shimada K, Shimamoto K, Suzuki H, Takishita S, Tanahashi N, Tsuchihashi T, Uchiyama M, Ueda S, Ueshima H, Umemura S, Ishimitsu T, Rakugi H. The Japanese Society of Hypertension Guidelines for the management of hypertension (JSH 2009). Hypertens Res. 2009;32:3–107.
Glaudemans B, Knoers NV, Hoenderop JG, Bindels RJ. New molecular players facilitating Mg(2+) reabsorption in the distal convoluted tubule. Kidney Int. 2010;77:17–22.
Abraham P, Indirani K, Sugumar E. Effect of cyclophosphamide treatment on selected lysosomal enzymes in the kidney of rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2007;59:143–9.
Morii T, Fujita H, Narita T, Shimotomai T, Fujishima H, Yoshioka N, Imai H, Kakei M, Ito S. Association of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 with renal tubular damage in diabetic nephropathy. J Diabetes Complicat. 2003;17:11–5.
Foster JE, Harpur ES, Garland HO. An investigation of the acute effect of gentamicin on the renal handling of electrolytes in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992;261:38–43.
Nijenhuis T, Hoenderop JG, Bindels RJ. Downregulation of Ca(2+) and Mg(2+) transport proteins in the kidney explains tacrolimus (FK506)-induced hypercalciuria and hypomagnesemia. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004;15:549–57.
Ettinger LJ, Gaynon PS, Krailo MD, Ru N, Baum ES, Siegel SE, Hammond GD. A phase II study of carboplatin in children with recurrent or progressive solid tumors. A report from the Childrens Cancer Group. Cancer. 1994;73:1297–301.
Shah GM, Kirschenbaum MA. Renal magnesium wasting associated with therapeutic agents. Miner Electrolyte Metab. 1991;17:58–64.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Financial Supporting Project for young investigators at Saitama Medical Center, Saitama Medical University (#24-C-1-C08), and was also supported, in part, by research grants from the Research Foundation for Community Medicine, Utsunomiya, Tochigi, Japan. We gratefully acknowledge Mr. T. Ozawa for his technical assistance.
Conflict of interest
The authors state that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Noiri, C., Shimizu, T., Takayanagi, K. et al. Clinical significance of fractional magnesium excretion (FEMg) as a predictor of interstitial nephropathy and its correlation with conventional parameters. Clin Exp Nephrol 19, 1071–1078 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-015-1099-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-015-1099-x