Abstract
Background
Combination therapy of aliskiren and an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) has been reported to be effective for reducing the level of proteinuria. However, it remains unclear whether this combination therapy contributes to suppression of kidney disease progression. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of aliskiren on hard renal endpoints, when added to an ARB, in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Methods
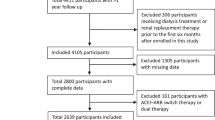
The study design was a prospective, randomized open-label design. 83 CKD patients (52 men and 31 women) were enrolled and assigned randomly to an aliskiren add-on group (n = 42) or control group (n = 41). Entry criteria included elevated serum creatinine ≥1.5 mg/dl, urine protein excretion (≥1+ on urine dipstick test), and hypertension. All participants were treated with an ARB. The follow-up period was 12 months. 12 participants were withdrawn during the study period and the study was terminated in January 2012 as a consequence of the results of the interim analysis of the ALTITUDE study.
Results
Nine patients in the aliskiren group and seven patients in the control group started dialysis. Doubling of the serum creatinine level occurred in one patient in the control group. A Cox proportional hazards test showed that dual blockade of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system with aliskiren and ARB was not associated with improvement in hard renal endpoints.
Conclusion
We conclude that aliskiren add-on therapy to an ARB may not give any benefit and, therefore, should not be recommended in CKD patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Remuzzi G, Ruggenenti P, Perico N. Chronic renal disease: renoprotective benefits of renin-angiotensin system inhibition. Ann Intern Med. 2002;136:604–15.
Jafar TH, Schmid CH, Landa M, Giatras I, Toto R, Remuzzi G, Maschio G, Brenner BM, Kamper A, Zucchelli P, Becker G, Himmelmann A, Bannister K, Landais P, Shahinfar S, de Jong PE, de Zeeuw D, Lau J, Levey AS. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and progression of nondiabetic renal disease. A meta-analysis of patient-level data. Ann Intern Med. 2001;135:73–87.
Lewis EJ, Hunsicker LG, Clarke WR, Berl T, Pohl MA, Lewis JB, Ritz E, Atkins RC, Rohde R, Raz I. Collaborative study group: renoprotective effect of the angiotensin-receptor antagonist irbesartan in patients with nephropathy due to type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:851–60.
Brenner BM, Cooper ME, de Zeeuw D, Keane WF, Mitch WE, Parving HH, Remuzzi G, Snapinn SM, Zhang Z, Shahinfar S. RENAAL study investigators: effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:861–9.
ONTARGET Investigators, Yusuf S, Teo KK, Pogue J, Dyal L, Copland I, Schumacher H, Dagenais G, Sleight P, Anderson C. Telmisartan, ramipril, or both in patients at high risk for vascular events. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:1547–59.
Mann JF, Schmieder RE, McQueen M, Dyal L, Schumacher H, Pogue J, Wang X, Maggioni A, Budaj A, Chaithiraphan S, Dickstein K, Keltai M, Metsärinne K, Oto A, Parkhomenko A, Piegas LS, Svendsen TL, Teo KK, Yusuf S, ONTARGET investigators. Renal outcomes with telmisartan, ramipril, or both, in people at high vascular risk (the ONTARGET study): a multicentre, randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. Lancet. 2008;372:547–53.
Miao Y, Dobre D, Heerspink HJ, Brenner BM, Cooper ME, Parving HH, Shahinfar S, Grobbee D, de Zeeuw D. Increased serum potassium affects renal outcomes: a post hoc analysis of the Reduction of Endpoints in NIDDM with the Angiotensin II Antagonist Losartan (RENAAL) trial. Diabetologia. 2011;54:44–50.
Staessen JA, Li Y, Richart T. Oral rennin inhibitors. Lancet. 2006;368:1449–56.
Parving H-H, Persson F, Lewis JB, Lewis EJ, Hollenberg NK. Aliskiren combined with losartan in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:2433–46.
de Zeeuw D, Remuzzi G, Parving HH, Keane WF, Zhang Z, Shahinfar S, Snapinn S, Cooper ME, Mitch WE, Brenner BM. Proteinuria, a target for renoprotection in patients with type 2 diabetic nephropathy :lessons from RENAAL. Kidney Int. 2004;65:2309–20.
Iseki K, Ikemiya Y, Iseki C, Takishita S. Proteinuria and the risk of developing end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int. 2003;63:1468–74.
Parving HH, Brenner BM, McMurray JJ, de Zeeuw D, Haffner SM, Solomon SD, Chaturvedi N, Ghadanfar M, Weissbach N, Xiang Z, Armbrecht J, Preffer MA. Aliskiren trial in type 2 diabetes using cardio-renal endpoints (ALTITUDE): rationale and study design. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009;24:1663–71.
Parving HH, Brenner BM, McMurray JJ, de Zeeuw D, Haffner SM, Solomon SD, Chaturvedi N, Persson F, Desai AS, Nicolaides M, Richard A, Xiang Z, Brunel P, Pfeffer MA. Cardiorenal end points in a trial of aliskiren for type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:2204–13.
Matsuo S, Imai E, Horio M, Yasuda Y, Tomita K, Nitta K, Yamagata K, Tomino Y, Yokoyama H, Hishida A. Collaborators developing the Japanese equation for estimated GFR. Revised equations for estimated GFR from serum creatinine in Japan. Am J Kidney Dis. 2009;53:982–92.
Watanabe N, Kamei S, Ohkubo A, Yamanaka M, Ohsawa S, Makino K, Tokuda K. Urinary protein as measured with a pyrogallol red-molybdate complex, manually and in a Hitachi 726 automated analyzer. Clin Chem. 1986;32:1551–4.
Ichihara A, Kinouchi K. Current knowledge of (pro)renin receptor as an accessory protein of vacular H+-ATPase. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2011;12:638–40.
Nishi T, Forgac M. The vacuolar (H+)-ATPases—nature’s most versatile proton pumps. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3:94–103.
Nguyen G, Delarue F, Burcklé C, Bouzhir L, Giller T, Sraer JD. Pivotal role of the renin/prorenin receptor in angiotensin II production and cellular responses to renin. J Clin Invest. 2002;109:1417–27.
Huang Y, Wongamorntham S, Kasting J, McQuillan D, Owens RT, Yu L, Noble NA, Border W. Renin increases mesangial cell transforming growth factor-beta1 and matrix proteins through receptor-mediated, angiotensin II-independent mechanisms. Kidney Int. 2006;69:105–13.
Huang Y, Noble NA, Zhang J, Xu C, Border WA. Renin-stimulated TGF-beta1 expression is regulated by a mitogen-activated protein kinase in mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 2007;72:45–52.
Sakoda M, Ichihara A, Kurauchi-Mito A, Narita T, Kinouchi K, Murohashi-Bokuda K, Saleem MA, Nishiyama A, Suzuki F, Itoh H. Aliskiren inhibits intracellular angiotensin II levels without affecting (pro)renin receptor signals in human podocytes. Am J Hypertens. 2010;23:575–80.
Feldman DL, Jin L, Xuan H, Contrepas A, Zhou Y, Webb RL, Mueller DN, Feldt S, Cumin F, Maniara W, Persohn E, Schuetz H, Jan Danser AH, Nguyen G. Effects of aliskiren on blood pressure, albuminuria, and (pro)renin receptor expression in diabetic TG(mRen-2)27 rats. Hypertension. 2008;52:130–6.
Ferrario CM, Varagic J. The ANG-(1-7)/ACE2/mas axis in the regulation of nephron function. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010;298:F1297–305.
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Soji, K., Doi, S., Nakashima, A. et al. Efficacy of add-on therapy of aliskiren to an angiotensin II receptor blocker on renal outcomes in advanced-stage chronic kidney disease: a prospective, randomized, open-label study. Clin Exp Nephrol 19, 631–638 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-014-1044-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-014-1044-4